C++设计模式 ==> 策略模式与简单工厂模式结合
简介
策略模式相较之于简单工厂模式适用于生产方法经常变化且方法较为繁多的情况,因为生产方法时常变化就会需要频繁修改工厂类,违背了开闭原则,这时就可以用策略选择类由客户端根据需求动态切换策略。且策略模式通过进一步封装了代码细节,没有像简单工厂模式那样在客户端创建详细的对象,而把任务交给了策略选择类去执行,所以客户端不会知道太多算法实现的细节。当然,在更多的情况下,策略模式一般可以与简单工厂模式并用,将进行策略选择的switch结构封装进策略选择类。
下面利用商场活动作为例子展示一段策略模式与简单工厂模式结合的代码,因为商场活动具体方案经常变化且种类繁多,所以适合策略模式的应用。
图示
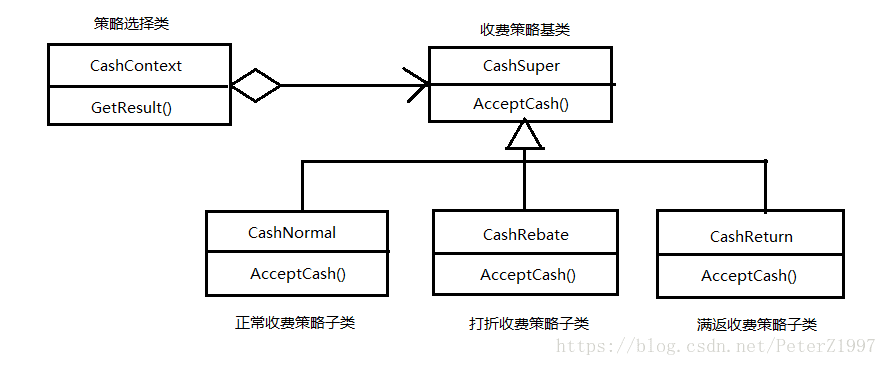
代码实现
///////////////////////////////
//
// @Author : PeterZheng
// @FileName : StrategyDefine.h
// @Date : 2018-08-07 22:00
//
///////////////////////////////
#pragma once
#ifndef STRATEGYDEFINE
#define STRATEGYDEFINE
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <string>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <tchar.h>
#endif
//策略父类,抽象接口
class CashSuper
{
public:
virtual double AcceptCash(double&) = 0;
};
//正常收费类
class CashNormal :public CashSuper
{
public:
virtual double AcceptCash(double&);
};
//打折类
class CashRebate :public CashSuper
{
public:
CashRebate(double mr) :moneyRebate(mr) {}
virtual double AcceptCash(double&);
private:
double moneyRebate;
};
//满返类(例如 满100返20)
class CashReturn :public CashSuper
{
public:
CashReturn(double so, double targ) :moneySource(so), moneyTarget(targ) {}
virtual double AcceptCash(double&);
private:
double moneySource; //满xx
double moneyTarget; //返xx
};
//策略类
class CashContext {
public:
CashContext(const std::wstring& type)
{
if (type == _T("Normal"))
{
CashNormal *cn = new CashNormal(); //不打折
cs = cn;
}
else if (type == _T("Rebate"))
{
CashRebate *crb = new CashRebate(0.8); //打8折
cs = crb;
}
else if (type == _T("Return"))
{
CashReturn *crt = new CashReturn(300, 100); // 满300返100
cs = crt;
}
else
{
MessageBoxW(NULL, _T("Type Error !!"), _T("Warning"), MB_OK);
ExitProcess(0);
}
}
double GetResult(double money) //购买商品的原价
{
return cs->AcceptCash(money);
}
private:
CashSuper * cs = NULL;
};
//具体策略接口实现
double CashNormal::AcceptCash(double& money)
{
return money;
}
//具体策略接口实现
double CashRebate::AcceptCash(double& money)
{
return money * moneyRebate;
}
//具体策略接口实现
double CashReturn::AcceptCash(double& money)
{
if (money >= moneySource)
{
return money - moneyTarget;
}
return money;
}
///////////////////////////////
//
// @Author : PeterZheng
// @FileName : StrategyModeDemo.cpp
// @Date : 2018-08-07 22:00
//
///////////////////////////////
#include "StrategyDefine.h"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(void)
{
CashContext *cscNom = new CashContext(_T("Normal"));
CashContext *cscReb = new CashContext(_T("Rebate"));
CashContext *cscRet = new CashContext(_T("Return"));
wcout.imbue(std::locale("chs"));
wcout << _T("不打折情况:") << cscNom->GetResult(1300) << endl;
wcout << _T("打折情况:") << cscReb->GetResult(1300) << endl;
wcout << _T("满反情况:") << cscRet->GetResult(1300) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
本文为博主总结文章,欢迎转载,请注明出处。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号