一、介绍
我们做开发的,尤其是做微软技术栈的,有一个方向是跳不过去的,那就是MVC开发。我相信大家,做ASP.NET MVC 开发有的有很长时间,当然,也有刚进入这个行业的。无论如何,如果有人问你,你知道ASP.NET MVC的生命周期吗?你知道它的来世今生吗?你知道它和 ASP.NET WEBFORM 有什么区别吗?估计,这些问题,有很多人会答不上来,或者说不清楚。今天,我就把我的理解写出来,也是对我自己学习的一次回顾和总结吧。当然,由于本人能力有限,在写的过程中也可能会有一些错误,希望大家多多包涵,当然,更希望大家能不灵赐教,我们共同进步。
在开始之前,我们先来说说,ASP.NET Web Form 和 Asp.net MVC 有什么区别,这里说的区别,当然是本质区别,不是适用语法那个层次的。其实,说起来,ASP.NET WEB FORM 和 ASP.NET MVC 它们两个没有本质区别,使用的都是ASP.NET WEB FORM 的管道处理模型,ASP.NET MVC 也是通过扩展 IHttpModule 和 IHttpHandler 来实现的,都是基于 ASP.NET 的 HttpApplication 的管道处理模型扩展的,在这个层面来说,它们是一样的。当然,大家不要抬杠,我说的本质区别都是在这个方面,不同意的勿喷。
有人会问,ASP.NET MVC 和 ASP.NET WEBAPI 它们会有什么不同吗?好像 WebAPi 能做的,WebMVC都可以完成,第一眼看上去,好像是这样,但是它们有着本质的不同。WebAPI 的处理管道是重新写过的,不是基于 HTTPApplication 管道扩展的。ASP.NET WEB API 类似专人做专事,它的管道处理模型更高效,并且有了 Restfull 的概念。当然,大家如何向了解更细的内容,就需要看源码了。或再说回来,到了 NET CORE 时代,二者又融合管道了。
二、MVC生命周期详述
1、我们既然要说 ASP.NET MVC的生命周期,为了给大家一个整体印象,俗话说,文不如图,我就贴一张图,按着箭头走,相信大家也会不能理解。
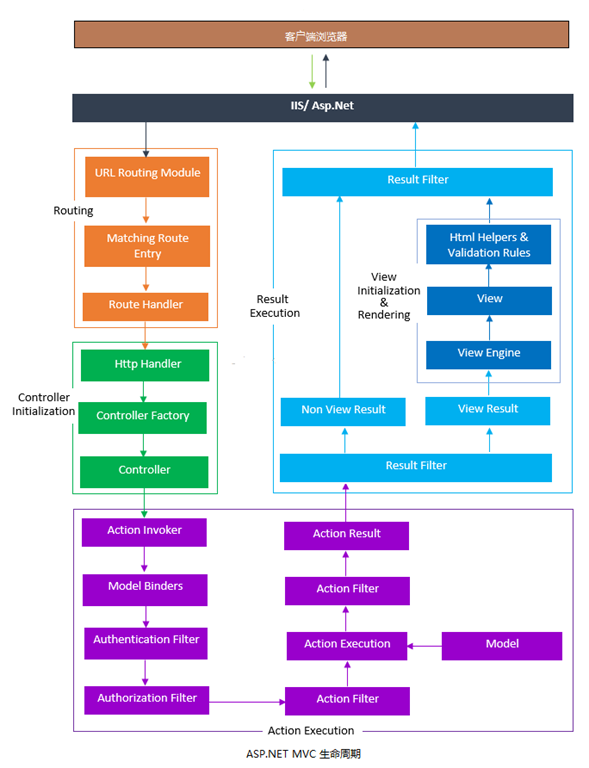
2、上图很简单,大家按着箭头走,也能理解的差不多。以下是按着我的理解,划分了4个模块。
(1)、路由模块
RouteBase 是对路由规则的抽象,也就是说,一个 RouteBase 对象,也就代表了一个条 路由规则。在 ASP.NET MVC 中,有一个唯一的子类实现就是 Route ,它同样也是路由规则的代表。我们有了路由规则,一定会把这个规则存放在一个地方,这个地方保存了很多路由规则,这个地方就是 RouteCollection,中文叫“路由集合”,因为这个集合里面包含的就是 RouteBase 对象。
RouteCollection 就是路由集合,用于保存路由规则对象,它的定义形式:
1 [TypeForwardedFrom("System.Web.Routing, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=Neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35")] 2 public class RouteCollection : Collection<RouteBase> 3 { 4 private class ReadLockDisposable : IDisposable 5 { 6 private ReaderWriterLockSlim _rwLock; 7 8 public ReadLockDisposable(ReaderWriterLockSlim rwLock) 9 { 10 this._rwLock = rwLock; 11 } 12 13 void IDisposable.Dispose() 14 { 15 this._rwLock.ExitReadLock(); 16 } 17 } 18 ......
RouteTable 就是路由表,其实它和 RouteCollection 是一样的。
1 public class RouteTable 2 { 3 private static RouteCollection _instance = new RouteCollection(); 4 5 public static RouteCollection Routes 6 { 7 get 8 { 9 return RouteTable._instance; 10 } 11 } 12 }
在ASP.NET MVC处理管线中的第一站就是路由模块。当请求到达路由模块后,ASP.NET MVC 框架就会根据 RouteTable 中配置的路由模板来匹配当前请求以获得对应的 Controller 和 Action 信息。具体的匹配过程就是有UrlRoutingModule(System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule)来实现的。如果遇到一个匹配的规则,就会立刻跳出下面的配置。也就是说,配置过程是有顺序的,如果有一个匹配,后面就算有匹配的也不会执行的。
1 namespace System.Web.Routing 2 { 3 [TypeForwardedFrom("System.Web.Routing, Version=3.5.0.0, Culture=Neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35")] 4 public class UrlRoutingModule : IHttpModule 5 { 6 private static readonly object _contextKey = new object(); 7 8 private static readonly object _requestDataKey = new object(); 9 10 private RouteCollection _routeCollection; 11 12 public RouteCollection RouteCollection 13 { 14 get 15 { 16 if (this._routeCollection == null) 17 { 18 this._routeCollection = RouteTable.Routes; 19 } 20 return this._routeCollection; 21 } 22 set 23 { 24 this._routeCollection = value; 25 } 26 } 27 28 protected virtual void Dispose() 29 { 30 } 31 32 protected virtual void Init(HttpApplication application) 33 { 34 if (application.Context.Items[UrlRoutingModule._contextKey] != null) 35 { 36 return; 37 } 38 application.Context.Items[UrlRoutingModule._contextKey] = UrlRoutingModule._contextKey; 39 application.PostResolveRequestCache += new EventHandler(this.OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache); 40 } 41 42 private void OnApplicationPostResolveRequestCache(object sender, EventArgs e) 43 { 44 HttpApplication httpApplication = (HttpApplication)sender; 45 HttpContextBase context = new HttpContextWrapper(httpApplication.Context); 46 this.PostResolveRequestCache(context); 47 } 48 49 [Obsolete("This method is obsolete. Override the Init method to use the PostMapRequestHandler event.")] 50 public virtual void PostMapRequestHandler(HttpContextBase context) 51 { 52 } 53 54 public virtual void PostResolveRequestCache(HttpContextBase context) 55 { 56 RouteData routeData = this.RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context); 第一步匹配路由规则 57 if (routeData == null) 58 { 59 return; 60 } 61 IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler; 第二步:如有匹配,就找到RouteHandler对象,该类型的实例是:MvcRouteHandler。 62 if (routeHandler == null) 63 { 64 throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoRouteHandler"), new object[0])); 65 } 66 if (routeHandler is StopRoutingHandler) 67 { 68 return; 69 } 70 RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(context, routeData); 71 context.Request.RequestContext = requestContext; 72 IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext);第三步,根据 RouteHandler 对象,找到最终处理请求的 IHttpHandler 的对象,该类型是 MvcHandler 73 if (httpHandler == null) 74 { 75 throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentUICulture, SR.GetString("UrlRoutingModule_NoHttpHandler"), new object[] 76 { 77 routeHandler.GetType() 78 })); 79 } 80 if (!(httpHandler is UrlAuthFailureHandler)) 81 { 82 context.RemapHandler(httpHandler);第四步,有找到的 IHttpHandler 处理请求。 83 return; 84 } 85 if (FormsAuthenticationModule.FormsAuthRequired) 86 { 87 UrlAuthorizationModule.ReportUrlAuthorizationFailure(HttpContext.Current, this); 88 return; 89 } 90 throw new HttpException(401, SR.GetString("Assess_Denied_Description3")); 91 } 92 93 void IHttpModule.Dispose() 94 { 95 this.Dispose(); 96 } 97 98 void IHttpModule.Init(HttpApplication application) 99 { 100 this.Init(application); 101 } 102 } 103 }
(2)、Controller 创建模块
经过了路由模块,生成了 RouteData 路由数据,它包含了根据路由规则匹配的 Controller 和 Action。有了路由数据,需要有处理器来处理请求,这个任务就交给了 RouteData 的 RouteHandler 属性,它的类型是 IRouteHandler,它的值就是MvcRouteHandler,MvcRouteHandler 调用 GetHttpHandler 获取处理请求的 IHttpHandler 对象,在 MVC 框架中就是 MvcHandler,详细代码如下:

1 namespace System.Web.Mvc 2 { 3 /// <summary>Selects the controller that will handle an HTTP request.</summary> 4 public class MvcHandler : IHttpAsyncHandler, IHttpHandler, IRequiresSessionState 5 { 6 private struct ProcessRequestState 7 { 8 internal IAsyncController AsyncController; 9 10 internal IControllerFactory Factory; 11 12 internal RequestContext RequestContext; 13 14 internal void ReleaseController() 15 { 16 this.Factory.ReleaseController(this.AsyncController); 17 } 18 } 19 20 [CompilerGenerated] 21 [Serializable] 22 private sealed class <>c 23 { 24 public static readonly MvcHandler.<>c <>9 = new MvcHandler.<>c(); 25 26 public static BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> <>9__20_0; 27 28 public static EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> <>9__20_1; 29 30 public static Func<KeyValuePair<string, object>, bool> <>9__26_0; 31 32 internal IAsyncResult <BeginProcessRequest>b__20_0(AsyncCallback asyncCallback, object asyncState, MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState innerState) 33 { 34 IAsyncResult result; 35 try 36 { 37 result = innerState.AsyncController.BeginExecute(innerState.RequestContext, asyncCallback, asyncState); 38 } 39 catch 40 { 41 innerState.ReleaseController(); 42 throw; 43 } 44 return result; 45 } 46 47 internal void <BeginProcessRequest>b__20_1(IAsyncResult asyncResult, MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState innerState) 48 { 49 try 50 { 51 innerState.AsyncController.EndExecute(asyncResult); 52 } 53 finally 54 { 55 innerState.ReleaseController(); 56 } 57 } 58 59 internal bool <RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters>b__26_0(KeyValuePair<string, object> entry) 60 { 61 return entry.Value == UrlParameter.Optional; 62 } 63 } 64 65 private static readonly object _processRequestTag = new object(); 66 67 internal static readonly string MvcVersion = MvcHandler.GetMvcVersionString(); 68 69 /// <summary>Contains the header name of the ASP.NET MVC version.</summary> 70 public static readonly string MvcVersionHeaderName = "X-AspNetMvc-Version"; 71 72 private ControllerBuilder _controllerBuilder; 73 74 internal ControllerBuilder ControllerBuilder 75 { 76 get 77 { 78 if (this._controllerBuilder == null) 79 { 80 this._controllerBuilder = ControllerBuilder.Current; 81 } 82 return this._controllerBuilder; 83 } 84 set 85 { 86 this._controllerBuilder = value; 87 } 88 } 89 90 /// <summary>Gets or sets a value that indicates whether the MVC response header is disabled.</summary> 91 /// <returns>true if the MVC response header is disabled; otherwise, false.</returns> 92 public static bool DisableMvcResponseHeader 93 { 94 get; 95 set; 96 } 97 98 /// <summary>Gets a value that indicates whether another request can use the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance.</summary> 99 /// <returns>true if the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance is reusable; otherwise, false.</returns> 100 protected virtual bool IsReusable 101 { 102 get 103 { 104 return false; 105 } 106 } 107 108 /// <summary>Gets the request context.</summary> 109 /// <returns>The request context.</returns> 110 public RequestContext RequestContext 111 { 112 get; 113 private set; 114 } 115 116 /// <summary>Gets a value that indicates whether another request can use the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance.</summary> 117 /// <returns>true if the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> instance is reusable; otherwise, false.</returns> 118 bool IHttpHandler.IsReusable 119 { 120 get 121 { 122 return this.IsReusable; 123 } 124 } 125 126 /// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="T:System.Web.Mvc.MvcHandler" /> class.</summary> 127 /// <param name="requestContext">The request context.</param> 128 /// <exception cref="T:System.ArgumentNullException">The <paramref name="requestContext" /> parameter is null.</exception> 129 public MvcHandler(RequestContext requestContext) 130 { 131 if (requestContext == null) 132 { 133 throw new ArgumentNullException("requestContext"); 134 } 135 this.RequestContext = requestContext; 136 } 137 138 /// <summary>Adds the version header by using the specified HTTP context.</summary> 139 /// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param> 140 protected internal virtual void AddVersionHeader(HttpContextBase httpContext) 141 { 142 if (!MvcHandler.DisableMvcResponseHeader) 143 { 144 httpContext.Response.AppendHeader(MvcHandler.MvcVersionHeaderName, MvcHandler.MvcVersion); 145 } 146 } 147 148 /// <summary>Called by ASP.NET to begin asynchronous request processing.</summary> 149 /// <returns>The status of the asynchronous call.</returns> 150 /// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param> 151 /// <param name="callback">The asynchronous callback method.</param> 152 /// <param name="state">The state of the asynchronous object.</param> 153 protected virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state) 154 { 155 HttpContextBase httpContext2 = new HttpContextWrapper(httpContext); 156 return this.BeginProcessRequest(httpContext2, callback, state); 157 } 158 159 /// <summary>Called by ASP.NET to begin asynchronous request processing using the base HTTP context.</summary> 160 /// <returns>The status of the asynchronous call.</returns> 161 /// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param> 162 /// <param name="callback">The asynchronous callback method.</param> 163 /// <param name="state">The state of the asynchronous object.</param> 164 protected internal virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state) 165 { 166 IController controller; 167 IControllerFactory factory; 168 this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out factory); 169 IAsyncController asyncController = controller as IAsyncController; 170 if (asyncController != null) 171 { 172 BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_51_0; 173 if ((arg_51_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0) == null) 174 { 175 arg_51_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0 = new BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_0)); 176 } 177 BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> beginDelegate = arg_51_0; 178 EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_71_0; 179 if ((arg_71_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1) == null) 180 { 181 arg_71_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1 = new EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_1)); 182 } 183 EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> endDelegate = arg_71_0; 184 MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState invokeState = new MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState 185 { 186 AsyncController = asyncController, 187 Factory = factory, 188 RequestContext = this.RequestContext 189 }; 190 SynchronizationContext synchronizationContext = SynchronizationContextUtil.GetSynchronizationContext(); 191 return AsyncResultWrapper.Begin<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(callback, state, beginDelegate, endDelegate, invokeState, MvcHandler._processRequestTag, -1, synchronizationContext); 192 } 193 Action action = delegate 194 { 195 try 196 { 197 controller.Execute(this.RequestContext); 198 } 199 finally 200 { 201 factory.ReleaseController(controller); 202 } 203 }; 204 return AsyncResultWrapper.BeginSynchronous(callback, state, action, MvcHandler._processRequestTag); 205 } 206 207 /// <summary>Called by ASP.NET when asynchronous request processing has ended.</summary> 208 /// <param name="asyncResult">The asynchronous result.</param> 209 protected internal virtual void EndProcessRequest(IAsyncResult asyncResult) 210 { 211 AsyncResultWrapper.End(asyncResult, MvcHandler._processRequestTag); 212 } 213 214 private static string GetMvcVersionString() 215 { 216 return new AssemblyName(typeof(MvcHandler).Assembly.FullName).Version.ToString(2); 217 } 218 219 /// <summary>Processes the request by using the specified HTTP request context.</summary> 220 /// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param> 221 protected virtual void ProcessRequest(HttpContext httpContext) 222 { 223 HttpContextBase httpContext2 = new HttpContextWrapper(httpContext); 224 this.ProcessRequest(httpContext2); 225 } 226 227 /// <summary>Processes the request by using the specified base HTTP request context.</summary> 228 /// <param name="httpContext">The HTTP context.</param> 229 protected internal virtual void ProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext) 230 { 231 IController controller; 232 IControllerFactory controllerFactory; 233 this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out controllerFactory); 234 try 235 { 236 controller.Execute(this.RequestContext); 237 } 238 finally 239 { 240 controllerFactory.ReleaseController(controller); 241 } 242 } 243 244 private void ProcessRequestInit(HttpContextBase httpContext, out IController controller, out IControllerFactory factory) 245 { 246 HttpContext current = HttpContext.Current; 247 if (current != null) 248 { 249 bool? flag = ValidationUtility.IsValidationEnabled(current); 250 bool flag2 = true; 251 if (flag.GetValueOrDefault() == flag2 & flag.HasValue) 252 { 253 ValidationUtility.EnableDynamicValidation(current); 254 } 255 } 256 this.AddVersionHeader(httpContext); 257 this.RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters(); 258 string requiredString = this.RequestContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller"); 259 factory = this.ControllerBuilder.GetControllerFactory(); 260 controller = factory.CreateController(this.RequestContext, requiredString); 261 if (controller == null) 262 { 263 throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, MvcResources.ControllerBuilder_FactoryReturnedNull, new object[] 264 { 265 factory.GetType(), 266 requiredString 267 })); 268 } 269 } 270 271 private void RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters() 272 { 273 IDictionary<string, object> arg_2F_0 = this.RequestContext.RouteData.Values; 274 Func<KeyValuePair<string, object>, bool> arg_2F_1; 275 if ((arg_2F_1 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__26_0) == null) 276 { 277 arg_2F_1 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__26_0 = new Func<KeyValuePair<string, object>, bool>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters>b__26_0)); 278 } 279 arg_2F_0.RemoveFromDictionary(arg_2F_1); 280 } 281 282 /// <summary>Enables processing of HTTP Web requests by a custom HTTP handler that implements the <see cref="T:System.Web.IHttpHandler" /> interface.</summary> 283 /// <param name="httpContext">An <see cref="T:System.Web.HttpContext" /> object that provides references to the intrinsic server objects (for example, Request, Response, Session, and Server) that are used to service HTTP requests.</param> 284 void IHttpHandler.ProcessRequest(HttpContext httpContext) 285 { 286 this.ProcessRequest(httpContext); 287 } 288 289 /// <summary>Called by ASP.NET to begin asynchronous request processing using the base HTTP context.</summary> 290 /// <returns>The status of the asynchronous call.</returns> 291 /// <param name="context">The HTTP context.</param> 292 /// <param name="cb">The asynchronous callback method.</param> 293 /// <param name="extraData">The data.</param> 294 IAsyncResult IHttpAsyncHandler.BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext context, AsyncCallback cb, object extraData) 295 { 296 return this.BeginProcessRequest(context, cb, extraData); 297 } 298 299 /// <summary>Called by ASP.NET when asynchronous request processing has ended.</summary> 300 /// <param name="result">The asynchronous result.</param> 301 void IHttpAsyncHandler.EndProcessRequest(IAsyncResult result) 302 { 303 this.EndProcessRequest(result); 304 } 305 } 306 }
HttpRuntime 调用 IHttpHandler 类型的调用 ProcessRequest() 方法,用于处理请求。
1 protected internal virtual void ProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext) 2 { 3 IController controller; 4 IControllerFactory controllerFactory; 5 this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out controllerFactory);创建 IControllerFactory,并创建 IController 对象。 6 try 7 { 8 controller.Execute(this.RequestContext);执行Controller,背后就是调用相应的 Action 方法。 9 } 10 finally 11 { 12 controllerFactory.ReleaseController(controller); 13 } 14 }
核心处理请求的方法是ProcessRequestInit(),用于创建 IController 和 IControllerFactory 实例。IControllerFactory 的实际类型是:DefaultControllerFactory,该类型用于创建 IController 类型的实例。
1 private void ProcessRequestInit(HttpContextBase httpContext, out IController controller, out IControllerFactory factory) 2 { 3 HttpContext current = HttpContext.Current; 4 if (current != null) 5 { 6 bool? flag = ValidationUtility.IsValidationEnabled(current); 7 bool flag2 = true; 8 if (flag.GetValueOrDefault() == flag2 & flag.HasValue) 9 { 10 ValidationUtility.EnableDynamicValidation(current); 11 } 12 } 13 this.AddVersionHeader(httpContext); 14 this.RemoveOptionalRoutingParameters(); 15 string requiredString = this.RequestContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller"); 16 factory = this.ControllerBuilder.GetControllerFactory(); 17 controller = factory.CreateController(this.RequestContext, requiredString); 18 if (controller == null) 19 { 20 throw new InvalidOperationException(string.Format(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture, MvcResources.ControllerBuilder_FactoryReturnedNull, new object[] 21 { 22 factory.GetType(), 23 requiredString 24 })); 25 } 26 }
以上加红的代码就是创建 IController 的实例的逻辑。IController 实例创建完成后,判断是否实现了 IAsyncController 接口,如果是,就异步执行 Controller 方法的调用,否则就同步执行。
1 protected internal virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state) 2 { 3 IController controller; 4 IControllerFactory factory; 5 this.ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out factory); 6 IAsyncController asyncController = controller as IAsyncController; 判读是否是需要异步执行 7 if (asyncController != null)异步执行 8 { 9 BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_51_0; 10 if ((arg_51_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0) == null) 11 { 12 arg_51_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_0 = new BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_0)); 13 } 14 BeginInvokeDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> beginDelegate = arg_51_0; 15 EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> arg_71_0; 16 if ((arg_71_0 = MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1) == null) 17 { 18 arg_71_0 = (MvcHandler.<>c.<>9__20_1 = new EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(MvcHandler.<>c.<>9.<BeginProcessRequest>b__20_1)); 19 } 20 EndInvokeVoidDelegate<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState> endDelegate = arg_71_0; 21 MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState invokeState = new MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState 22 { 23 AsyncController = asyncController, 24 Factory = factory, 25 RequestContext = this.RequestContext 26 }; 27 SynchronizationContext synchronizationContext = SynchronizationContextUtil.GetSynchronizationContext(); 28 return AsyncResultWrapper.Begin<MvcHandler.ProcessRequestState>(callback, state, beginDelegate, endDelegate, invokeState, MvcHandler._processRequestTag, -1, synchronizationContext); 29 } 30 Action action = delegate//同步执行。 31 { 32 try 33 { 34 controller.Execute(this.RequestContext); 35 } 36 finally 37 { 38 factory.ReleaseController(controller); 39 } 40 }; 41 return AsyncResultWrapper.BeginSynchronous(callback, state, action, MvcHandler._processRequestTag); 42 }
(3)、Action 执行模块,通过 ControllerActionInvoker 调用 InvokeAction() 执行其方法。Action 方法的执行也有2个版本,一个是异步版本,一个是同步版本。由于 ActionInvoker 实现了 IAsyncActionInvoker 接口,所以也是以已方式执行。该类型是 AsyncControllerActionInvoker。
A、当Controller对象被创建之后,紧接着就会执行Controler 对象的 Execute(),其实背后就是调用 InvokeAction() 方法:
1 public virtual bool InvokeAction(ControllerContext controllerContext, string actionName) 2 { 3 if (controllerContext == null) 4 { 5 throw new ArgumentNullException("controllerContext"); 6 } 7 if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(actionName) && !controllerContext.RouteData.HasDirectRouteMatch()) 8 { 9 throw new ArgumentException(MvcResources.Common_NullOrEmpty, "actionName"); 10 } 11 ControllerDescriptor controllerDescriptor = this.GetControllerDescriptor(controllerContext); 12 ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor = this.FindAction(controllerContext, controllerDescriptor, actionName); 13 if (actionDescriptor != null) 14 { 15 FilterInfo filters = this.GetFilters(controllerContext, actionDescriptor); 获取所有过滤器,全局的、控制器的和方法的 16 try 17 { 18 AuthenticationContext authenticationContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFilters(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor);认证过滤器的执行。 19 if (authenticationContext.Result != null) 20 { 21 AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, authenticationContext.Result); 22 this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, authenticationChallengeContext.Result ?? authenticationContext.Result); 23 } 24 else 25 { 26 AuthorizationContext authorizationContext = this.InvokeAuthorizationFilters(controllerContext, filters.AuthorizationFilters, actionDescriptor);授权过滤器的执行。 27 if (authorizationContext.Result != null) 28 { 29 AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext2 = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, authorizationContext.Result); 30 this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, authenticationChallengeContext2.Result ?? authorizationContext.Result); 31 } 32 else 33 { 34 if (controllerContext.Controller.ValidateRequest) 35 { 36 ControllerActionInvoker.ValidateRequest(controllerContext); 37 } 38 IDictionary<string, object> parameterValues = this.GetParameterValues(controllerContext, actionDescriptor); 获取方法执行参数。 39 ActionExecutedContext actionExecutedContext = this.InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(controllerContext, filters.ActionFilters, actionDescriptor, parameterValues); 执行action,同时执行执行方法前后的 IAcctionFilter 40 AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext3 = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, actionExecutedContext.Result); 41 this.InvokeActionResultWithFilters(controllerContext, filters.ResultFilters, authenticationChallengeContext3.Result ?? actionExecutedContext.Result); 执行 ActionResult,同时执行方法前后的 IResultFilter 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 catch (ThreadAbortException) 46 { 47 throw; 48 } 49 catch (Exception exception) 50 { 51 ExceptionContext exceptionContext = this.InvokeExceptionFilters(controllerContext, filters.ExceptionFilters, exception); 52 if (!exceptionContext.ExceptionHandled) 53 { 54 throw; 55 } 56 this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, exceptionContext.Result);//异常过滤器的执行。 57 } 58 return true; 59 } 60 return false; 61 }
B、当选择完合适的Action后,接着就是 ModelBinder(默认是System.Web.Mvc.DefaultModelBinder),它会从http请求的参数中提取数据并实现类型转换,数据校验(例如是否必填,数据格式等)以及是否自动装配到action方法的参数中System.Web.Mvc.DefaultModelBinder
1 protected virtual IDictionary<string, object> GetParameterValues(ControllerContext controllerContext, ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor) 2 { 3 Dictionary<string, object> dictionary = new Dictionary<string, object>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase); 4 ParameterDescriptor[] parameters = actionDescriptor.GetParameters(); 5 for (int i = 0; i < parameters.Length; i++) 6 { 7 ParameterDescriptor parameterDescriptor = parameters[i]; 8 dictionary[parameterDescriptor.ParameterName] = this.GetParameterValue(controllerContext, parameterDescriptor); 9 } 10 return dictionary; 11 }
1 protected virtual object GetParameterValue(ControllerContext controllerContext, ParameterDescriptor parameterDescriptor) 2 { 3 Type parameterType = parameterDescriptor.ParameterType; 4 IModelBinder arg_92_0 = this.GetModelBinder(parameterDescriptor); 5 IValueProvider valueProvider = controllerContext.Controller.ValueProvider; 6 string modelName = parameterDescriptor.BindingInfo.Prefix ?? parameterDescriptor.ParameterName; 7 Predicate<string> propertyFilter = ControllerActionInvoker.GetPropertyFilter(parameterDescriptor); 8 ModelBindingContext bindingContext = new ModelBindingContext 9 { 10 FallbackToEmptyPrefix = parameterDescriptor.BindingInfo.Prefix == null, 11 ModelMetadata = ModelMetadataProviders.Current.GetMetadataForType(null, parameterType), 12 ModelName = modelName, 13 ModelState = controllerContext.Controller.ViewData.ModelState, 14 PropertyFilter = propertyFilter, 15 ValueProvider = valueProvider 16 }; 17 return arg_92_0.BindModel(controllerContext, bindingContext) ?? parameterDescriptor.DefaultValue; 18 }
C、Authentication Filter是mvc5中新增的一个Filter,它会先于authorization filter执行,目的是对访问用户的认证。在MVC5之前,认证和授权都是通过authorization filter来实现的,但现在这2个操作就分开来了,各自管各自喽。
1 AuthenticationContext authenticationContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFilters(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor); 2 if (authenticationContext.Result != null) 3 { 4 AuthenticationChallengeContext authenticationChallengeContext = this.InvokeAuthenticationFiltersChallenge(controllerContext, filters.AuthenticationFilters, actionDescriptor, authenticationContext.Result); 5 this.InvokeActionResult(controllerContext, authenticationChallengeContext.Result ?? authenticationContext.Result); 6 }
D、Action filters有2个方法OnActionExecuting和OnActionExecuted分别在action执行前后执行。我们也可以通过实现IActionFilter接口来实现你个性化的过滤机制
1 protected virtual ActionExecutedContext InvokeActionMethodWithFilters(ControllerContext controllerContext, IList<IActionFilter> filters, ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor, IDictionary<string, object> parameters) 2 { 3 ActionExecutingContext preContext = new ActionExecutingContext(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, parameters); 4 Func<ActionExecutedContext> seed = () => new ActionExecutedContext(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, false, null) 5 { 6 Result = this.InvokeActionMethod(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, parameters) 7 }; 8 return filters.Reverse<IActionFilter>().Aggregate(seed, (Func<ActionExecutedContext> next, IActionFilter filter) => () => ControllerActionInvoker.InvokeActionMethodFilter(filter, preContext, next))(); 9 }
E、接下来就是执行我们平时在Action方法中写的代码了(根据请求相应结果)
1 protected virtual ActionResult InvokeActionMethod(ControllerContext controllerContext, ActionDescriptor actionDescriptor, IDictionary<string, object> parameters) 2 { 3 object actionReturnValue = actionDescriptor.Execute(controllerContext, parameters); 4 return this.CreateActionResult(controllerContext, actionDescriptor, actionReturnValue); 5 }
(4)、ActionResult 执行模块。
A、在 ActionResult 执行前后,仍然会有一个filter(IResultFilter),同样的,通过实现 IResultFilter 接口你可以定制自己的过滤逻辑。
1 namespace System.Web.Mvc 2 { 3 /// <summary>Defines the methods that are required for a result filter.</summary> 4 public interface IResultFilter 5 { 6 /// <summary>Called before an action result executes.</summary> 7 /// <param name="filterContext">The filter context.</param> 8 void OnResultExecuting(ResultExecutingContext filterContext); 9 10 /// <summary>Called after an action result executes.</summary> 11 /// <param name="filterContext">The filter context.</param> 12 void OnResultExecuted(ResultExecutedContext filterContext); 13 } 14 }
B、ActionResult 就是把处理的用户请求结果返回。因此 ViewResult, PartialViewResult, RedirectToRouteResult, RedirectResult, ContentResult, JsonResult, FileResult and EmptyResult就是具体的返回类型。
C、上面的返回类型可以大致分为2类:ViewResult 和非ViewResult。对于需要生成html页面给客户端的划到ViewResult,而其他的例如返回文本,json数据等则划分到非ViewResult,对于非ViewResult直接返回就可以了。
View的初始化和渲染呈现
A、对于 ViewResult 最终是由合适的 View Engine 通过调用 IView 的 Render() 方法来渲染的:
1 namespace System.Web.Mvc 2 { 3 /// <summary>Defines the methods that are required for a view engine.</summary> 4 public interface IViewEngine 5 { 6 /// <summary>Finds the specified partial view by using the specified controller context.</summary> 7 /// <returns>The partial view.</returns> 8 /// <param name="controllerContext">The controller context.</param> 9 /// <param name="partialViewName">The name of the partial view.</param> 10 /// <param name="useCache">true to specify that the view engine returns the cached view, if a cached view exists; otherwise, false.</param> 11 ViewEngineResult FindPartialView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string partialViewName, bool useCache); 12 13 /// <summary>Finds the specified view by using the specified controller context.</summary> 14 /// <returns>The page view.</returns> 15 /// <param name="controllerContext">The controller context.</param> 16 /// <param name="viewName">The name of the view.</param> 17 /// <param name="masterName">The name of the master.</param> 18 /// <param name="useCache">true to specify that the view engine returns the cached view, if a cached view exists; otherwise, false.</param> 19 ViewEngineResult FindView(ControllerContext controllerContext, string viewName, string masterName, bool useCache); 20 21 /// <summary>Releases the specified view by using the specified controller context.</summary> 22 /// <param name="controllerContext">The controller context.</param> 23 /// <param name="view">The view.</param> 24 void ReleaseView(ControllerContext controllerContext, IView view); 25 } 26 }
1 namespace System.Web.Mvc 2 { 3 /// <summary>Defines the methods that are required for a view.</summary> 4 public interface IView 5 { 6 /// <summary>Renders the specified view context by using the specified the writer object.</summary> 7 /// <param name="viewContext">The view context.</param> 8 /// <param name="writer">The writer object.</param> 9 void Render(ViewContext viewContext, TextWriter writer); 10 } 11 }
B、整个处理过程是由 IViewEngine 来实现的。ASP.NET MVC 默认提供 WebForm(.aspx)和 Razor(.cshtml) 模板引擎,你可以通过实现 IViewEngine 接口来实现自己的 ViewEngine,然后在Application_Start方法中做如下注册:
protected void Application_Start() { //移除所有的View引擎包括Webform和Razor ViewEngines.Engines.Clear(); //注册你自己的View引擎 ViewEngines.Engines.Add(new CustomViewEngine()); }
C、最后,Html Helpers将帮我们生成 input 标签,基于AJAX的 form 等等。
(5)、作为总结,将每个节点主要的代码类贴出来。
这就是整个流程的代码节点,有些是同步执行,有些是异步执行,把握关键点,我这里只是谢了一个大概。
UrlRoutingModule-----RouteCollection.GetRouteData(context)----->IRouteHandler routeHandler = routeData.RouteHandler------》IHttpHandler httpHandler = routeHandler.GetHttpHandler(requestContext)-----》context.RemapHandler(httpHandler)------->MvcHandler------->ProcessRequest()------>ProcessRequestInit()--------》IController------>controller.Execute(this.RequestContext)-------->ControllerActionInvoker------->InvoleAction()--------->InvoleActionMethod()------->InvoleActionReslt()
三、结束
今天就到这里了,东西虽然不多,但是也写了2个多小时。今天就算自己有学习了一边,大家一定要好好的把握这个流程,对于解决程序中的问题,扩展框架都有很大的好处。我们作为程序员的,应该要知道其一,也要知道其二。没事,看看源码,我们对框架和我们自己的代码有更深的了解。当然,这样做也是有代价的,需要更多的时间去支持,我相信我们的付出是值得。不忘初心,继续努力。老天不会辜负努力的人。




