C# 多线程 Parallel.ForEach 和 ForEach 效率问题研究及理解
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/li315171406/article/details/78450534
最近要做一个大数据dataTable循环操作,开始发现 运用foreach,进行大数据循环,并做了一些逻辑处理。在循环中耗费的时间过长。后来换成使用Parallel.ForEach来进行循环。 一开始认为, 数据比较大时,Parallel.ForEach肯定比 ForEach效率高,后来发现,其实并不是这样。
我用了1000万次循环测试:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Stopwatch Watch1 = new Stopwatch(); Watch1.Start(); List<entityA> source = new List<entityA>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++) { source.Add(new entityA { name = "悟空" + i, sex = i % 2 == 0 ? "男" : "女", age = i }); } Watch1.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("list循环插入耗时:" + Watch1.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch2 = new Stopwatch(); Watch2.Start(); loop1(source); Watch2.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("一般for循环耗时:" + Watch2.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch3 = new Stopwatch(); Watch3.Start(); loop2(source); Watch3.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("一般foreach循环耗时:" + Watch3.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch4 = new Stopwatch(); Watch4.Start(); loop3(source); Watch4.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("并行for循环耗时:" + Watch4.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch5 = new Stopwatch(); Watch5.Start(); loop4(source); Watch5.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("并行foreach循环耗时:" + Watch5.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } //普通的for循环 static void loop1(List<entityA> source) { int count = source.Count(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { source[0].age= + 10; //System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); } } //普通的foreach循环 static void loop2(List<entityA> source) { foreach (entityA item in source) { item.age =+ 10; //System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); } } //并行的for循环 static void loop3(List<entityA> source) { int count = source.Count(); Parallel.For(0, count, item => { //source[count].age= source[count].age + 10; //System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); }); } //并行的foreach循环 static void loop4(List<entityA> source) { Parallel.ForEach(source, item => { item.age = item.age + 10; //System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); }); } } //简单的实体 class entityA { public string name { set; get; } public string sex { set; get; } public int age { set; get; } } }
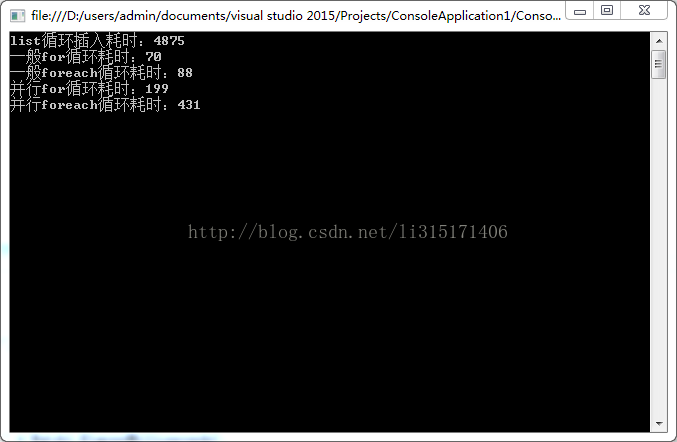
运行结果:
结果居然是并行比一般的循环还耗时,但这是为什么呢?
这是因为循环体内执行的任务开销太小,仅仅是age+10 而已。微软的文章已经指出任务的开销大小对并行任务的影响。如果任务很小,那么由于并行管理的附加开销(任务分配,调度,同步等成本),可能并行执行并不是优化方案。这也是上述程序Foreach与For效率高出的原因。
基于这一点,我们对程序进行调整,循环1000次,每次里面线程sleep(10),这样我们试试。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Stopwatch Watch1 = new Stopwatch(); Watch1.Start(); List<entityA> source = new List<entityA>(); for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { source.Add(new entityA { name = "悟空" + i, sex = i % 2 == 0 ? "男" : "女", age = i }); } Watch1.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("list循环插入耗时:" + Watch1.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch2 = new Stopwatch(); Watch2.Start(); loop1(source); Watch2.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("一般for循环耗时:" + Watch2.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch3 = new Stopwatch(); Watch3.Start(); loop2(source); Watch3.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("一般foreach循环耗时:" + Watch3.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch4 = new Stopwatch(); Watch4.Start(); loop3(source); Watch4.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("并行for循环耗时:" + Watch4.ElapsedMilliseconds); Stopwatch Watch5 = new Stopwatch(); Watch5.Start(); loop4(source); Watch5.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("并行foreach循环耗时:" + Watch5.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } //普通的for循环 static void loop1(List<entityA> source) { int count = source.Count(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { source[0].age= + 10; System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); } } //普通的foreach循环 static void loop2(List<entityA> source) { foreach (entityA item in source) { item.age =+ 10; System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); } } //并行的for循环 static void loop3(List<entityA> source) { int count = source.Count(); Parallel.For(0, count, item => { //source[count].age= source[count].age + 10; System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); }); } //并行的foreach循环 static void loop4(List<entityA> source) { Parallel.ForEach(source, item => { item.age = item.age + 10; System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(10); }); } } //简单的实体 class entityA { public string name { set; get; } public string sex { set; get; } public int age { set; get; } } }
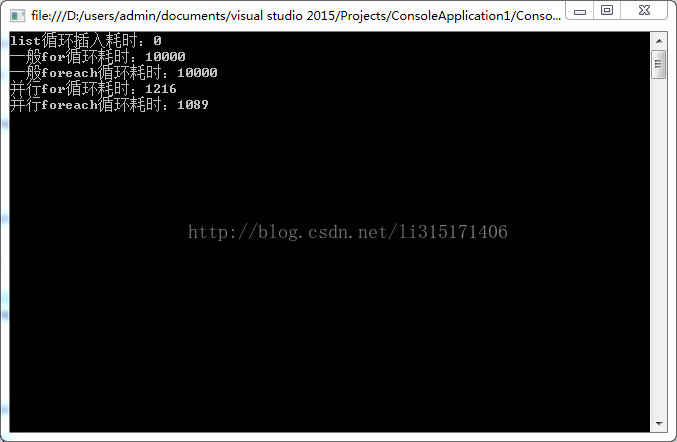
执行结果:
效率一目了然。
这样的结果认证了我们上面的结论。当我们在循环中执行时间过长时,我们需要采用并行循环,效率较高。当时间过短,我们需要用foreach和for.

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号