代码随想录算法训练营第64天 | 图论:Floyd 算法+A * 算法
97.小明逛公园
https://kamacoder.com/problempage.php?pid=1155
Floyd 算法精讲
https://www.programmercarl.com/kamacoder/0097.小明逛公园.html#floyd-算法精讲
Floyd 算法精讲
-
问题总结:双向道路;路径规划;多个起点到多个终点
-
核心思想:动态规划
- 确定dp数组和下标含义:grid[i][j][k] = m 含义:节点i到节点j以【1...k】集合为中间节点的最短距离为m k是集合
- 确定递推公式:
- 节点i->节点j最短路径经过节点k:
grid[i][j][k] = grid[i][k][k-1]+grid[k][j][k-1] - 节点i->节点j最短路径不经过节点k
grid[i][j][k] = grid[i][j][k-1] - 最终递推式为:
grid[i][j][k] = min(grid[i][k][k-1]+grid[k][j][k-1],grid[i][j][k-1])
- 节点i->节点j最短路径经过节点k:
- dp数组初始化
grid[i][j][0]:节点0无意义;从节点0开始初始化;
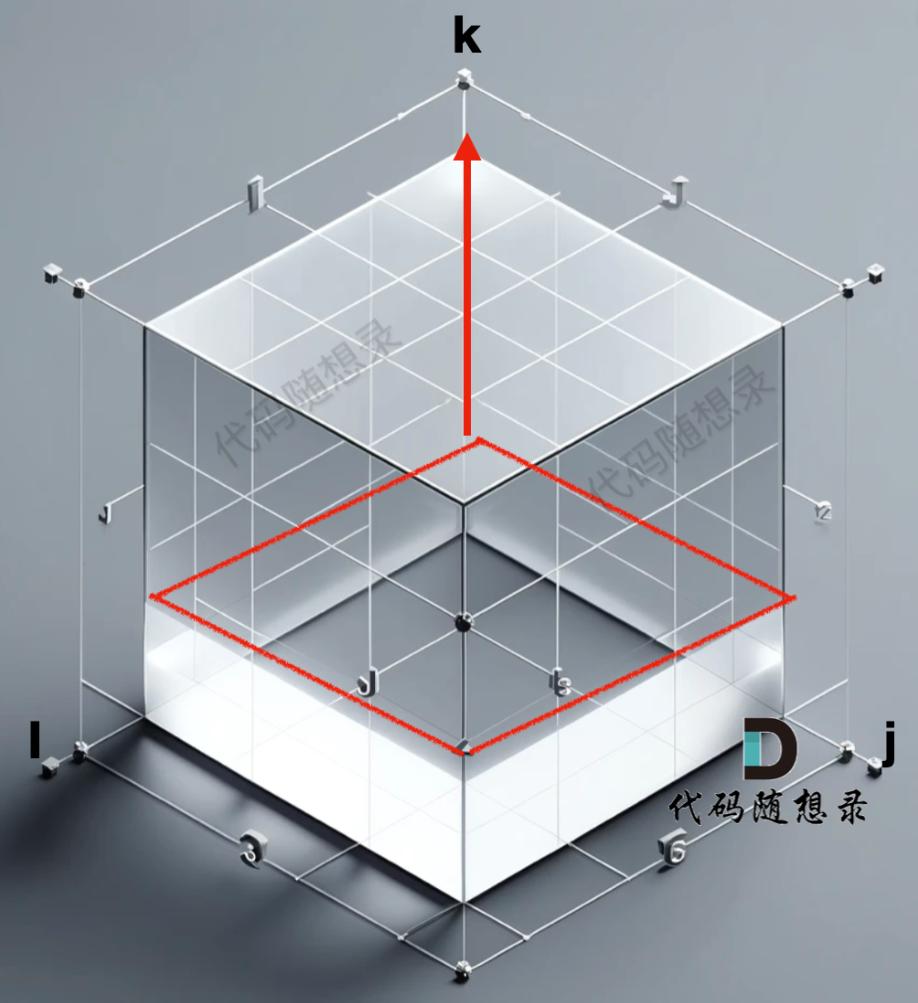
- 确定遍历顺序:从底层一层一层遍历上去;
- 推导dp数组
点击查看代码
def floyd(n,grid): for k in range(1,n+1): for i in range(1,n+1): for j in range(1,n+1): grid[i][j][k] = min(grid[i][k][k-1]+grid[k][j][k-1],grid[i][j][k-1]) return grid def main(): max_int = 10005 n,m = map(int,input().split()) grid = [[[max_int]*(n+1) for _ in range(n+1)] for _ in range(n+1)] for _ in range(m): p1,p2,w = map(int,input().split()) grid[p1][p2][0] = w grid[p2][p1][0] = w grid = floyd(n,grid) q = int(input()) for _ in range(q): start,end = map(int,input().split()) if grid[start][end][n]==max_int: print(-1) else: print(grid[start][end][n]) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
Astar算法
-
其实是BFS的变形;
-
BFS和Astar算法的动画如图:https://kamacoder.com/tools/knight.html
-
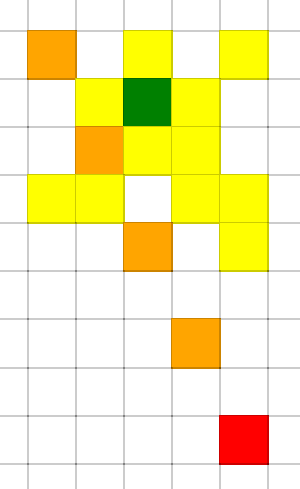
Astar遍历:
-
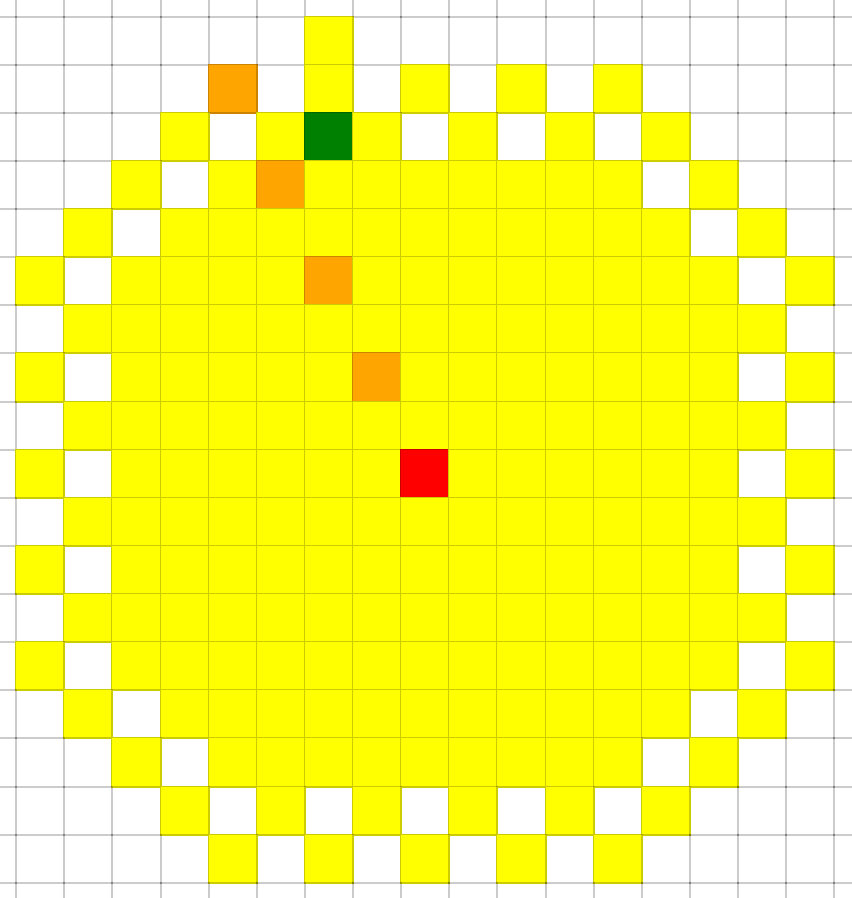
BFS遍历:
-
BFS 是没有目的性的 一圈一圈去搜索, 而 A * 是有方向性的去搜索。
-
其关键在于 启发式函数。
-
每个节点的权值为F,给出公式为:F = G + H
- G:起点达到目前遍历节点的距离
- F:目前遍历的节点到达终点的距离
-
本题的图是无权网格状,在计算两点距离通常有如下三种计算方式:
- 曼哈顿距离,计算方式: d = abs(x1-x2)+abs(y1-y2)
- 欧氏距离(欧拉距离) ,计算方式:d = sqrt( (x1-x2)^2 + (y1-y2)^2
- 切比雪夫距离,计算方式:d = max(abs(x1 - x2), abs(y1 - y2))
-
计算出来 F 之后,按照 F 的 大小,来选去出队列的节点。可以使用 优先级队列 帮我们排好序,每次出队列,就是F最小的节点。
-
多个目标找最近目标(特别是潜在目标数量很多的时候),可以考虑 Dijkstra ,BFS 或者 Floyd
点击查看代码
import heapq import math def heuristic(x1, y1, x2, y2): # 欧式距离作为启发式函数 return math.sqrt((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2) def a_star(a1,a2,b1,b2): # 定义骑士的8个移动方向 directions = [(-2, -1), (-1, -2), (1, -2), (2, -1), (2, 1), (1, 2), (-1, 2), (-2, 1)] pq = [] heapq.heappush(pq,(0,0,a1,a2)) visited = set() while pq: total_cost,curr_cost,x,y = heapq.heappop(pq) if (x,y) == (b1,b2): return curr_cost if (x,y) in visited: continue visited.add((x,y)) for dx,dy in directions: nx,ny = x+dx,y+dy if 1<=nx<=1000 and 1<=ny<=1000 and (nx,ny) not in visited: new_cost = curr_cost+1 total_cost = new_cost+heuristic(nx,ny,b1,b2) heapq.heappush(pq,(total_cost,new_cost,nx,ny)) return -1 def main(): # 定义骑士的8个移动方向 directions = [(-2, -1), (-1, -2), (1, -2), (2, -1), (2, 1), (1, 2), (-1, 2), (-2, 1)] n = int(input()) res = [] for _ in range(n): a1,a2,b1,b2 = map(int,input().split()) res_i = a_star(a1,a2,b1,b2) res.append(res_i) for res_i in res: print(res_i) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
路径规划算法总结
| 算法 | 源点数 | 边的权值是否为负数 | 检测负权回路 | 有限节点最短路径 | 思路 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dijkstra朴素版 | 单源 | 不可以 | 不可以 | 不可以 | 遍历未被访问的节点更新mindist |
| dijkstra堆优化版 | 单源 | 不可以 | 不可以 | 不可以 | 用堆栈优化 |
| Bellman_ford | 单源 | 可以 | 可以 | 可以 | 遍历边更新mindist |
| SPFA | 单源 | 可以 | 可以 | 可以 | 只优化当前节点相连的点 |
| Floyd | 多源 | 可以 | 可以 | 不可以 | 三维动态优化 |
图算法总结
- 深搜与广搜:遍历;
- 并查集:判断是否相连;
- 最小生成树;
- 拓扑排序;
- 最短路径算法;
分类:
代码随想录算法打卡





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)