Codeforces675D(SummerTrainingDay06-J)
D. Tree Construction
During the programming classes Vasya was assigned a difficult problem. However, he doesn't know how to code and was unable to find the solution in the Internet, so he asks you to help.
You are given a sequence a, consisting of n distinct integers, that is used to construct the binary search tree. Below is the formal description of the construction process.
- First element a1 becomes the root of the tree.
- Elements a2, a3, ..., an are added one by one. To add element ai one needs to traverse the tree starting from the root and using the following rules:
- The pointer to the current node is set to the root.
- If ai is greater than the value in the current node, then its right child becomes the current node. Otherwise, the left child of the current node becomes the new current node.
- If at some point there is no required child, the new node is created, it is assigned value ai and becomes the corresponding child of the current node.
Input
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the length of the sequence a.
The second line contains n distinct integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — the sequence a itself.
Output
Output n - 1 integers. For all i > 1 print the value written in the node that is the parent of the node with value ai in it.
Examples
input
3
1 2 3
output
1 2
input
5
4 2 3 1 6
output
4 2 2 4
Note
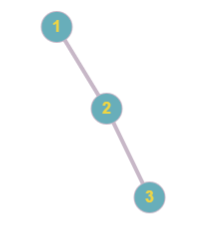
Picture below represents the tree obtained in the first sample.
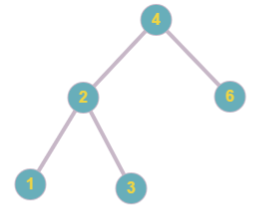
Picture below represents the tree obtained in the second sample.
1 //2017-09-05 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <map> 7 #include <set> 8 9 using namespace std; 10 11 int n; 12 map<int, int> pos; 13 set<int> st; 14 set<int>::iterator iter, it; 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); 19 cin.tie(0); 20 freopen("inputJ.txt", "r", stdin); 21 while(cin>>n){ 22 st.clear(); 23 pos.clear(); 24 int a; 25 cin>>a; 26 st.insert(a); 27 st.insert(0); 28 pos[a] = 1; 29 for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){ 30 cin>>a; 31 iter = st.lower_bound(a);//返回第一个大于等于a的数 32 it = iter; 33 it--;//比a小的最大的数 34 if(pos[*it] > pos[*iter]) 35 cout<<*it<<" "; 36 else cout<<*iter<<" "; 37 pos[a] = i; 38 st.insert(a); 39 } 40 cout<<endl; 41 } 42 43 return 0; 44 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号