【BigData】Java基础_反射
1.反射是什么?
比较官方点的解释
- Java反射机制是在运行状态中
- 对于任意一个类,都能知道这个类的所以属性和方法;
- 对于任何一个对象,都能够调用它的任何一个方法和属性;
- 这样动态获取新的以及动态调用对象方法的功能就叫做反射
个人理解:
反射也是自己看了教程以后发现比较有趣的一个东西,此处写的是个人对于反射的理解,个人理解的反射就是:不管你的实现类写好没,我们约定好定义好一个配置文件放在那,我需要调用到你的方法的时候我就从配置文件中动态获取,这样一来,我们之间的开发就不会冲突,并且开发完成后,我的代码也不需要动,只需要修改配置文件即可。
2.案例解释
代码结构图:
(1)TestReflect.java (测试类的main方法)
package cn.test.logan.day10.reflect; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.util.HashMap; /** * 一个典型的面向接口编程的案例 * @author QIN * */ public class TestReflect { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { HashMap<String, String> applicationContext = new HashMap<>(); /** * 解析配置文件,将配置文件中的接口名与其需要调用的实现类名存储到hashmap中 */ BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("d:/mapping.txt"))); String line = ""; while((line = br.readLine())!=null){ String[] arr = line.split(":"); applicationContext.put(arr[0], arr[1]); } /** * 调SayInterface中的实现类的say方法 */ Class<?> forNameSay = Class.forName(applicationContext.get("SayInterface")); SayInterface SayInstance = (SayInterface)forNameSay.newInstance(); SayInstance.say(); /** * 调EatInterface中的实现类的eat方法 */ Class<?> forNameEat = Class.forName(applicationContext.get("EatInterface")); EatInterface EatInstance = (EatInterface)forNameEat.newInstance(); EatInstance.eat(); } }
(2)SayInterface.java(say接口)
package cn.test.logan.day10.reflect; /** * say接口 * @author QIN * */ public interface SayInterface { public void say(); }
say接口的第一个实现方法
package cn.test.logan.day10.reflect; public class SayInterfaceimpl1 implements SayInterface { @Override public void say() { System.out.println("我是SayInterface接口中的第1个实现方法"); } }
say接口的第二个实现方法
package cn.test.logan.day10.reflect; public class SayInterfaceimpl2 implements SayInterface { @Override public void say() { System.out.println("我是SayInterface接口中的第2个实现方法"); } }
(3)EatInterface.java(eat接口)
package cn.test.logan.day10.reflect; /** * eat接口 * @author QIN * */ public interface EatInterface { public void eat(); }
eat接口的第一个实现方法
package cn.test.logan.day10.reflect; public class EatInterfaceimpl1 implements EatInterface { @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("我是EatInterface接口中的第1个实现方法"); } }
eat接口的第二个实现方法
package cn.test.logan.day10.reflect; public class EatInterfaceimpl2 implements EatInterface { @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("我是EatInterface接口中的第2个实现方法"); } }
测试
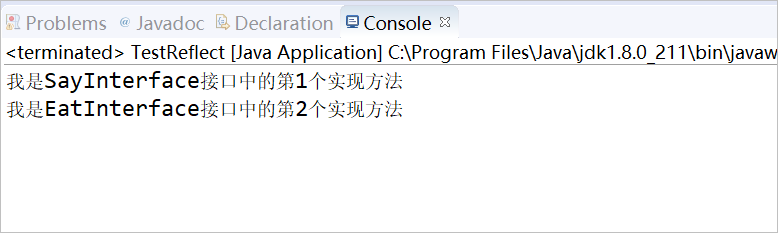
(1)当配置文件mapping.txt内容如下
SayInterface:cn.test.logan.day10.reflect.SayInterfaceimpl1
EatInterface:cn.test.logan.day10.reflect.EatInterfaceimpl2
输出结果:
(2)当配置文件修改后
SayInterface:cn.test.logan.day10.reflect.SayInterfaceimpl2
EatInterface:cn.test.logan.day10.reflect.EatInterfaceimpl1
输出结果:

通过上述实验,我们不难发现,每次需要调用不同实现类的时候,我们只需要修改配置文件即可,不需要修改相应的代码
作者:奔跑的金鱼
声明:书写博客不易,转载请注明出处,请支持原创,侵权将追究法律责任
个性签名:人的一切的痛苦,本质上都是对自己无能的愤怒
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!

