C++编程基础练习
注:本文练习题均出自《Essential C++》第一章
练习1,1 从一个简单程序开始
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string user_name; cout << "Please enter your first name :"; cin >> user_name; cout << '\n' << "Hello," << user_name << "... and goodbye!\n"; return 0; }
1,将string头文件注释掉,重新编译这个程序,会发生什么事?
目前还没有发现会发生什么事。
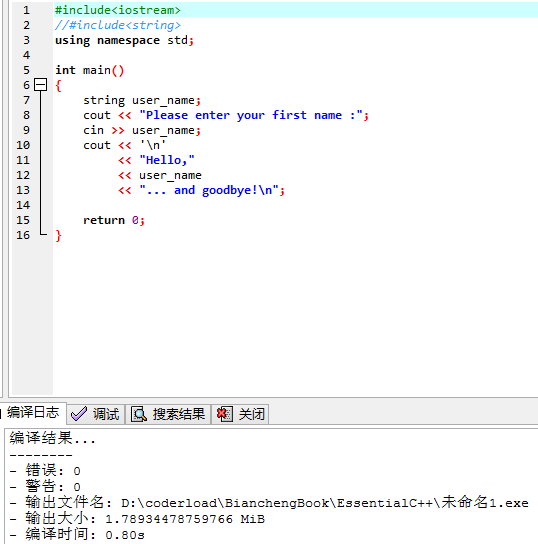
2,将using namespace std注释掉,重新编译,会发生什么事?
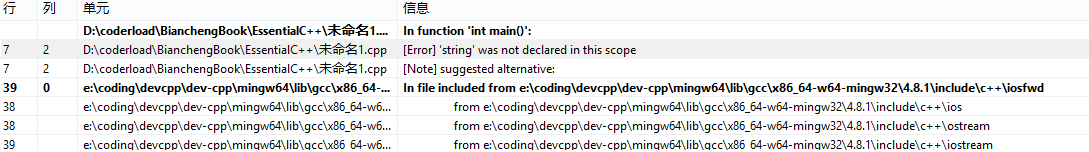
3,将函数名main()改为my_main(),然后重新编译,有什么结果?

练习1.2
将上述程序的内容进行扩充(1)要求用户同时输入名字(first name)和姓氏(last name);(2)修改输出结果,同时打印姓氏和名字。
1,定义两个string对象:string first_name,last_name;
2,定义一个vector,储存两个string对象:vector<string> usr_name(2);
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string first_name,last_name; cout << "Please enter your first name :"; cin >> first_name; cout << "hi, " << first_name << "Please enter your last name: "; cin >> last_name; cout << '\n'; cout << "Hello, " << first_name << ' ' << last_name << "... and goodbye!\n"; return 0; }
练习1.3
编写一个程序,能够询问用户的姓名,并读取用户所输入的内容。请确保用户输入的名称长度大于两个字符。如果用户的确输入了有效名称,就响应一些信息。
请以两种方式实现:第一种使用C-style字符串,第二种使用string对象。
1,C-style字符串
首先,我们必须决定user_name的长度;接下来,利用标准库的strlen()函数获得user_name的长度,cstring头文件中有strlen()的声明。
如果用户输入的字符串长度大于之前已经输入的字符,就没有足够的空间来存放终止字符(null字符)。为了防止这种事情的发生,我以iostream操纵符(manipulator)setw()保证不会读入超过127个字符。由于用到了setw()操纵符,因此必须包含iomanip头文件。
#include<iostream> #include<iomanip> #include<cstring> using namespace std; int main() { const int nm_size = 128; //必须分配一个大小固定的空间 char user_name[nm_size]; cout << "Please enter your name: "; cin >> setw(nm_size) >> user_name; switch(strlen(user_name)) { case 127: cout << "That is a very big name,indeed --" << "we may have needed to shorten it\n" << "In any case,\n"; default: cout << "Hello, " << user_name << " -- happy to make your acquaintance!\n"; break; } return 0; }
2,string对象(推荐)
#include<iostream> #include<string> using namespace std; int main() { string user_name; cout << "Please enter your name: "; cin >> user_name; switch(user_name.size()){ case 0: cout << "Ah,the user with no name. "; break; case 1: cout << "A 1-character name? Hmm,have you read Kafka?: "; break; default: cout << "Hello, " << user_name << "-- happy to make your acquaintance!\n"; break; } return 0; }
练习1.4
编写一个程序,从标准输入设备读取一串整数,并将读入的整数依次放到array及vector,然后遍历这两种容器,求取数值综合。将总和及平均值输出至标准输出设备。
两者之间的区别
- array的大小必须固定,vector可以动态地随着元素的插入而扩展储存空间。
- array并不储存自身大小。
//使用vector #include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { vector<int> ivec; int ival,sum; while(cin >> ival) ivec.push_back(ival); for(int sum = 0,ix = 0;ix < ivec.size();++ix) //遍历vector元素,一一累加 sum += ivec[ix]; int average = sum / ivec.size(); cout << "Sum of " << ivec.size() << " elements: " << sum << ". Average: " << average << endl; }
//使用array #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { const int array_size = 120; int ia[array_size],sum; int ival,icnt = 0; while(cin >> ival && icnt < array_size) ia[icnt++] = ival; for(int sum = 0,ix = 0;ix < icnt;++ix) sum += ia[ix]; int average = sum / icnt; cout << "Sum of " << icnt << " elements: " << sum << ". Average: " << average << endl; }
练习1.5
使用你最称手的编辑工具,输入两行(或更多)文字并存盘。然后编写一个程序,打开该文本文件,将其中每个字都读取到一个vector<string>对象中。遍历该vector,将内容显示到cout。然后利用泛型算法sort(),对所有文字排序:
#include<algorithm>
sort( container.begin(),container.end() );
再将排序后的结果输出到另一个文件。
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<algorithm> #include<string> #include<vector> using namespace std; int main() { string word; ifstream in_file("D:\\Documents\\text.txt"); if(!in_file) { cerr << "oops! unable to open input file\n"; return -1; } ofstream out_file("D:\\Documents\\text.sort"); if(!out_file) { cerr << "oops! unable to open output file\n"; return -2; } string world; vector < string > text; while(in_file >> word) text.push_back(word); int ix; cout << "unsorted text: \n"; for(ix = 0;ix < text.size();++ix) cout << text[ix] << ' '; cout << endl; sort(text.begin(),text.end()); out_file << "sorted text: \n"; for(ix = 0;ix < text.size();++ix) out_file << text[ix] << ' '; out_file << endl; return 0; }





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号