Javascript Ajax
1.基本使用
- AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML,即异步 JavaScript 和 XML, 是一种在无需重新加载整个网页的情况下,能够更新部分网页的技术
- get请求:参数拼接到url后面
<script>
function getMsg(){
var url = '/process_get?year=2019&mouth=10&day=25'
//1.创建xhr对象
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//2.初始化参数
xhr.open('GET',url,true)
//3.监听state变化
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if (xhr.readyState==4 && xhr.status==200)
{
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
}
//执行发送
xhr.send(null)
}
</script>
- post请求:参数放在请求体中,需要在请求投中为不同的参数类型设定不同的Content-type
<script>
function postMsg(){
var url = '/process_post'
//1.创建xhq对象
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//2.初始化参数
xhr.open('POST',url,true)
//3.监听state变化
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if (xhr.readyState==4 && xhr.status==200)
{
console.log(xhr.responseText)
}
}
//为send()内的数据设置文档类型,方便服务器解析
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
//xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/json");
//xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type","multipart/form-data");
xhr.withCredentials = true;//跨域访问时携带cookie
//将要发送的数据传入send()方法
xhr.send('year=2019&mouth=10&day=25')
}
</script>
- 设置超时以及超时后的回调
//其他代码略
//超时后的回调
xhr.ontimeout = function () {
console.error('The request for ' + url + ' timed out.');
}
// 指定 10 秒钟超时
xhr.timeout = 10 * 1000
xhr.send(null)
- 终止请求:通过xhr.abort()方法终止此次请求
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//abort 事件(请求中止,比如用户调用了abort()方法)的监听函数
xhr.onabort = function () {
console.log('The request was aborted');
}
//其他代码略
xhr.abort()
2.参数数据类型
- 如果是get请求,无需设置Content-type,将要发送的数据以 username=xxx&pass=xxx 的形式拼接到url后面
var url = '/process_get?year=2019&mouth=10&day=25'
- 如果是post请求,发送的数据通过 xhr.send() 进行发送,并在请求头中为其设置正确的数据类型,因为它告诉服务器请求体的数据类型是什么。这有助于服务器正确解析请求体中的数据
//urlencoded
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/x-www-form-urlencoded")
xhr.send('year=2019&mouth=10&day=25')
//JSON数据
xhr.setRequestHeader("Content-type","application/json")
xhr.send(JSON.stringify({}))
//表单 无需设置Content-type
var formData = new FormData()
formData.append('username', '张三')
xhr.send(formData)
3.事件及状态
- onreadystatechange事件,触发事件时xhr.readyState值发生改变
| 状态码 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 请求未初始化 |
| 1 | 服务器连接已建立 |
| 2 | 请求已接收 |
| 3 | 请求处理中 |
| 4 | 请求已完成,且响应已就绪 |
<script>
function getMsg(){
var url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8097/api/data.json'
//创建xhq对象
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//监听state变化
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
console.log('xhr.readyState = ',xhr.readyState)
}
//load 事件(请求成功完成)的监听函数,不一定有数据返回
xhr.onload = function() {
console.log('onload',xhr.response)
};
//abort 事件(请求中止,比如用户调用了abort()方法)的监听函数
xhr.onabort = function () {
console.log('The request was aborted');
};
//progress事件(正在发送和加载数据)的监听函数
xhr.onprogress = function (event) {
console.log('onprogress',event.loaded,event.total);
};
//error 事件(请求失败)的监听函数
xhr.onerror = function() {
console.log('There was an error!');
};
//发送请求
xhr.open('GET',url,true)
xhr.send()
}
getMsg()
</script>
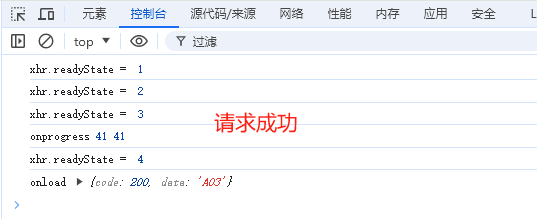
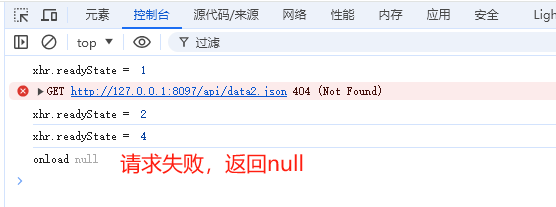
- 服务器响应状态通过xhr.status进行判断,他表示HTTP状态码
| 常用状态码 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 200 | 请求已成功,服务器正常处理并返回请求的资源 |
| 3xx系列 | 重定向状态码 |
| 401 | 需要用户进行身份验证 |
| 403 | 没有权限访问 |
| 404 | 未找到页面 |
| 5xx系列 | 服务器错误状态码 |
- 一个正常的请求应该是:请求已完成,且响应已就绪 (xhr.readyState4) 且 请求已成功,服务器正常处理并返回请求的资源 (xhr.status200)
4.服务器的响应
- 如需获得来自服务器的响应,请使用 XMLHttpRequest 对象的 response / responseText / responseXML 属性
- response/responseText 获得字符串形式的响应数据,可以自主转换成其他类型的数据
- responseXML 获得 XML 形式的响应数据,在没有收到任何数据或数据类型错误的情况下返回的 null
<script>
//创建服务
var xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
//其他代码略
var result = JSON.parse(xhr.response)
</script>
5.将token添加到请求头中
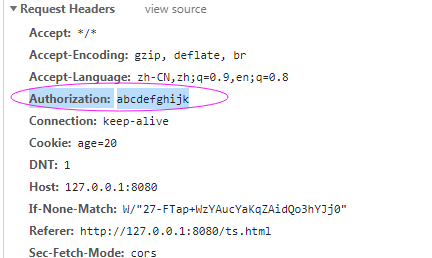
- 从localStorage读取token,并使用setRequestHeader()添加到请求头中
xhr.setRequestHeader("Authorization",window.localStorage.getItem('token'));
6.跨域携带cooikie
- 前端设置
xhr.withCredentials = true;//跨域访问时携带cookie
- 后端设置
//1.Access-Control-Allow-Credentials 设置为 true
//2.不能把 Access-Control-Allow-Origin 设置为 “” 或 *,而要设置为客户端发送请求时的IP地址
7.get/post区别
- 用途:Get 是用来从服务器上获得数据,而 Post 是用来向服务器上传递数据
- 参数的位置:get的提交的数据通过?key=val拼接到url后面,而post提交的数据在请求体中
- 数据长度:Get 传输的数据量小,这主要是因为受 URL 长度限制;而 Post 可以传输大量的数据,所以在上传文件只能使用 Post
- 安全性:post安全性更高,get方法请求的信息因为拼接在url中,对所有人都是可见的。
- 浏览器历史:GET 请求保留在浏览器历史记录中,而POST 请求不会
- 可被缓存:GET 请求可被缓存,POST 请求不会被缓存,所谓缓存,指的就是浏览器直接读取本地已经缓存资源,而不是每次都从原始服务器上重新获取





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了