010面向对象编程(上)-3
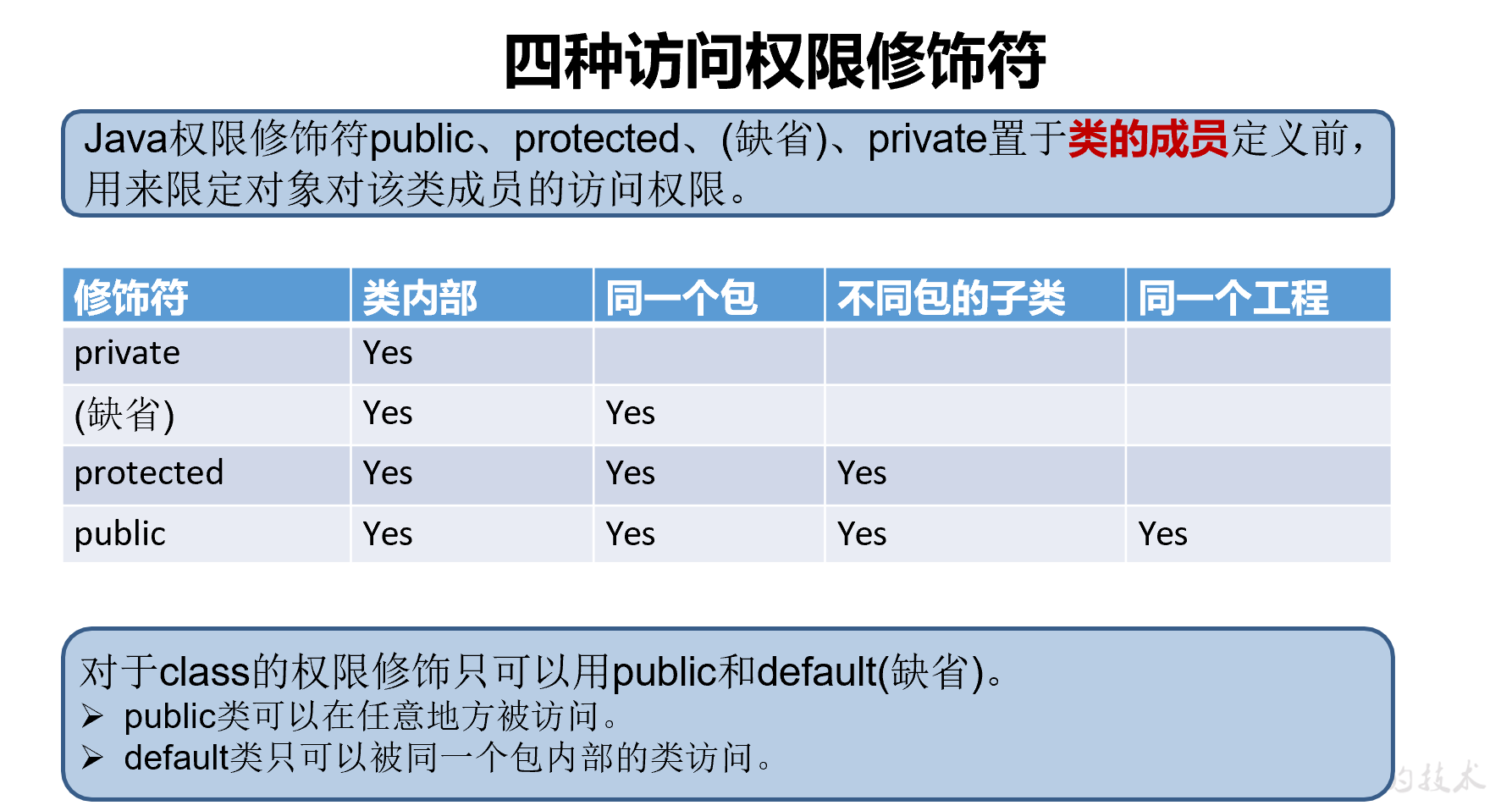
封装和隐藏


测试封装
package com.atguigu.exer;
public class PersonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person test = new Person();
test.setAge(131);
System.out.println(test.getAge());
// test.age = 10; //The field Person.age is not visible
}
}
class Person{
private int age;
public void setAge(int i){
if(i<0 || i>130){
System.out.println("输入违规");
}else{
age = i;
}
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
}
构造器


测试构造器
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* 3.编写两个类,TriAngle和TriAngleTest,其中TriAngle类中声明私有的底 边长base和高height,
* 同时声明公共方法访问私有变量。
* 此外,提供类 必要的构造器。另一个类中使用这些公共方法,计算三角形的面积。
*/
public class TriAngleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TriAngle triangle = new TriAngle();
double base = triangle.getBase();
double height = triangle.getHeight();
double area = triangle.getArea();
System.out.println("长:" + base + ",高:" + height + ",面积:" + area);
triangle.setBase(10);
triangle.setHeight(5);
System.out.println(triangle.getArea());
}
}
class TriAngle{
private double base;
private double height;
TriAngle(){
base = 5;
height = 5;
}
public double getBase(){
return base;
}
public void setBase(double b){
base = b;
}
public double getHeight(){
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double h){
height = h;
}
public double getArea(){
return height * base / 2;
}
}

测试构造器重载
package com.atguigu.exer;
/*
* 定义Student类,有4个属性: String name; int age; String school; String major;
定义Student类的3个构造器:
第一个构造器Student(String n, int a)设置类的name和age属性;
第二个构造器Student(String n, int a, String s)设置类的name, age 和school属性;
第三个构造器Student(String n, int a, String s, String m)
设置类的name, age ,school和major属性;
在main方法中分别调用不同的构造器创建的对象,并输出其属性值。
*/
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
Student student1 = new Student("tom",18);
Student student2 = new Student("tom",18,"霍格沃兹");
Student student3 = new Student("tom",18,"霍格沃兹","麻瓜魔法术");
}
}
class Student{
private String name;
private int age;
private String school;
private String major;
Student(){
}
Student(String n, int a){
name = n;
age = a;
System.out.println(name + "\t" + age);
}
Student(String n, int a, String s){
name = n;
age = a;
school = s;
System.out.println(name + "\t" + age + "\t" + school);
}
Student(String n, int a, String s, String m){
name = n;
age = a;
school = s;
major = m;
System.out.println(name + "\t" + age + "\t" + school + "\t" + major);
}
}


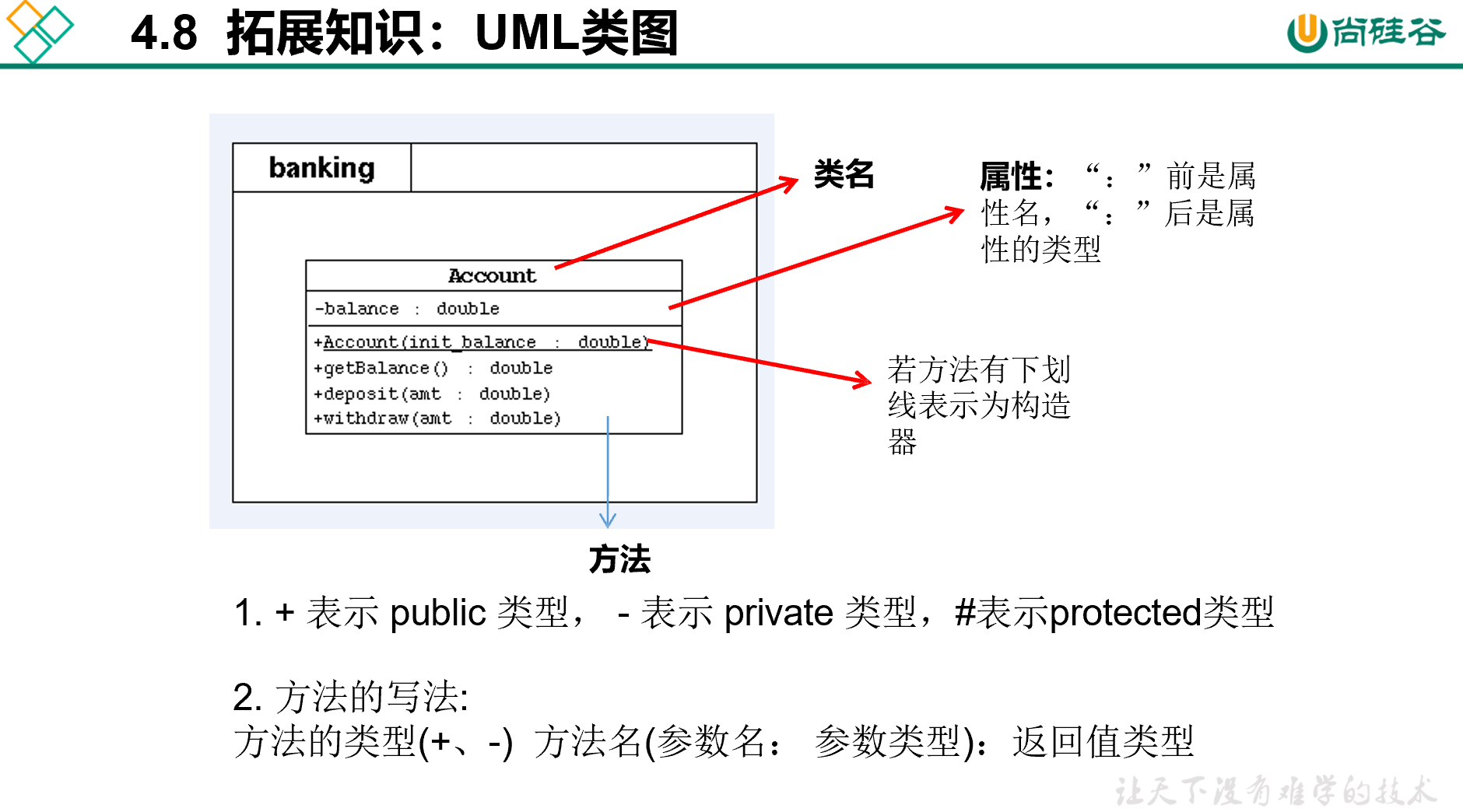
this的使用

使用this访问属性和方法时, 如果在本类中未找到,会从父 类中查找


实验1:Account_Customer
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
* 1、写一个名为 Account 的类模拟账户。该类的属性和方法如下图所示。该类包括的属性:
账号 id,余额 balance,年利率 annualInterestRate;包含的方法:访问器方法(getter 和 setter
方法),取款方法 withdraw(),存款方法 deposit()。
*/
public class Account {
private int id;
private double balance;
private double annualInterestRate;
public Account(){
this.balance = 10000;
}
public Account(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate ){
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return annualInterestRate;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public void withdraw (double amount){ //取钱
if(amount<=this.balance && amount>0){
this.balance -= amount;
System.out.println("成功取出:" + amount);
}else{
System.out.println("余额不足,取款失败");
}
}
public void deposit (double amount){ //存钱
if(amount>0){
this.balance += amount;
System.out.println("成功存入:" + amount);
}else{
System.out.println("请存入有效的数字");
}
}
}
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
* a. 声明三个私有对象属性:firstName、lastName 和 account。
b. 声明一个公有构造器,这个构造器带有两个代表对象属性的参数(f 和 l)
c. 声明两个公有存取器来访问该对象属性,方法 getFirstName 和 getLastName 返回相应的属
性。
d. 声明 setAccount 方法来对 account 属性赋值。
e. 声明 getAccount 方法以获取 account 属性。
*/
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(){
}
public Customer(String f,String l){
this.firstName = f;
this.lastName = l;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account){
this.account = account;
}
}
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
* (1) 创建一个 Customer ,名字叫 Jane Smith, 他有一个账号为 1000,余额为 2000 元,
年利率为 1.23% 的账户。
(2) 对 Jane Smith 操作。
存入 100 元,再取出 960 元。再取出 2000 元。
打印出 Jane Smith 的基本信息
*/
public class TestCustomer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Customer customer = new Customer("Smith","Jane");
Account account = new Account();
customer.setAccount(account);
customer.getAccount().setId(1000);
customer.getAccount().setBalance(2000);
customer.getAccount().setAnnualInterestRate(1.23);
customer.getAccount().deposit(100);
customer.getAccount().withdraw(960);
customer.getAccount().withdraw(2000);
System.out.println("Customer [" + customer.getFirstName() + ", " + customer.getLastName() +
"] has a account: id is " + customer.getAccount().getId() + ", " +
"annualInterestRate is " + customer.getAccount().getAnnualInterestRate() + "%"
+ ", " + "balance is " + customer.getAccount().getBalance());
}
}
实验2:Account_Customer_Bank
package com.atguigu.java2;
import javax.swing.plaf.synth.SynthSeparatorUI;
public class Account {
private double balance;
public Account(){
}
public Account(double init_balance){ //初始化
this.balance = init_balance;
}
public double getBalance(){ //返回余额
return balance;
}
public void deposit(double amt){ //存钱
if(amt > 0){
balance += amt;
System.out.println("成功存款: " + amt);
}else{
System.out.println("存款失败");
}
}
public void withdraw(double amt){ //取款
if(amt > 0 && amt <= balance){
balance -= amt;
System.out.println("成功取款: " + amt);
}else{
System.out.println("取款失败");
}
}
}
package com.atguigu.java2;
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Account account;
public Customer(){
}
public Customer(String f, String l){
firstName = f;
lastName = l;
}
public Account getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(Account account) {
this.account = account;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
}
package com.atguigu.java2;
public class Bank {
private Customer[] customers;
private int numberOfCustomer;
public Bank(){
customers = new Customer[10];
}
public void addCustomer(String f, String l){
Customer cust = new Customer(f, l);
customers[numberOfCustomer++] = cust;
}
public int getNumberOfCustomer(){
return numberOfCustomer;
}
public Customer getCustomer(int index){
return customers[index];
}
}
package com.atguigu.java2;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BankTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
Bank bank = new Bank();
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
System.out.print("请输入名字:" + "\n");
String firstName = scanner.next();
System.out.print("请输入姓氏:" + "\n");
String lastName = scanner.next();
bank.addCustomer(firstName, lastName);
bank.getCustomer(i).setAccount(new Account(2000));
bank.getCustomer(i).getAccount().deposit(200);
bank.getCustomer(i).getAccount().withdraw(1000);
System.out.println("当前客户为: [" + bank.getCustomer(i).getFirstName() + ", " + bank.getCustomer(i).getLastName() + "], 余额为: " + bank.getCustomer(i).getAccount().getBalance());
System.out.println("当前客户数量: " + (i + 1));
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("****************************");
System.out.println("当前客户数量为: " + bank.getNumberOfCustomer());
}
}
package和import的使用





练习1:内存调用
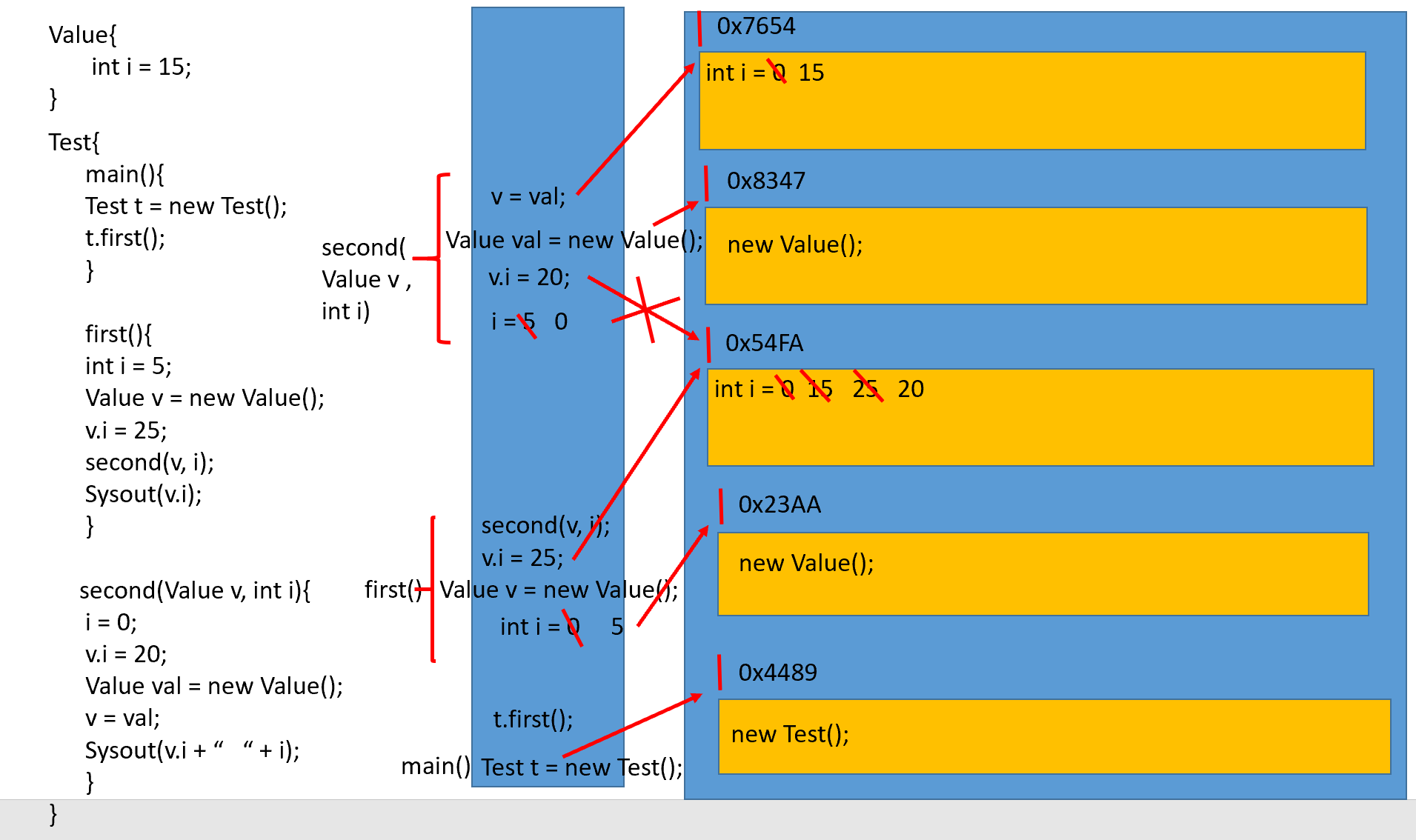
package com.atguigu.exer1;
class Value{
int i = 15;
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String argv[]) {
Test t = new Test();
t.first();
}
public void first() {
int i = 5;
Value v = new Value();
v.i = 25;
second(v, i);
System.out.println(v.i);
}
public void second(Value v, int i) {
i = 0;
v.i = 20;
Value val = new Value();
v = val;
System.out.print(v.i + " " + i);
}
}
练习2:运行结果
package com.atguigu.exer1;
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
change(i);
i = i++;
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
public static void change(int i){
i++;
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer1;
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("world");
char[] ch = new char[]{'h','e','l','l','o'};
change(str,ch);
System.out.println(str);
System.out.println(String.valueOf(ch));
}
public static void change(String str, char[] arr){
str = "change";
arr[0] = 'a';
arr[1] = 'b';
arr[2] = 'c';
arr[3] = 'd';
arr[4] = 'e';
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer1;
class Circle {
private double radius;
public Circle(double r) {
radius = r;
}
public Circle compare(Circle cir) {
return (this.radius>cir.radius)?this: cir;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Circle cir1 = new Circle(1.0);
Circle cir2 = new Circle(2.0);
Circle cir;
cir = cir1.compare(cir2);
if (cir1 == cir)
System.out.println("圆1的半径比较大");
else
System.out.println("圆2的半径比较大");
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号