2020软件工程作业04
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE/homework/11406 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 算法(区间k大数查询,二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历) |
| 其他参考文献 | 《大话数据结构》 |
1.区间k大数查询
-
解题思路
1.创建一个数组来保存区间的值
2.将保存区间的值的数组从大到小排序
3.直接输出第K大的值 -
解题代码
package ruanjiangongcheng;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class zuoye1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入序列的个数:");
int n=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入序列:");
int[] arr=new int[n+1];//数组长度
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
arr[i]=sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("请输入要询问的个数:");
int[] a = new int[n+1];
int temp;
int l,r,k;
int m=sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入三个数:");
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++) {
a[j]=arr[j];
}
l=sc.nextInt();
r=sc.nextInt();
k=sc.nextInt();
//序列从大往小冒泡排序
for(int x=l;x<=r;x++) {
for(int j=x;j<=r;j++) {
if(a[j]>a[x]) {
temp=a[j];
a[j]=a[x];
a[x]=temp;
}
}
}
System.out.println("从左往右地k大的数为:");
System.out.println(a[l+k-1]);
}
}
}

2.二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
- 解题思路
先序遍历的递归过程为
(1)访问根结点
(2)先序遍历根结点的左子树
(3)先序遍历根结点的右子树
中序遍历的递归过程为
(1)中序遍历根结点的左子树
(2)访问根结点
(3)中序遍历根结点的右子树
后序遍历的递归过程为
(1)后序遍历二叉树的左子树
(2)后序遍历二叉树的右子树
(3)访问根结点。
层次遍历的递归过程为
(1)根结点入队列
(2)根结点出队列,根结点的左子树、右子树相继入队列
(3)根结点的左子树结点出队列,左子树结点的左子树、右子树相继入队列
(4).......
- 解题代码
package ruanjiangongcheng;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class zuoye2 {
/* 二叉树的结构
A
/ \
T 6
/
D
/ \
N 5
/ \ /
B 4 1
\
9
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = into();
// 先序遍历
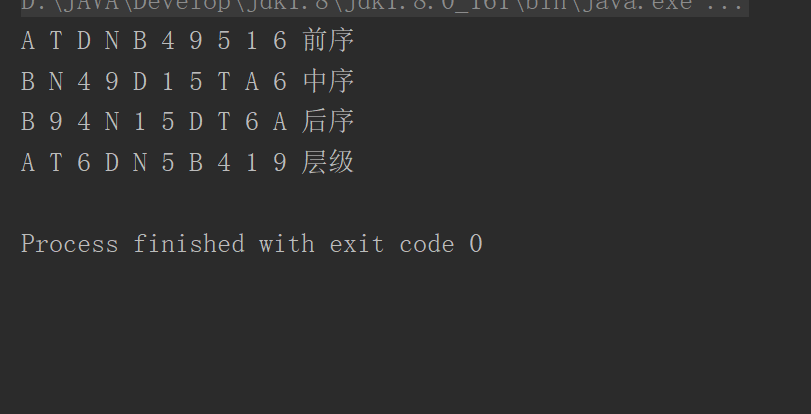
A(root);
System.out.println("前序");
// 中序遍历
B(root);
System.out.println("中序");
// 后序遍历
C(root);
System.out.println("后序");
// 层级遍历
D(root);
System.out.println("层级");
}
private static void A(Node tree) {
// TODO 先序遍历
if (tree != null) {
System.out.print(tree.data + " ");
A(tree.l);
A(tree.r);
}
}
private static void B(Node tree) {
// TODO 中序遍历
if (tree != null) {
B(tree.l);
System.out.print(tree.data + " ");
B(tree.r);
}
}
private static void C(Node tree) {
// TODO 后续遍历
if (tree != null) {
C(tree.l);
C(tree.r);
System.out.print(tree.data + " ");
}
}
private static void D(Node tree) {
// TODO 层级遍历
if (tree != null) {
LinkedList<Node> linkedList = new LinkedList<Node>();
//先将根节点入队
linkedList.offer(tree);
Node node = null;
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
node = (Node) linkedList.pop();
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
if (node.l != null) {
//将出队结点的左子树根入队
linkedList.offer(node.l);
}
if (node.r != null) {
//将出队结点的右子树根入队
linkedList.offer(node.r);
}
}
}
}
// 构建一颗树,返回根节点
private static Node into(){
Node root = new Node("A");
Node node1 = new Node("T");
Node node2 = new Node("D");
Node node3 = new Node("N");
Node node4 = new Node("B");
Node node5 = new Node("6");
Node node6 = new Node("5");
Node node7 = new Node("4");
Node node8 = new Node("9");
Node node9 = new Node("1");
root.l = node1;
node1.l = node2;
node2.l = node3;
node2.r = node6;
node3.r = node7;
node7.r = node8;
node6.l = node9;
node3.l = node4;
root.r = node5;
return root;
}
// 节点
static class Node{
// 数据
Object data;
// 左孩子
Node l;
// 右孩子
Node r;
public Node(){}
public Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.l = null;
this.r = null;
}
public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) {
this.data = data;
this.l = l;
this.r = r;
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号