【Oracle11g】21_游标
1.游标简介
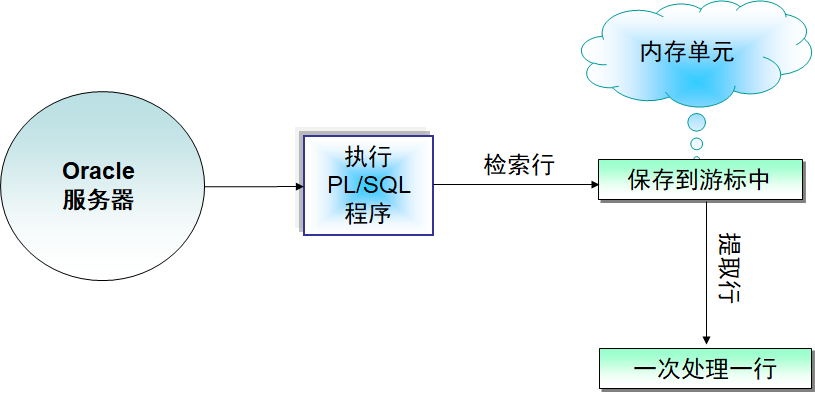
逐行处理查询结果,以编程的方式访问数据。
2.游标的类型
(1)隐式游标:在 PL/SQL 程序中执行DML SQL 语句时自动创建隐式游标,名字固定叫sql。
(2)显式游标:显式游标用于处理返回多行的查询。
(3)REF 游标:REF 游标用于处理运行时才能确定的动态SQL查询的结果。
2.1 隐式游标
在PL/SQL中使用DML语句时自动创建隐式游标。
隐式游标自动声明、打开和关闭,其名为 SQL
通过检查隐式游标的属性可以获得最近执行的DML 语句的信息。
隐式游标的属性有:
- %FOUND – SQL 语句影响了一行或多行时为 TRUE
- %NOTFOUND – SQL 语句没有影响任何行时为TRUE
- %ROWCOUNT – SQL 语句影响的行数
- %ISOPEN - 游标是否打开,始终为FALSE
实战演练:%found 的使用
SQL> select * from t1;
ID NAME AGE
---------- ---------- ----------
1 Jack 19
2 Tom 22
3 Alice 11
SQL> set serveroutput on
----------
begin
update t1 set age = age + 1 where age > 30;
if sql%found then
dbms_output.put_line('更新了记录');
else
dbms_output.put_line('没有更新记录');
end if;
end;
/
执行结果:没有更新记录
实战演练:select into的时候的两个异常(too_many_rows , no_data_found)
declare
sname1 varchar2(10);
begin
select name into sname1 from t1;
dbms_output.put_line(sname1);
exception
when too_many_rows then
dbms_output.put_line('取出的名字多于一个');
end;
/
2.2 显示游标
2.2.1 一般游标
显式游标在 PL/SQL 块的声明部分定义查询,该查询可以返回多行。
显式游标的操作过程:

步骤:声明游标 -->> 打开游标 -->> 使用游标取出记录 -->> 关闭游标
实战演练:
declare
st1 t1%rowtype;
cursor mycursor is select * from t1;
begin
open mycursor;
fetch mycursor into st1;
while mycursor%found loop
dbms_output.put_line('ID是:'|| st1.ID || ',姓名是:' || st1.name);
fetch mycursor into st1;
end loop;
close mycursor;
end;
/
输出结果:
ID是:1,姓名是:Jack
ID是:2,姓名是:Tom
ID是:3,姓名是:Alice
2.2.1 带参数的显式游标
声明显式游标时可以带参数以提高灵活性
声明带参数的显式游标的语法如下:
CURSOR <cursor_name>(<param_name> <param_type>) IS select_statement;
实战演练
declare
v1 t1.ID%type;
st1 t1%rowtype;
cursor mycursor(input_id number) is select * from t1 where id > input_id;
begin
v1 := &学生学号;
open mycursor(v1);
fetch mycursor into st1;
while mycursor%found loop
dbms_output.put_line('ID是:'|| st1.ID || ',姓名是:' || st1.name);
fetch mycursor into st1;
end loop;
close mycursor;
end;
/
输出结果:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
输入 学生学号 的值: 1
原值 6: v1 := &学生学号;
新值 6: v1 := 1;
2.2.1 允许使用游标删除或更新活动集中的行
声明游标时必须使用 SELECT … FOR UPDATE语句
-- 更新的语法
CURSOR <cursor_name> IS
SELECT statement FOR UPDATE;
UPDATE <table_name>
SET <set_clause>
WHERE CURRENT OF <cursor_name>
-- 删除的语法
DELETE FROM <table_name>
WHERE CURRENT OF <cursor_name>
实战演练
declare
st1 t1%rowtype;
cursor mycursor is select * from t1 where id = 1 or id = 2 for update;
begin
open mycursor;
fetch mycursor into st1;
while mycursor%found loop
update t1 set id = id + 10 where current of mycursor;
fetch mycursor into st1;
end loop;
close mycursor;
end;
/
2.3 循环游标
循环游标用于简化游标处理代码
当用户需要从游标中提取所有记录时使用
循环游标的语法如下:
FOR <record_index> IN <cursor_name>
LOOP
<executable statements>
END LOOP;
实战演练:
declare
st1 t1%rowtype;
cursor mycursor is select * from t1;
begin
for cur_2 in mycursor loop
dbms_output.put_line('ID是:'|| cur_2.ID || ',姓名是:' || cur_2.name);
end loop;
end;
/
3.fetch ... bulk collect into
fetch ... bulk collect into取数据的速度要远远高于普通游标。
declare
cursor my_cursor is select ename from emp where deptno=10;
type ename_table_type is table of varchar2(10);
ename_table ename_table_type;
begin
open my_cursor;
fetch my_cursor bulk collect into ename_table;
for i in 1..ename_table.count loop
dbms_output.put_line(ename_table(i));
end loop;
close my_cursor;
end;
4.实战案例
-- 建表并插入数据
create table student (xh number, xm varchar2(10));
insert into student values(1,'A');
insert into student values(2,'B');
insert into student values(3,'C');
insert into student values(4,'D');
create table address (xh number, zz varchar2(10));
insert into address values(2,'昆明');
insert into address values(1,'曲靖');
insert into address values(3,'红河');
insert into address values(4,'昭通');
commit;
--需求描述
完成的任务:给表student添加一列zz,是varchar2(10)类型;
再从address中,将zz字段的数值取出来,对应的插入到
student新增的zz列中。
即:得到的结果:student表中,是:
XH XM ZZ
-- ---------- ------
1 A 曲靖
2 B 昆明
3 C 红河
4 D 昭通
-- 实现
alter table student add zz varchar2(10);
declare
xh1 number;
zz1 varchar2(10);
cursor cursor1 is select xh, zz from address;
begin
open cursor1;
fetch cursor1 into xh1, zz1;
while cursor1%found loop
update student set zz = zz1 where xh = xh1;
fetch cursor1 into xh1, zz1;
end loop;
close cursor1;
end;
--- 上述游标功能等同于关联更新SQL
update student a set zz=(select zz from address b where a.xh=b.xh);
5.REF游标(参照游标)
REF 游标和游标变量用于处理运行时动态执行的 SQL 查询
创建游标变量需要两个步骤:
- 声明 REF 游标类型
- 声明 REF 游标类型的变量
用于声明 REF 游标类型的语法为:
TYPE <ref_cursor_name> IS REF CURSOR
[RETURN <return_type>];
打开游标变量的语法如下:
OPEN cursor_name FOR select_statement;
实战演练
-- REF游标
declare
type refcur is ref cursor;
cursor2 refcur;
tab varchar2(50);
tb_name varchar2(50);
id1 t1.id%type;
name1 t1.name%type;
begin
tb_name := '&tab';
if tb_name = 't1' then
open cursor2 for select id, name from t1;
fetch cursor2 into id1,name1;
while cursor2%found
loop
dbms_output.put_line(cursor2%rowcount||'.ID是:'||id1||',姓名是:'||name1);
fetch cursor2 into id1,name1;
end loop;
close cursor2;
else
dbms_output.put_line('输入的表名不正确~!');
end if;
end;
/
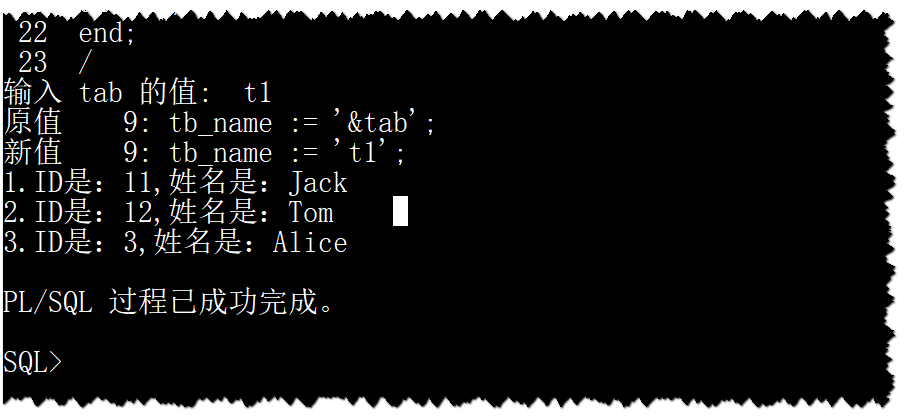
执行结果:

声明:书写博客不易,转载请注明出处,请支持原创,侵权将追究法律责任
个性签名:人的一切的痛苦,本质上都是对自己无能的愤怒
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!
