【LeetCode】10.二叉树系列——属性
总目录:
1.判定对称二叉树
1.1.问题描述
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root , 检查它是否轴对称。
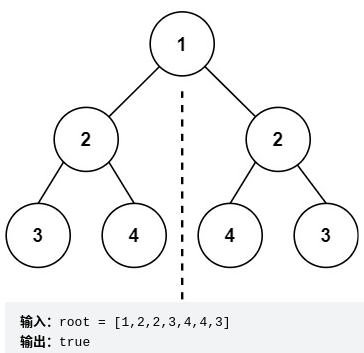
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/symmetric-tree/
1.2.要点
对称与否,一看是否都有/无节点,二看值是否相同
1递归
2迭代,用栈实现、用队列实现
1.3.代码实例
递归

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isMirrored(TreeNode* leftNode,TreeNode* rightNode){ 4 //中止条件 5 if((leftNode==NULL)!=(rightNode==NULL)){ 6 return false; 7 } 8 if(leftNode==NULL){ 9 return true; 10 } 11 if(leftNode->val!=rightNode->val){ 12 return false; 13 } 14 15 //调用递归 16 bool isOk=false; 17 isOk=isMirrored(leftNode->left,rightNode->right); 18 if(!isOk){ 19 return false; 20 } 21 isOk=isMirrored(leftNode->right,rightNode->left); 22 if(!isOk){ 23 return false; 24 } 25 26 //能到这肯定是对称的,包括子树 27 return true; 28 } 29 bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { 30 //中止条件 31 if(root==NULL){ 32 return true; 33 } 34 35 return isMirrored(root->left, root->right); 36 } 37 };
迭代+队列

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { 4 if (root == NULL) return true; 5 queue<TreeNode*> que; 6 que.push(root->left); // 将左子树头结点加入队列 7 que.push(root->right); // 将右子树头结点加入队列 8 9 while (!que.empty()) { // 接下来就要判断这两个树是否相互翻转 10 TreeNode* leftNode = que.front(); que.pop(); 11 TreeNode* rightNode = que.front(); que.pop(); 12 if (!leftNode && !rightNode) { // 左节点为空、右节点为空,此时说明是对称的 13 continue; 14 } 15 16 // 左右一个节点不为空,或者都不为空但数值不相同,返回false 17 if ((!leftNode || !rightNode || (leftNode->val != rightNode->val))) { 18 return false; 19 } 20 que.push(leftNode->left); // 加入左节点左孩子 21 que.push(rightNode->right); // 加入右节点右孩子 22 que.push(leftNode->right); // 加入左节点右孩子 23 que.push(rightNode->left); // 加入右节点左孩子 24 } 25 return true; 26 } 27 };
迭代+栈

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) { 4 if (root == NULL) return true; 5 stack<TreeNode*> st; // 这里改成了栈 6 st.push(root->left); 7 st.push(root->right); 8 while (!st.empty()) { 9 TreeNode* leftNode = st.top(); st.pop(); 10 TreeNode* rightNode = st.top(); st.pop(); 11 if (!leftNode && !rightNode) { 12 continue; 13 } 14 if ((!leftNode || !rightNode || (leftNode->val != rightNode->val))) { 15 return false; 16 } 17 st.push(leftNode->left); 18 st.push(rightNode->right); 19 st.push(leftNode->right); 20 st.push(rightNode->left); 21 } 22 return true; 23 } 24 };
2.完全二叉树的节点个数
2.1.问题描述
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-complete-tree-nodes
2.2.要点
仍属于遍历范畴,方法任选
2.3.代码实例
迭代——层序遍历

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int countNodes(TreeNode* root) { 4 if(root == NULL){ 5 return 0; 6 } 7 8 int nodeCnt=0; 9 int nodeCntInQ=0; 10 queue<TreeNode*> q; 11 q.push(root); 12 13 TreeNode* curNode=NULL; 14 while(!q.empty()){ 15 nodeCntInQ=q.size(); 16 nodeCnt+=nodeCntInQ; 17 18 for(int i=0;i<nodeCntInQ;i++){ 19 curNode=q.front(); 20 q.pop(); 21 22 if(curNode->left) q.push(curNode->left); 23 if(curNode->right) q.push(curNode->right); 24 } 25 } 26 27 return nodeCnt; 28 } 29 };
3.判定平衡二叉树
3.1.问题描述
给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
本题中,一棵高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/balanced-binary-tree
3.2.要点
1递归
深度搜索左右子树的最大深度,然后比较差值。
前、后序遍历都可。
3.3.代码实例
递归

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int getDepth(TreeNode* root){ 4 if(root==NULL){ 5 return 0; 6 } 7 8 int leftDepth=getDepth(root->left); 9 int rightDepth=getDepth(root->right); 10 11 return max(leftDepth,rightDepth)+1; 12 } 13 bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) { 14 if(root==NULL){ 15 return true; 16 } 17 18 int leftDepth=getDepth(root->left); 19 int rightDepth=getDepth(root->right); 20 if(abs(leftDepth-rightDepth)>1){ 21 return false; 22 } 23 24 bool isBalInLeft=isBalanced(root->left); 25 bool isBalInRight=isBalanced(root->right); 26 27 return isBalInLeft&&isBalInRight; 28 } 29 };
4.二叉树的所有路径
4.1.问题描述
给你一个二叉树的根节点 root ,按 任意顺序 ,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-paths/
4.2.要点
路径需要累加,中间需要缓存前序路径,在走完一条路径之后又需要回溯。
注意在递归中回溯算法的技巧。递归中带着回溯
1向下递归
2向上递归
4.3.代码实例
向下递归

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 void recurve(TreeNode* root,string path,vector<string>& ret){ 4 path+=to_string(root->val); 5 //如果是叶子节点 6 if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL){ 7 ret.push_back(path); 8 return; 9 } 10 11 if(root->left){ 12 recurve(root->left,path+"->",ret); 13 } 14 if(root->right){ 15 recurve(root->right,path+"->",ret); 16 } 17 } 18 19 vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) { 20 vector<string> ret; 21 if(root==NULL){ 22 return ret; 23 } 24 25 recurve(root,"",ret); 26 27 return ret; 28 } 29 };
向上递归,盖帽算法

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 vector<string> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode* root) { 4 vector<string> res; 5 if (root == NULL) 6 return res; 7 //到达叶子节点,把路径加入到集合中 8 if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) { 9 res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + ""); 10 return res; 11 } 12 //遍历左子节点的路径 13 for (string path : binaryTreePaths(root->left)) { 14 res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + path); 15 } 16 //遍历右子节点的路径 17 for (string path : binaryTreePaths(root->right)) { 18 res.push_back(to_string(root->val) + "->" + path); 19 } 20 return res; 21 } 22 };
5.左叶子之和
5.1.问题描述
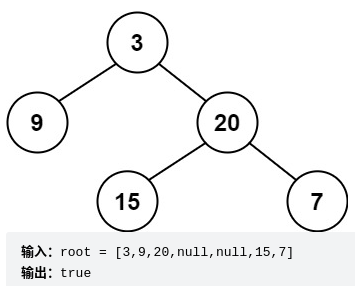
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] ;输出: 24 ;解释: 在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 24
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-left-leaves
5.2.要点
只统计左叶子
5.3.代码实例
递归

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int leftSum=0; 4 int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode* root) { 5 if(root==NULL){ 6 return 0; 7 } 8 9 if(root->left){ 10 if(root->left->left==NULL&&root->left->right==NULL){ 11 leftSum+=root->left->val; 12 } 13 else{ 14 sumOfLeftLeaves(root->left); 15 } 16 } 17 18 if(root->right){ 19 sumOfLeftLeaves(root->right); 20 } 21 22 return leftSum; 23 } 24 };
6.找树左下角的值
6.1.问题描述
给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
输入: root = [2,1,3];输出: 1
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/
6.2.要点
层序遍历时保存当前层的第一个元素
6.3.代码实例
迭代、层序遍历

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) { 4 int ret=0; 5 queue<TreeNode*> que; 6 if (root != NULL) que.push(root); 7 while (!que.empty()) { 8 int size = que.size(); 9 // 这里一定要使用固定大小size,不要使用que.size(),因为que.size是不断变化的 10 for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 11 if(i==0){ 12 ret=que.front()->val; 13 } 14 TreeNode* node = que.front(); 15 que.pop(); 16 17 if (node->left) que.push(node->left); 18 if (node->right) que.push(node->right); 19 } 20 } 21 return ret; 22 } 23 };
7.路径之和是否存在
7.1.问题描述
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。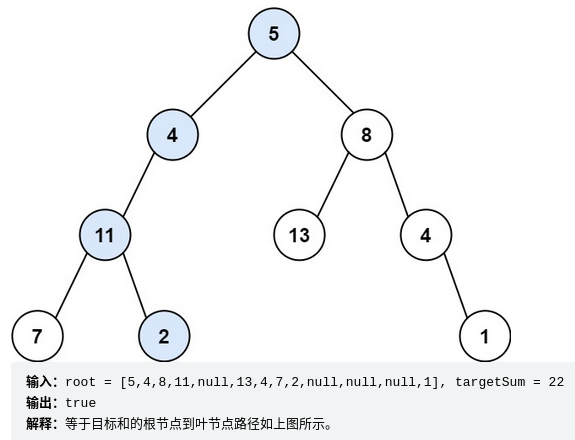
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum
7.2.要点
递归+回溯,找到了匹配路径则立即返回
7.3.代码实例
递归+回溯

1 class Solution { 2 public: 3 bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) { 4 //中止条件 5 if(root==NULL){ 6 return false; 7 } 8 9 //本层逻辑 10 if(root->left==NULL&&root->right==NULL){ 11 return root->val==targetSum; 12 } 13 14 bool isExist=false; 15 isExist=hasPathSum(root->left,targetSum-root->val); 16 if(isExist){ 17 return true; 18 } 19 isExist=hasPathSum(root->right,targetSum-root->val); 20 if(isExist){ 21 return true; 22 } 23 24 return false; 25 } 26 };
8.路径之和是否存在2
8.1.问题描述
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii
8.2.要点
路径搜索很正常,关键是要缓存中间路径以便回溯。
注意解法中使用数组进行回溯的方式。
8.3.代码实例
递归+缓存

1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 private: 14 vector<vector<int>> result; 15 vector<int> path; 16 // 递归函数不需要返回值,因为我们要遍历整个树 17 void traversal(TreeNode* cur, int count) { 18 // 遇到了叶子节点 19 if (cur->left==NULL && cur->right==NULL) { 20 if(count==0){//找到了和为sum的路径 21 result.push_back(path); 22 } 23 return; 24 } 25 26 if (cur->left) { // 左 (空节点不遍历) 27 path.push_back(cur->left->val); 28 count -= cur->left->val; 29 traversal(cur->left, count); // 递归 30 count += cur->left->val; // 回溯 31 path.pop_back(); // 回溯 32 } 33 if (cur->right) { // 右 (空节点不遍历) 34 path.push_back(cur->right->val); 35 count -= cur->right->val; 36 traversal(cur->right, count); // 递归 37 count += cur->right->val; // 回溯 38 path.pop_back(); // 回溯 39 } 40 return ; 41 } 42 43 public: 44 vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { 45 result.clear(); 46 path.clear(); 47 if (root == NULL) return result; 48 path.push_back(root->val); // 把根节点放进路径 49 traversal(root, sum - root->val); 50 return result; 51 } 52 };
9.总结
9.1.要点
二叉树的属性,主要包括:
(1)左右结构;
(2)层次结构;
(3)前、中、后遍历方式与递归、迭代的结合策略;
xxx.问题
xxx.1.问题描述
111
xxx.2.要点
222
xxx.3.代码实例
333




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号