[Java]-集合框架
Java集合框架是非常普遍使用,也是非常重要的部分,同时也是很基础的部分,熟练掌握很重要,它对于数据的操作提供了良好的接口,下面将从整个集合框架的体系介绍重要的集合框架类,使用方法,以及内部原理。
一、简介:
1、集合框架分两大类(接口):
- Collection:存储单个数据或者对象。
- |-List:列表:
- |-LinkedList :基于链表的List
- |-ArrayList :基于数组的List
- |-SubList:一个List的视图
- |-Vector:一个线程安全的List
-
-
- |-Stack:
-
- |-Queue:队列 ,通常作为数据存储结构,不作为操作容器。集合框架中应用比较少,主要在在并发包(java.util.concurrent)中实现的阻塞队列(消息队列)。
-
- |-ArrayDeque:基于数组实现的尾插队列(包含head,tail头尾指针).
- |-PriorityQueue:基于数组的自排序优先级队列(基于数组实现存储的二叉树堆排)。
-
- |-Set:一个不允许重复数据的集合
- |-HashSet:基于Hash+数组+链表实现的Set。
- |-LinkedHashSet:一个基于LinkedHashMap实现的Set。
- |-TreeSet:一个基于TreeMap实现的Set。
- |-EnumSet:
- |-JumboEnumSet
- |-RegularEnumSet
- |-HashSet:基于Hash+数组+链表实现的Set。
- |-List:列表:
- Map:存储一组K-V键值对。
- |-HashMap:基于Hash+数组+链表实现的Map。
- |-LinkedHashMap:基于HashMap实现的双向链表。
- |-HashTable:基于Hash+数组+链表实现的线程安全(sync)Map。
- |-TreeMap:基于红黑树实现的有序Map。
- |-WeakHashMap:K为弱引用的HashMap,使用中,若k没有被引用则会自动回收掉。
- |-HashMap:基于Hash+数组+链表实现的Map。
2、集合操作类:Conllections
- 提供了一系列的Collection接口实现类的静态操作方法。
- 比如:集合排序,二分查找,列表反转

- 比如:list初始化填充fill,复制,求最大最小值。。
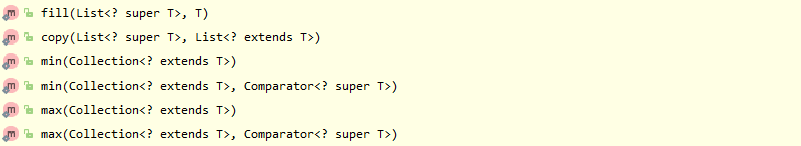
- 比如:如何获取一个线程安全的Map,List,Set:
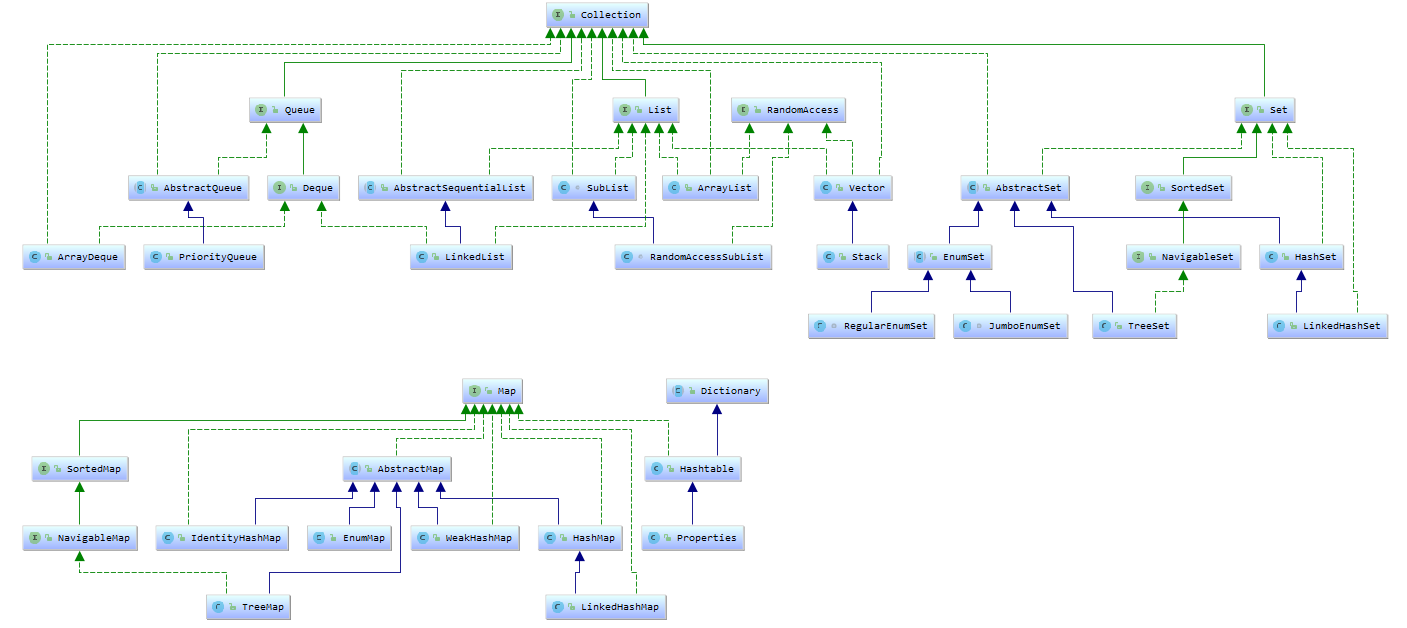
二、整体结构类图:点击图片看原图。
三、接口实现类:
List接口实现类: |
Map接口实现类 |
Set接口实现类 | Queue接口实现 |
| ArrayList |
HashMap |
HashSet | ArrayDeque |
|
LinkedList |
Hashtable | PriorityQueue | |
|
Vector |
TreeMap | TreeSet | |
|
Stack |
LinkedHashMap |
LinkedHashSet |
1、集合框架中的数据结构:
- 哈希算法:
-
*哈希算法: * 0、哈希算法即散列函数,又称哈希函数。它是一种单向密码体制,即它是一个从明文到密文的不可逆的映射,只有加密过程,没有解密过程。同时,哈希函数 * 可以将任意长度的输入经过变化以后得到固定长度的输出。哈希函数的这种单向特征和输出数据长度固定的特征使得它可以生成消息或者数据 * 1、哈希算法将任意长度的二进制值映射为较短的固定长度的二进制值,这个小的二进制值称为哈希值。哈希值是一段数据唯一且极其紧凑的 * 数值表示形式。因此java中每一个对象都有一个hashcode值,用于表明对象的唯一性,可用于比较对象是否相同。 * 2、“===”和equals * 在对象比较的时候我们很容易就纠结用equals方法,还是“==”号,equals用于比较对象的内容或者值,而“==”不仅要比较值还要比较hashcode. * * 3、哈希算法的不可逆和无冲突<hash值,>的特性,让它产生巨大的作用: * 3.1、不同的数据产生的hash值不同: * 用于校验数据的完整性<我们经常下载官网的一些软件时都会又有一个MD5校验码,它是用于校验软件是否被恶意更改>,当然 * 也可以做加密,信息摘要。 * 3.2、哈希表+哈希函数+碰撞冲突处理: * 用于数据的存储和快速查找,<我们只需要一个输入就可以找到数据存储的位置,相比于遍历速度几何倍数提升> * 3.3、常见的hash表的方法 * 4、典型的Hash算法: * MD2、MD4、MD5 和 SHA-1 * 5、得到一个好的hash算法分为两步: * 5.1 构造hash函数:计算值->散列得到坐标/位置<散列法> * 好的hash函数表现是数据冲突尽量少,hash表长度合理。不同的函数产生的表长度是不一样的,hash函数的构造方法也很多,也可 * 以多方法组合使用,最常用的hash函数:http://blog.csdn.net/mycomputerxiaomei/article/details/7641221 * ------- * 除法散列法:ndex = value % 16 * 平方散列法:index = (value * value) >> 28 (右移,除以2^28。记法:左移变大,是乘。右移变小,是除。) * 斐波那契(Fibonacci)散列法 * 5.2 解决碰撞冲突: * 5.2.1开放定址法: * 线性探测再散列: * 二次探测在散列: * 为随机探测再散列: * 5.2.2再哈希法: * 5.2.3链地址法: * 5.2.4建立公共溢出区
- 红黑树:http://www.cnblogs.com/yangecnu/p/Introduce-Red-Black-Tree.html
- 链表,数组:
2、集合框架中唯一的两个线程安全集合:
- Vector(Stack是Vector的子类也是安全的)
- Hashtable
3、为什么线程安全的集合框架(Vector,Hashtable)现在越来越少用??

-
Vector实现了RandomAccess和List接口,可以随机读取,底层是数组实现,拥有和ArrayList性能,但是它实现了线程同步,使用同步锁:sychonrized,在非同步情况下,完全没必要使用,比ArrayList要慢很多。而hashTable也是采用的sychonrized对方法枷锁,且锁定的是整个哈希表,高并发情况下很容易出现瓶颈。相比于单线程使用Vector,hashtable无非是吃力不讨好。而在于并发情况下,已经有更好的线程安全的Map,List,Set,在性能上远超Vector和hashtable。
4、ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector和synchronizedList(List)异同点:
- List是数组的封装接口,所有实现类都可与数组转换,且进行index(索引下标)获取,对于ArrayList和LinkedList只不过是不同的实现方式,自然性能也是不同的。ArrayList是对数组的封装,使得对数组的操作更加方便,LinkedList是链表的实现。两种结构的优缺点无非就是数组和链表的优缺点即在查找和删除的性能差异。
- Arraylist:实现了RandomAccess,可随机读取。可指定初始空间大小,默认为10,超过此空间,数组空间增加以前的一半。
-
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; /** * 默认初始空间10 */ private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; /** * 数组的最大容量 */ private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** *用于存储数据的数组 */ transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
- 数组扩容:变为以前的1.5倍。
-
private void grow(int minCapacity) { // overflow-conscious code int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //新的容量=old容量+old/2 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); // minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win: elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); }
- LinkedList:通过实现AbstractSequentialList来实现随机的索引读取。每个节点是Node,存有两个指针Next,Prev,是个双向链表。初始size=0,动态增加,不需预先分配空间,且实现了queue接口,,可以查看首(first)尾(last)元素.
-
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { transient int size = 0; /** * Pointer to first node.指向头节点 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (first.prev == null && first.item != null) */ transient Node<E> first; /** * Pointer to last node.指向尾节点 * Invariant: (first == null && last == null) || * (last.next == null && last.item != null) */ transient Node<E> last;
-
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next;//指向下一个元素 Node<E> prev;//指向前一个元素 Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }

- 获取一个线程安全的List:通过集合的操作类Collections的synchronizedList方法将一个普通List变成一个线程安全的List。
-
/** * 获取一个线程安全的LinkedList */ List synLinkedList = Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList()); /** * 获取一个线程安全的ArrayList */ List synArrayList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList());
5、HashMap,HashSet,HashTable中的关联和差异。
HashMap:
-
K,V都可为null,存在get返回null的方法并不能确定当前k是否存在(返回null一种代表V==null,一种代表未查询到K,需用containskey)迭代器:Iterator。支持fail-fast
- HashMap:集合框架中尤为重要,高效的存储和查询能力使得他被广泛的运用和考察,这得益于hash算法的高效,通过一次计算就可得到存储的位置,非常方便。理想状态的hash算法是哈希表中的元素都是正常分布(不存在冲突)的,get,put操作时间复杂度都是O(1).迭代一个哈希表所需要的时间与哈希表的容量成正比,因此如果迭代性能不是很重要,不要将初始容量设置太高(或负载因子太低).
- HashMap采用数组链表的结构<拉链法>来处理冲突,将散列到同一位置的数据头插法插入一个链表。在java8中对处理冲突的方式进行了优化,当链表的长度大于8的时候将这个链表重构成红黑树。
- 初始容量initial capacity:16和负载因子local Factor:0.75:两个影响性能的重要因素。
-
/** * The default initial capacity - MUST be a power of two. * 默认初始容量16,指的是桶的数量(数组的长度),必须是2的N次幂 */ static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // 16 /** * The maximum capacity, used if a higher value is implicitly specified * by either of the constructors with arguments. * MUST be a power of two <= 1<<30. * 最大的容量,可以在构造的时候传入参数,但是必需是小于2的30次幂=1073741824 */ static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; /** * The load factor used when none specified in constructor. * 默认的负载因子0.75,即使用容量超过初始容量*0.75必须扩容 */ static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; /** * 链表转红黑树的阈值,大于这个值转换 */ static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8; /** * 红黑树转链表的阈值,小于这个值转换 */ static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
负载因子的默认值是0.75, 它平衡了时间和空间复杂度。 负载因子越大会降低空间使用率,但提高了查询性能(表现在哈希表的大多数操作是读取和查询)
- hashMap的结构:一个Node<K,V>类型的数组
-
/** * 哈希表,每个节点是Node<K,V>结构,容量总是保持2的N次幂。 */ transient Node<K,V>[] table;
数组的每个节点Node又是一个链表存储下一个节点的位置Next,这个Next仍然是个Node:这种结构决定了头插法来链接链表的节点。同时也解决了我们的一个困惑,以往在get的时候以为节点只存储了Value,Node说明了它连K,V一起存储的,碰撞的时候hash值相同,我们也可以比较K的值来确定要返回的Value
-
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Node<K,V> next; }
- 获取数据的在哈希表的位置:散列过程
-
static final int hash(Object key) { int h; return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16); }
- 哈希表扩容:容量翻倍,threshold表示当HashMap的size(Node<K,V>的数量)大于threshold时会执行resize操作。 threshold=capacity*loadFactor
-
final Node<K,V>[] resize() { Node<K,V>[] oldTab = table; int oldCap = (oldTab == null) ? 0 : oldTab.length;//旧表容量 int oldThr = threshold; int newCap, newThr = 0; if (oldCap > 0) { if (oldCap >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) {//容量达到最大值 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;//把扩展阈值修改为最大,这样以后就不能扩容了 return oldTab; } else if ((newCap = oldCap << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && oldCap >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) newThr = oldThr << 1; // double threshold 阈值翻倍 } else if (oldThr > 0) // initial capacity was placed in threshold newCap = oldThr; else { // zero initial threshold signifies using defaults newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY); } if (newThr == 0) { float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor; newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ? (int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE); } threshold = newThr; @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"}) Node<K,V>[] newTab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[newCap]; table = newTab; if (oldTab != null) { for (int j = 0; j < oldCap; ++j) { Node<K,V> e; if ((e = oldTab[j]) != null) { oldTab[j] = null; if (e.next == null) newTab[e.hash & (newCap - 1)] = e; else if (e instanceof TreeNode) ((TreeNode<K,V>)e).split(this, newTab, j, oldCap); else { // preserve order Node<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; Node<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; Node<K,V> next; do { next = e.next; if ((e.hash & oldCap) == 0) { if (loTail == null) loHead = e; else loTail.next = e; loTail = e; } else { if (hiTail == null) hiHead = e; else hiTail.next = e; hiTail = e; } } while ((e = next) != null); if (loTail != null) { loTail.next = null; newTab[j] = loHead; } if (hiTail != null) { hiTail.next = null; newTab[j + oldCap] = hiHead; } } } } } return newTab; }
- get的实现:
-
/** * Implements Map.get and related methods * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @return the node, or null if none */ final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k; if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node ((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return first; if ((e = first.next) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode)//如果是树形Node,则调用TreeNode的get方法 return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); do {//否则直接查询Next比较Key值。 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) return e; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } return null;//查询不到返回null }+
- Put的实现:
-
/** * Implements Map.put and related methods * * @param hash hash for key * @param key the key * @param value the value to put * @param onlyIfAbsent if true, don't change existing value * @param evict if false, the table is in creation mode. * @return previous value, or null if none */ final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) { Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i; if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null); else { Node<K,V> e; K k; if (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))//hash,k都相同,节点覆盖掉 e = p; else if (p instanceof TreeNode)//如果是树形Node调用putTreeNode方法 e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else {//否则链表Node链接 for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) { if ((e = p.next) == null) { p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st,当节点容量bincount>=转化因子的时候转化成红黑树结构 treeifyBin(tab, hash); break; } if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) break; p = e; } } if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key V oldValue = e.value; if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) e.value = value; afterNodeAccess(e); return oldValue; } } ++modCount; if (++size > threshold) resize(); afterNodeInsertion(evict); return null; }
HashTable:
- 线程安全,K,V都不能为null,继承Dictionry,拥有不同的迭代器:Enumeration(枚举类)
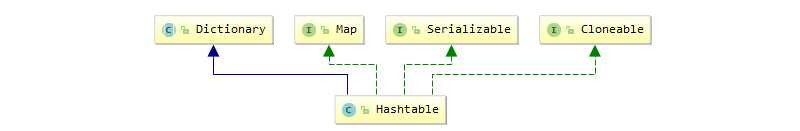
- 同样采用hash表存储:
-
public class Hashtable<K,V> extends Dictionary<K,V> implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { /** * The hash table data. */ private transient Entry<?,?>[] table; }
-
/** * Hashtable bucket collision list entry */ private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final int hash; final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; protected Entry(int hash, K key, V value, Entry<K,V> next) { this.hash = hash; this.key = key; this.value = value; this.next = next; }
- 初始容量:11,负载因子:0.75f
-
/** * Constructs a new, empty hashtable with a default initial capacity (11) * and load factor (0.75). */ public Hashtable() { this(11, 0.75f); }
- get方法:实现要比hashMap简单的多但是效率问题并不知道,但是可以看到它是线程安全的。
-
public synchronized V get(Object key) { Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;//索引位置计算 for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) { if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) { return (V)e.value; } } return null; }
HashSet:hashSet放在这里是因为HashSet完全就是HashMap的包装版本,内部直接是用了HashMap.

-
public HashSet() {//无参构造直接构造一个hashmap map = new HashMap<>(); } public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {//传入集合直接调用hashmap的默认参数构造map map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16)); addAll(c); } public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor); } HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {//使用LinkedHashmap构造 map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor); }
- add方法:将传入的值作为K,一个静态的final对象PRESENT作为Value存入map,那么他的特点是不能存重复数据,因为map中会K相同会散列到同一位置覆盖掉。跟Hashmap中不能存储K相同的元素是一样的。
-
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
public boolean add(E e) { return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; }
- 获取安全的Map和Set:
-
Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Object, Object>()); Collections.synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap<Object, Object>()); Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<Object>()); Collections.synchronizedSet(new TreeSet<Object>());
HashMap与HashTable最大的区别在于hashtable是线程安全的,HashMap数据结构也经过不断地优化,就链表结构转红黑树的在极端情况带来的性能提升就是很大的进步。所以在线程安全的情况下首选hashMap存储K-V键值对,存储单值选hashSet(前提是数据不重复,否则就会丢失数据)查找速度理想是O(1)。hashMap K-V都可为null,hashTable K-V都不能够为null.
6、Iterator和Enumeration的区别:
Enumeration 是JDK 1.0添加的接口。使用到它的函数包括Vector、Hashtable等类,这些类都是JDK 1.0中加入的,Enumeration存在的目的就是为它们提供遍历接口。Enumeration本身并没有支持同步,而在Vector、Hashtable实现Enumeration时,添加了同步。
Iterator 是JDK 1.2才添加的接口,它也是为了HashMap、ArrayList等集合提供遍历接口。Iterator是支持fail-fast机制的:当多个线程对同一个集合的内容进行操作时,就可能会产生fail-fast事件。
7、TreeMap和TreeSet:
TreeMap:
- 类图:
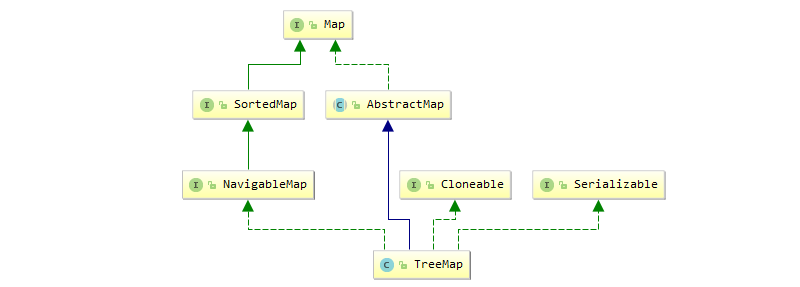
- 基于红黑树实现的有序Map。默认是K的字典比较排序,可传入比较器。
-
/** * The comparator used to maintain order in this tree map, or * null if it uses the natural ordering of its keys. * * @serial */ private final Comparator<? super K> comparator; /** * 构造一个带比较器的Treemap */ public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) { this.comparator = comparator; }
- get操作:
-
final Entry<K,V> getEntry(Object key) { // Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance if (comparator != null) return getEntryUsingComparator(key); if (key == null) throw new NullPointerException(); @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; Entry<K,V> p = root; while (p != null) { int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key); if (cmp < 0) p = p.left; else if (cmp > 0) p = p.right; else return p; } return null; }
完全是基于一个树的查找。put操作也一样是基于树的插入操作。。
TreeSet
- 类图:
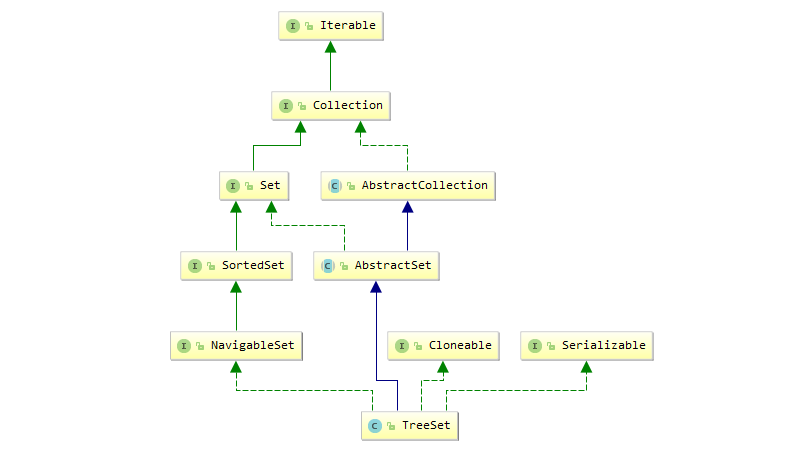
- 基于TreeMap构造的Set,基本操作都是TreeMap的操作
-
public TreeSet() { this(new TreeMap<E,Object>()); }
四、线程安全并不安全:
1、为什么并不安全:
- Collections类可以创建线程安全的集合类,当然他的每一个方法都是枷锁的,可以保证每一步的操作是安全的,但是对于一个类似事务来说(包含多种操作)不能保证原子性。所以Collections创建的线程安全类,又叫做有条件的线程安全。如下:
-
Map synmap = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<Object, Object>()); if(synmap.containsKey(K)){//synmap.containsKey(K)安全的操作 ....... //这是个不安全的位置,因为这个空挡期间,可能有多个线程进入到了这里,其中一个执行remove之后,其他线程就会报错 synmap .remove(K);//安全的操作: }
所以要保证上面操作的安全性必须给整个操作枷锁。等等一些和删除,修改相关的操作都可能会出现类似的问题。
2、Collections类的线程安全集合相比于Vector,hashtable性能有多大的优势?
- 优势一个在于原本数据结构的优势,在安全方面,collections采用的是Object 对象锁,对代码块枷锁,而Vector,hashtable是方法锁,加在实例对象上。至于两种方式有没有性能差异,暂时没有测试。
3、终极大杀招:java.util.concurrent并发包中的ConcurrentHashMap...从代码上重构hashmap,实现并发安全。
❤如果这篇文章对你有一点点的帮助请给一份推荐! 谢谢!你们的鼓励是我继续前进的动力。更多内容欢迎访问我的个人博客
❤本博客只适用于研究学习为目的,大多为学习笔记,如有错误欢迎指正,如有误导概不负责(本人尽力保证90%的验证和10%的猜想)。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号