ASP.NET视图的保存与加载解析(二)——视图的加载
2、视图的加载
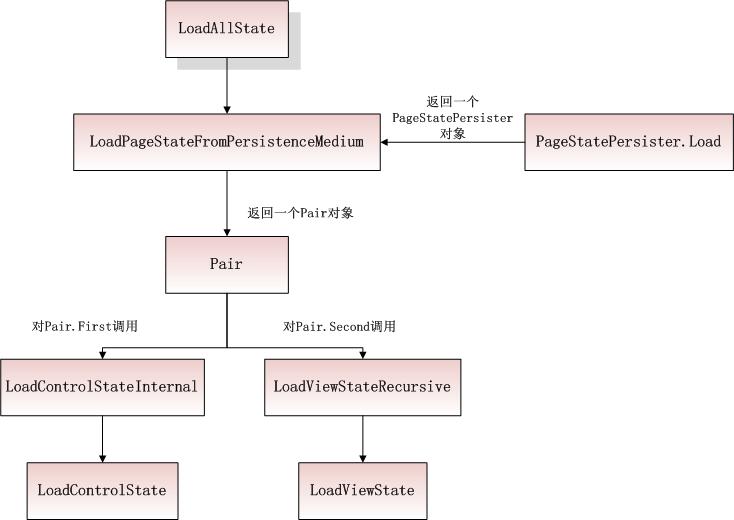
图2
如图2所示在加载视图的时候会调用LoadAllState函数:
 代码
代码
{
object obj2 = this.LoadPageStateFromPersistenceMedium();
IDictionary first = null;
Pair second = null;
Pair pair2 = obj2 as Pair;
if (obj2 != null)
{
first = pair2.First as IDictionary;
second = pair2.Second as Pair;
}
if (first != null)
{
this._controlsRequiringPostBack = (ArrayList) first["__ControlsRequirePostBackKey__"];
if (this._registeredControlsRequiringControlState != null)
{
foreach (Control control in (IEnumerable) this._registeredControlsRequiringControlState)
{
control.LoadControlStateInternal(first[control.UniqueID]);
}
}
}
if (second != null)
{
string s = (string) second.First;
int num = int.Parse(s, NumberFormatInfo.InvariantInfo);
this._fPageLayoutChanged = num != this.GetTypeHashCode();
if (!this._fPageLayoutChanged)
{
base.LoadViewStateRecursive(second.Second);
}
}
}
在LoadAllState中最先调用的是object obj2 = this.LoadPageStateFromPersistenceMedium()其中LoadPageStateFromPersistenceMedium实际上返回的是一个Pair对象(请对比视图保存中的SavePageStateToPersistenceMedium传入的参数也是个Pair)
深入LoadPageStateFromPersistenceMedium:
protected internal virtual object LoadPageStateFromPersistenceMedium()
{
PageStatePersister pageStatePersister = this.PageStatePersister;
try
{
pageStatePersister.Load();
}
catch (HttpException exception)
{
if (this._pageFlags[8])
{
return null;
}
exception.WebEventCode = 0xbba;
throw;
}
return new Pair(pageStatePersister.ControlState, pageStatePersister.ViewState);
}
这个函数其实就是构造了个PageStatePersister对象pageStatePersister,然后用pageStatePersister.Load()将回发页面上的input信息进行读取并且反序列化还原成pageStatePersister.ControlState和pageStatePersister.ViewState,最后利用还原的值返回个Pair对象
回到LoadAllState:
IDictionary first = null;
Pair second = null;
Pair pair2 = obj2 as Pair;
if (obj2 != null)
{
first = pair2.First as IDictionary;
second = pair2.Second as Pair;
}
这几句就是将LoadPageStateFromPersistenceMedium返回的Pair对象进行拆分,将First还原成IDictionary散列集合这就是页面所有的控件状态,然后将Second还原成个Pair,这个Pair就包含了页面控件树的视图信息,其实这里就是将SaveAllState里用控件状态和控件视图构造的Pair对象state又拆分并还原了。
if (first != null)
{
this._controlsRequiringPostBack = (ArrayList) first["__ControlsRequirePostBackKey__"];
if (this._registeredControlsRequiringControlState != null)
{
foreach (Control control in (IEnumerable) this._registeredControlsRequiringControlState)
{
control.LoadControlStateInternal(first[control.UniqueID]);
}
}
}
这几句是对页面上所有注册要使用控件状态的控件进行遍历,并依次用控件的唯一ID在first 散列集合里找到控件对应的控件状态信息(散列集合的每个都是Pair对象,如果不清楚请参考视图保存的SaveAllState逻辑)并调用LoadControlStateInternal
internal void LoadControlStateInternal(object savedStateObj)
{
if (!this.flags[0x100000])
{
this.flags.Set(0x100000);
Pair pair = (Pair) savedStateObj;
if (pair != null)
{
Page page = this.Page;
if ((page == null) || page.ShouldLoadControlState(this))
{
if (pair.First != null)
{
this.LoadControlState(pair.First);
}
if ((this._adapter != null) && (pair.Second != null))
{
this._adapter.LoadAdapterControlState(pair.Second);
}
}
}
}
}
LoadControlStateInternal中首先将传入的参数转换为了Pair对象,然后对pair.First调用LoadControlState读取本控件的控件状态(和SaveControlState一样这是个虚拟的空函数要自己实现逻辑),this._adapter != null如果适配器不为空,对pair.Second调用LoadAdapterControlState从适配器的角度加载本控件的控件状态,LoadAdapterControlState是一个虚拟的空函数,如果为控件指定了适配器,也要实现适配器控件状态加载逻辑,可见LoadControlStateInternal为SaveControlStateInternal的逆过程——加载控件状态。
回到LoadAllState
if (second != null)
{
string s = (string) second.First;
int num = int.Parse(s, NumberFormatInfo.InvariantInfo);
this._fPageLayoutChanged = num != this.GetTypeHashCode();
if (!this._fPageLayoutChanged)
{
base.LoadViewStateRecursive(second.Second);
}
}
前面说了LoadPageStateFromPersistenceMedium返回的Pair的Second是控件的视图,所以上面这几句的核心就是base.LoadViewStateRecursive(second.Second)对pair.Second.Second递归读取控件树的视图信息,请看LoadViewStateRecursive:
internal void LoadViewStateRecursive(object savedState)
{
if ((savedState != null) && !this.flags[4])
{
if ((this.Page != null) && this.Page.IsPostBack)
{
object first = null;
object state = null;
ArrayList childState = null;
Pair pair = savedState as Pair;
if (pair != null)
{
first = pair.First;
childState = (ArrayList) pair.Second;
}
else
{
Triplet triplet = (Triplet) savedState;
first = triplet.First;
state = triplet.Second;
childState = (ArrayList) triplet.Third;
}
try
{
if ((state != null) && (this._adapter != null))
{
this._adapter.LoadAdapterViewState(state);
}
if (first != null)
{
this.LoadViewState(first);
}
if (childState != null)
{
if (this.LoadViewStateByID)
{
this.LoadChildViewStateByID(childState);
}
else
{
this.LoadChildViewStateByIndex(childState);
}
}
}
catch (InvalidCastException)
{
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Controls_Cant_Change_Between_Posts"));
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
throw new HttpException(SR.GetString("Controls_Cant_Change_Between_Posts"));
}
}
this._controlState = ControlState.ViewStateLoaded;
}
}
首先
object first = null;
object state = null;
ArrayList childState = null;
Pair pair = savedState as Pair;
if (pair != null)
{
first = pair.First;
childState = (ArrayList) pair.Second;
}
else
{
Triplet triplet = (Triplet) savedState;
first = triplet.First;
state = triplet.Second;
childState = (ArrayList) triplet.Third;
}
这是根据传入LoadViewStateRecursive的参数值savedState 判断其是Pair还是Triplet ,并根据相应的情况还原为first本控件的视图,state适配器的视图,childState子控件视图的散列集合(对比SaveViewStateRecursive中相应的逆过程来理解)
接着
if ((state != null) && (this._adapter != null))
{
this._adapter.LoadAdapterViewState(state);
}
if (first != null)
{
this.LoadViewState(first);
}
if ((state != null) && (this._adapter != null))表示如果还原的适配器视图信息不为空且控件的适配器也不为空,那么就用this._adapter.LoadAdapterViewState(state)从适配器角度读取控件的视图信息(LoadAdapterViewState是虚拟空函数逻辑要自己实现),然后this.LoadViewState(first)通过LoadViewState加载first视图信息到本控件:
protected virtual void LoadViewState(object savedState)
{
if (savedState != null)
{
this.ViewState.LoadViewState(savedState);
object obj2 = this.ViewState["Visible"];
if (obj2 != null)
{
if (!((bool) obj2))
{
this.flags.Set(0x10);
}
else
{
this.flags.Clear(0x10);
}
this.flags.Set(0x20);
}
}
}
可见LoadViewState的核心就是this.ViewState.LoadViewState(savedState)加载本控件的ViewState集合,当然根据试图的保存所讲SaveViewState返回一个ArrayList那么这里传入的savedState也应该是个ArrayList
回到LoadViewStateRecursive
if (childState != null)
{
if (this.LoadViewStateByID)
{
this.LoadChildViewStateByID(childState);
}
else
{
this.LoadChildViewStateByIndex(childState);
}
}
这几句就是根据实际情况根据子控件ID加载视图信息或根据子控件在控件树中的序列加载视图信息
internal void LoadChildViewStateByID(ArrayList childState)
{
int count = childState.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i += 2)
{
string id = (string) childState[i];
object savedState = childState[i + 1];
Control control = this.FindControl(id);
if (control != null)
{
control.LoadViewStateRecursive(savedState);
}
else
{
this.EnsureOccasionalFields();
if (this._occasionalFields.ControlsViewState == null)
{
this._occasionalFields.ControlsViewState = new Hashtable();
}
this._occasionalFields.ControlsViewState[id] = savedState;
}
}
}
internal void LoadChildViewStateByIndex(ArrayList childState)
{
ControlCollection controls = this.Controls;
int count = controls.Count;
int num2 = childState.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < num2; i += 2)
{
int num4 = (int) childState[i];
object savedState = childState[i + 1];
if (num4 < count)
{
controls[num4].LoadViewStateRecursive(savedState);
}
else
{
this.EnsureOccasionalFields();
if (this._occasionalFields.ControlsViewState == null)
{
this._occasionalFields.ControlsViewState = new Hashtable();
}
this._occasionalFields.ControlsViewState[num4] = savedState;
}
}
}
前面在视图的保存讲到数组列表中控件的视图和控件本身是一对一对存在的,所以不管是LoadChildViewStateByID或LoadChildViewStateByIndex从数组中读取视图信息也是一对一对的在读取,然后根据读取的数据找到相应的控件并对其视图信息savedState(是个Pair或Triplet)调用LoadViewStateRecursive递归加载子控件的视图。
这样在LoadAllState中通过调用循环调用LoadControlStateInternal和递归调用LoadViewStateRecursive就将页面所有控件的视图状态和所有控件的视图信息加载完毕了
可见视图的加载就是视图保存的的逆过程,你会发现在加载过程的每一步都可以在保存过程中找到相应的步骤与其对应,所以要通过比较来理解两个过程。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号