Spring原理系列一:Spring Bean的生命周期
一.前言
在日常开发中,spring极大地简化了我们日常的开发工作。spring为我们管理好bean, 我们拿来就用。但是我们不应该只停留在使用层面,深究spring内部的原理,才能在使用时融汇贯通。
这是spring原理系列的第一篇,本篇主要讲解spring容器中bean的生命周期。这是基础,先从全貌上了解spring bean的生命周期,有利于我们更好地深入理解bean的生命周期各阶段发生了什么。
二. spring bean生命周期
spring bean从出生到死亡经历如下历程:
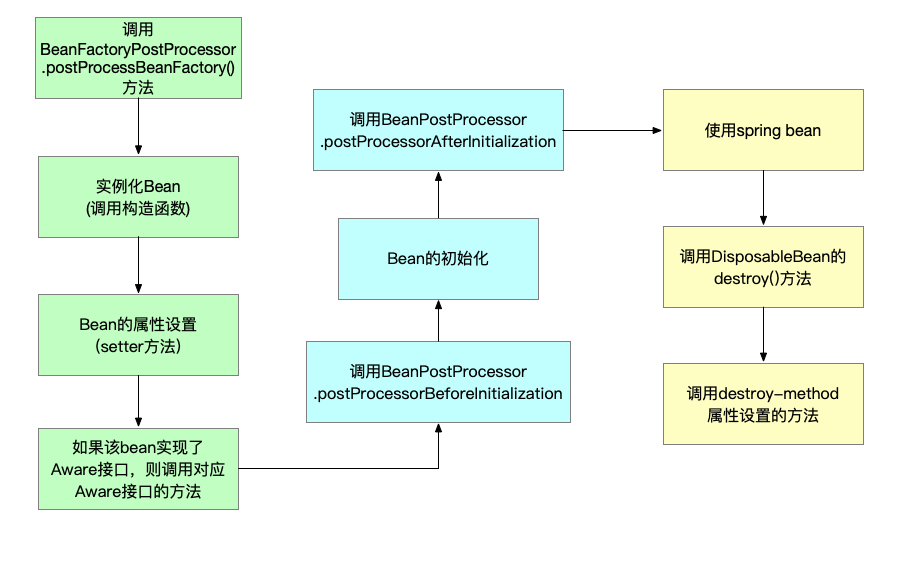
(1)调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory()方法
(2)实例化Bean
(3)Bean的属性设置
(4)调用Aware接口的方法
(5)调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessorBeforeInitialization()方法
(6)Bean的初始化
(7) 调用BeanPostProcessor的postProcessorAfterInitialization()方法
(8)Bean的销毁
上面的方法分为两类:
(1)容器级别的方法
例如BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor
注意: BeanFactoryPostProcessor只会在容器启动时调用一次postProcessBeanFactory()方法,而BeanPostProcessor在每个bean初始化前后都会调用对应的方法。
(2)bean级别的方法
例如各种Aware接口的方法(常见的ApplicationContextAware), 初始化方法, bean销毁时的方法。
在AbstractApplicatonContext的refresh()方法中,可以清楚地看到spring容器刷新时的整个步骤,源代码如下:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } ....
后面的系列篇其实都是来解读上面这段代码的。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号