Linux之openssl实现私有CA
一、简介
Centos7.9通过openssl工具构建一个私有的CA,用于颁发证书。
验证私有CA为httpd应用签署证书
二、构建私有CA
1、编辑CA的配置文件
[root@HLWHOST tls]# pwd
/etc/pki/tls
[root@HLWHOST tls]# cat /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
...
####################################################################
[ CA_default ]
dir = /etc/pki/CA # Where everything is kept
certs = $dir/certs # Where the issued certs are kept
crl_dir = $dir/crl # Where the issued crl are kept
database = $dir/index.txt # database index file.
#unique_subject = no # Set to 'no' to allow creation of
# several ctificates with same subject.
new_certs_dir = $dir/newcerts # default place for new certs.
certificate = /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem # The CA certificate
serial = $dir/serial # The current serial number
crlnumber = $dir/crlnumber # the current crl number
# must be commented out to leave a V1 CRL
crl = $dir/crl.pem # The current CRL
private_key = /etc/pki/CA/private/cakey.pem# The private key
RANDFILE = $dir/private/.rand # private random number file
x509_extensions = usr_cert # The extentions to add to the cert
...
[ req_distinguished_name ]
countryName = Country Name (2 letter code)
countryName_default = CN
countryName_min = 2
countryName_max = 2
stateOrProvinceName = State or Province Name (full name)
#stateOrProvinceName_default = Default Province
localityName = Locality Name (eg, city)
localityName_default = beijing
0.organizationName = Organization Name (eg, company)
0.organizationName_default = Default Company Ltd
...
2、生成rsa私钥
[root@HLWHOST ca]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)
[root@HLWHOST ca]# cd /etc/pki/
CA/ ca-trust/ java/ nssdb/ nss-legacy/ rpm-gpg/ rsyslog/ tls/
[root@HLWHOST ca]# cd /etc/pki/CA/
[root@HLWHOST CA]# ls
certs crl newcerts private
[root@HLWHOST CA]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out private/cakey.pem 2048)
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus (2 primes)
.....................................+++++
..................+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
[root@HLWHOST CA]# ls -l private/
总用量 4
-rw-------. 1 root root 1675 1月 26 11:25 cakey.pem
[root@HLWHOST CA]#
3、生成CA自身的证书
[root@HLWHOST CA]# openssl req -new -x509 -key private/cakey.pem -out cacert.pem
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:
Locality Name (eg, city) []:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:HLWHOST
Email Address []:
* 一定确保以下几个目录存在,不存在创建
[root@HLWHOST CA]# ls
cacert.pem certs crl newcerts private
[root@HLWHOST CA]# touch index.txt
[root@HLWHOST CA]# touch serial
[root@HLWHOST CA]# echo 01 > serial
[root@HLWHOST CA]# ls
cacert.pem certs crl index.txt newcerts private serial
以上一个私有的CA机构构建完成
三、Web服务通过私有CA进行证书签署
第一步:生成客户端的密钥,即客户端的公私钥对,且要保证私钥只有客户端自己拥有。
第二步:以客户端的密钥和客户端自身的信息(国家、机构、域名、邮箱等)为输入,生成证书请求文件。其中客户端的公钥和客户端信息是明文保存在证书请求文件中的,而客户端私钥的作用是对客户端公钥及客户端信息做签名,自身是不包含在证书请求中的。然后把证书请求文件发送给CA机构。
第三步:CA机构接收到客户端的证书请求文件后,首先校验其签名,然后审核客户端的信息,最后CA机构使用自己的私钥为证书请求文件签名,生成证书文件,下发给客户端。此证书就是客户端的身份证,来表明用户的身份。
1、在httpd配置文件目录创建证书存放目录
[root@HLWHOST CA]# cd /etc/httpd/
[root@HLWHOST httpd]# mkdir ssl
[root@HLWHOST httpd]# cd ssl/
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# pwd
/etc/httpd/ssl
2、生成httpd自己的密钥
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# (umask 077;openssl genrsa -out httpd.key 1024)
Generating RSA private key, 1024 bit long modulus (2 primes)
...........................................+++++
..........+++++
e is 65537 (0x010001)
3、生成一个证书颁发请求
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# openssl req -new -key httpd.key -out httpd.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:
Locality Name (eg, city) []:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:HLWHOST
Email Address []:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# ls
httpd.csr httpd.key
注意:server FQDN or YOUR name为使用证书的web的主机名,不要填错。
4、CA对httpd的证书签署请求做签署
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# openssl ca -in httpd.csr -out httpd.crt -days 365 -config /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Using configuration from /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf
Can't load /root/.rnd into RNG
140691121755968:error:2406F079:random number generator:RAND_load_file:Cannot open file:crypto/rand/randfile.c:98:Filename=/root/.rnd
Check that the request matches the signature
Signature ok
Certificate Details:
Serial Number: 1 (0x1)
Validity
Not Before: Jan 27 02:28:26 2024 GMT
Not After : Jan 26 02:28:26 2025 GMT
Subject:
countryName = AU
stateOrProvinceName = Some-State
organizationName = Internet Widgits Pty Ltd
commonName = HLWHOST
X509v3 extensions:
X509v3 Basic Constraints:
CA:FALSE
Netscape Comment:
OpenSSL Generated Certificate
X509v3 Subject Key Identifier:
9C:FD:D7:D6:25:9C:6E:9B:55:54:D7:99:5D:33:40:D7:E5:8C:90:28
X509v3 Authority Key Identifier:
keyid:62:FE:15:14:9F:9A:AE:BD:4A:28:8F:DF:3A:59:D0:77:CA:8D:DC:F2
Certificate is to be certified until Jan 26 02:28:26 2025 GMT (365 days)
Sign the certificate? [y/n]:y
1 out of 1 certificate requests certified, commit? [y/n]y
Write out database with 1 new entries
Data Base Updated
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# ll
总用量 12
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3692 1月 27 10:34 httpd.crt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 627 1月 27 10:22 httpd.csr
-rw-------. 1 root root 887 1月 27 10:19 httpd.key
- 查看CA数据库已经更新
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# cat /etc/pki/CA/index.txt
V 250126022826Z 01 unknown /C=AU/ST=Some-State/O=Internet Widgits Pty Ltd/CN=HLWHOST
四、基于https访问页面
1、安装mod_ssl模块
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# yum -y install mod_ssl
...
已安装:
mod_ssl.x86_64 1:2.4.6-99.el7.centos.1
2、修改配置文件
[root@HLWHOST tls]# vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
SSLEngine on
# Server Certificate:
# Point SSLCertificateFile at a PEM encoded certificate. If
# the certificate is encrypted, then you will be prompted for a
# pass phrase. Note that a kill -HUP will prompt again. A new
# certificate can be generated using the genkey(1) command.
#SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/localhost.crt
SSLCertificateFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.key
SSLCACertificateFile /etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem
# Server Private Key:
# If the key is not combined with the certificate, use this
# directive to point at the key file. Keep in mind that if
# you've both a RSA and a DSA private key you can configure
# both in parallel (to also allow the use of DSA ciphers, etc.)
#SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/localhost.key
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/httpd/ssl/httpd.key
3、重启httpd服务
[root@HLWHOST tls]# systemctl restart httpd
[root@HLWHOST tls]# netstat -nutlp | grep 81
tcp6 0 0 :::81 :::* LISTEN 46454/httpd
udp6 0 0 fe80::f816:3eff:fea:123 :::* 17542/ntpd
4、准备测试页面
[root@HLWHOST tls]# echo "http_ssl_test" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@HLWHOST tls]# cat /var/www/html/index.html
http_ssl_test
5、验证基于https访问默认页面
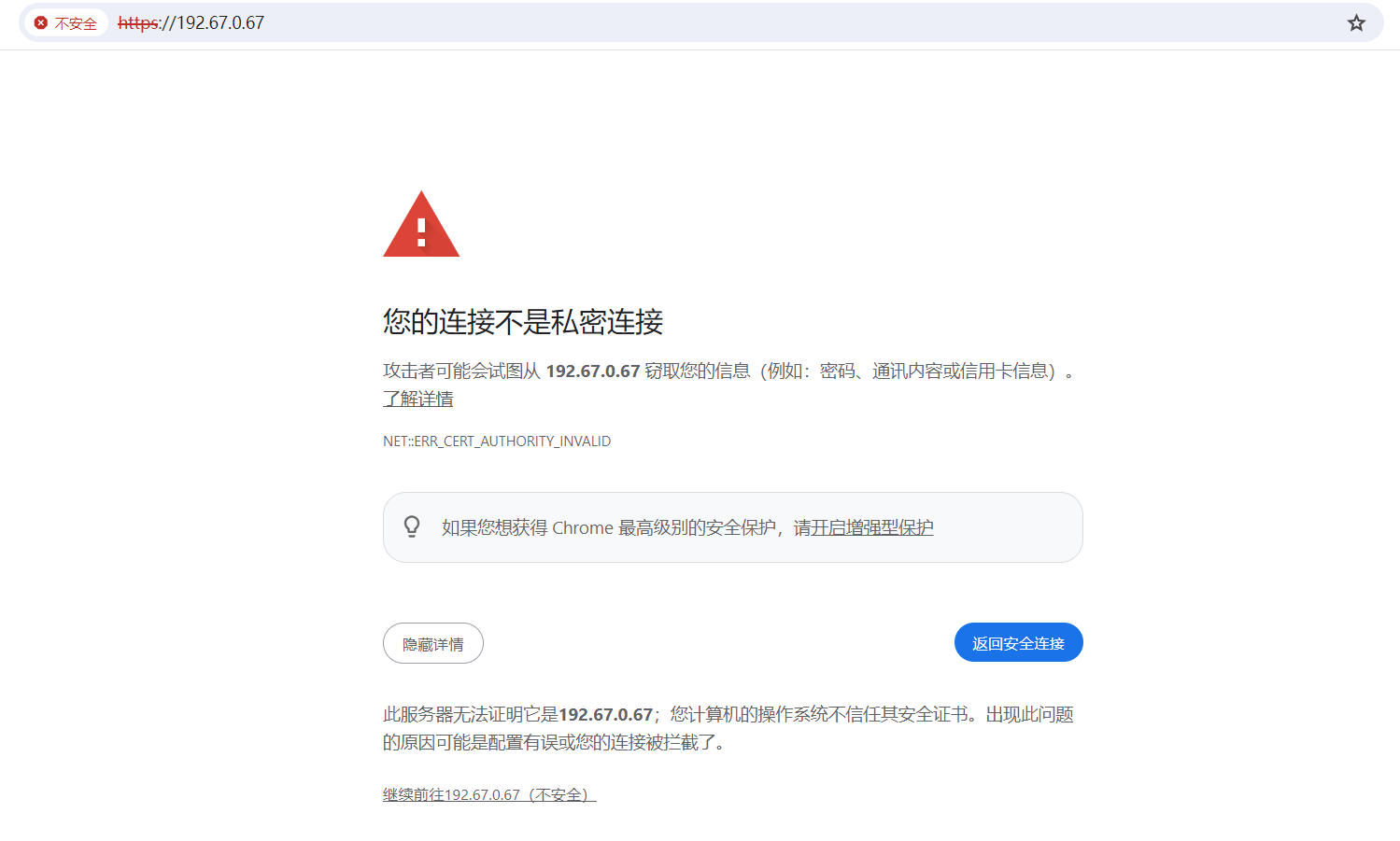
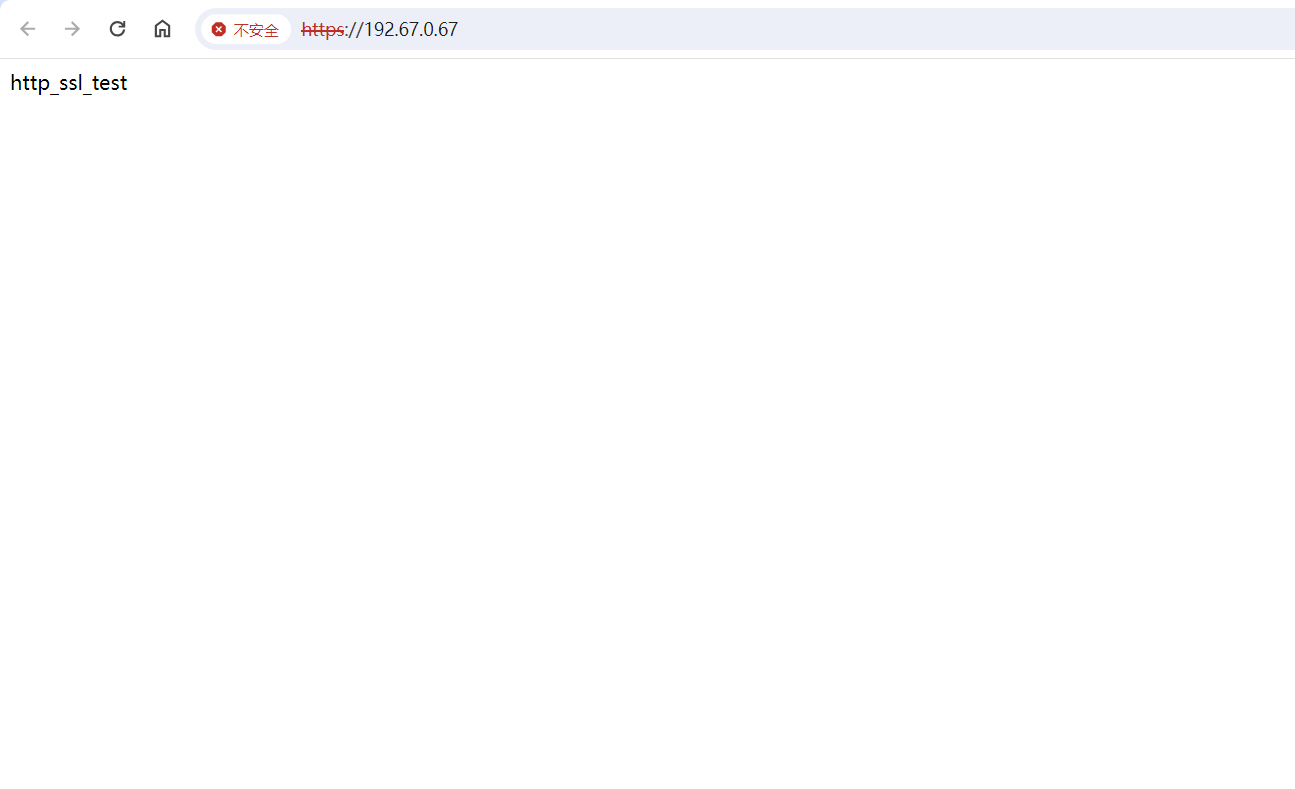
注意:可以将cacert.pem证书发给客户端,实现证书导入。
五、遇到的问题
[root@HLWHOST ssl]# openssl ca -in httpd.csr -out httpd.crt -days 365
Using configuration from /usr/local/openssl-1.1.1q/ssl/openssl.cnf
Can't open ./demoCA/private/cakey.pem for reading, No such file or directory
140473297381184:error:02001002:system library:fopen:No such file or directory:crypto/bi o/bss_file.c:69:fopen('./demoCA/private/cakey.pem','r')
140473297381184:error:2006D080:BIO routines:BIO_new_file:no such file:crypto/bio/bss_fi le.c:76:
unable to load CA private key
此报错是因为签署的时候找openssl.cnf文件去源码包安装的路径去找了,需要在签署的时候指定一下openssl.cnf的绝对路径。
六、一键生成ssl自签名证书脚本
查看
#!/bin/bash -e
# * 为必改项
# * 更换为你自己的域名
CN='' # 例如: demo.rancher.com
# 扩展信任IP或域名
## 一般ssl证书只信任域名的访问请求,有时候需要使用ip去访问server,那么需要给ssl证书添加扩展IP,
## 多个IP用逗号隔开。如果想多个域名访问,则添加扩展域名(SSL_DNS),多个SSL_DNS用逗号隔开
SSL_IP='' # 例如: 1.2.3.4
SSL_DNS='' # 例如: demo.rancher.com
# 国家名(2个字母的代号)
C=CN
# 证书加密位数
SSL_SIZE=2048
# 证书有效期
DATE=${DATE:-3650}
# 配置文件
SSL_CONFIG='openssl.cnf'
if [[ -z $SILENT ]]; then
echo "----------------------------"
echo "| SSL Cert Generator |"
echo "----------------------------"
echo
fi
export CA_KEY=${CA_KEY-"cakey.pem"}
export CA_CERT=${CA_CERT-"cacerts.pem"}
export CA_SUBJECT=ca-$CN
export CA_EXPIRE=${DATE}
export SSL_CONFIG=${SSL_CONFIG}
export SSL_KEY=$CN.key
export SSL_CSR=$CN.csr
export SSL_CERT=$CN.crt
export SSL_EXPIRE=${DATE}
export SSL_SUBJECT=${CN}
export SSL_DNS=${SSL_DNS}
export SSL_IP=${SSL_IP}
export K8S_SECRET_COMBINE_CA=${K8S_SECRET_COMBINE_CA:-'true'}
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "--> Certificate Authority"
if [[ -e ./${CA_KEY} ]]; then
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Using existing CA Key ${CA_KEY}"
else
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Generating new CA key ${CA_KEY}"
openssl genrsa -out ${CA_KEY} ${SSL_SIZE} > /dev/null
fi
if [[ -e ./${CA_CERT} ]]; then
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Using existing CA Certificate ${CA_CERT}"
else
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Generating new CA Certificate ${CA_CERT}"
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -new -nodes -key ${CA_KEY} \
-days ${CA_EXPIRE} -out ${CA_CERT} -subj "/CN=${CA_SUBJECT}" > /dev/null || exit 1
fi
echo "====> Generating new config file ${SSL_CONFIG}"
cat > ${SSL_CONFIG} <<EOM
[req]
req_extensions = v3_req
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
[req_distinguished_name]
[ v3_req ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage = clientAuth, serverAuth
EOM
if [[ -n ${SSL_DNS} || -n ${SSL_IP} ]]; then
cat >> ${SSL_CONFIG} <<EOM
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
EOM
IFS=","
dns=(${SSL_DNS})
dns+=(${SSL_SUBJECT})
for i in "${!dns[@]}"; do
echo DNS.$((i+1)) = ${dns[$i]} >> ${SSL_CONFIG}
done
if [[ -n ${SSL_IP} ]]; then
ip=(${SSL_IP})
for i in "${!ip[@]}"; do
echo IP.$((i+1)) = ${ip[$i]} >> ${SSL_CONFIG}
done
fi
fi
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Generating new SSL KEY ${SSL_KEY}"
openssl genrsa -out ${SSL_KEY} ${SSL_SIZE} > /dev/null || exit 1
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Generating new SSL CSR ${SSL_CSR}"
openssl req -sha256 -new -key ${SSL_KEY} -out ${SSL_CSR} \
-subj "/CN=${SSL_SUBJECT}" -config ${SSL_CONFIG} > /dev/null || exit 1
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Generating new SSL CERT ${SSL_CERT}"
openssl x509 -sha256 -req -in ${SSL_CSR} -CA ${CA_CERT} \
-CAkey ${CA_KEY} -CAcreateserial -out ${SSL_CERT} \
-days ${SSL_EXPIRE} -extensions v3_req \
-extfile ${SSL_CONFIG} > /dev/null || exit 1
if [[ -z $SILENT ]]; then
echo "====> Complete"
echo "keys can be found in volume mapped to $(pwd)"
echo
echo "====> Output results as YAML"
echo "---"
echo "ca_key: |"
cat $CA_KEY | sed 's/^/ /'
echo
echo "ca_cert: |"
cat $CA_CERT | sed 's/^/ /'
echo
echo "ssl_key: |"
cat $SSL_KEY | sed 's/^/ /'
echo
echo "ssl_csr: |"
cat $SSL_CSR | sed 's/^/ /'
echo
echo "ssl_cert: |"
cat $SSL_CERT | sed 's/^/ /'
echo
fi
if [[ -n $K8S_SECRET_NAME ]]; then
if [[ -n $K8S_SECRET_COMBINE_CA ]]; then
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Adding CA to Cert file"
cat ${CA_CERT} >> ${SSL_CERT}
fi
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Creating Kubernetes secret: $K8S_SECRET_NAME"
kubectl delete secret $K8S_SECRET_NAME --ignore-not-found
if [[ -n $K8S_SECRET_SEPARATE_CA ]]; then
kubectl create secret generic \
$K8S_SECRET_NAME \
--from-file="tls.crt=${SSL_CERT}" \
--from-file="tls.key=${SSL_KEY}" \
--from-file="ca.crt=${CA_CERT}"
else
kubectl create secret tls \
$K8S_SECRET_NAME \
--cert=${SSL_CERT} \
--key=${SSL_KEY}
fi
if [[ -n $K8S_SECRET_LABELS ]]; then
[[ -z $SILENT ]] && echo "====> Labeling Kubernetes secret"
IFS=$' \n\t' # We have to reset IFS or label secret will misbehave on some systems
kubectl label secret \
$K8S_SECRET_NAME \
$K8S_SECRET_LABELS
fi
fi
echo "4. 重命名服务证书"
mv ${CN}.key tls.key
mv ${CN}.crt tls.crt
七、参考页面
https://www.cnblogs.com/kcxg/p/10671831.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号