/error处理
1 BasicErrorController
1.1 简述
SpringMVC框架在出现错误时有一个默认的错误请求 /error;出现异常之后执行/error请求之前框架会判断出现异常的请求类型,然后根据请求类型判断是返回一个HTML页面还是JSON格式的错误信息
1.2 源码分析
BasicErrorController主要处理 /error 请求,该类中有两个处理 /error 请求的方法,分别是 errorHtml 和 error,前者返回的是HTML页面后者返回的是JSON格式的数据
技巧01:如果是浏览器发出的请求出现异常后跳转到 /error 就会执行 errorHtml,然后返回一个HTML页面
技巧02:如果是其他客户端发出请求出现异常后跳转到 /error 就会执行 error ,然后返回一个JSON格式数据

// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorProperties; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorProperties.IncludeStacktrace; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorAttributes; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.util.Assert; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; @Controller @RequestMapping({"${server.error.path:${error.path:/error}}"}) public class BasicErrorController extends AbstractErrorController { private final ErrorProperties errorProperties; public BasicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties) { this(errorAttributes, errorProperties, Collections.emptyList()); } public BasicErrorController(ErrorAttributes errorAttributes, ErrorProperties errorProperties, List<ErrorViewResolver> errorViewResolvers) { super(errorAttributes, errorViewResolvers); Assert.notNull(errorProperties, "ErrorProperties must not be null"); this.errorProperties = errorProperties; } public String getErrorPath() { return this.errorProperties.getPath(); } @RequestMapping( produces = {"text/html"} ) public ModelAndView errorHtml(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) { HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request); Map<String, Object> model = Collections.unmodifiableMap(this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.TEXT_HTML))); response.setStatus(status.value()); ModelAndView modelAndView = this.resolveErrorView(request, response, status, model); return modelAndView != null ? modelAndView : new ModelAndView("error", model); } @RequestMapping @ResponseBody public ResponseEntity<Map<String, Object>> error(HttpServletRequest request) { Map<String, Object> body = this.getErrorAttributes(request, this.isIncludeStackTrace(request, MediaType.ALL)); HttpStatus status = this.getStatus(request); return new ResponseEntity(body, status); } protected boolean isIncludeStackTrace(HttpServletRequest request, MediaType produces) { IncludeStacktrace include = this.getErrorProperties().getIncludeStacktrace(); if (include == IncludeStacktrace.ALWAYS) { return true; } else { return include == IncludeStacktrace.ON_TRACE_PARAM ? this.getTraceParameter(request) : false; } } protected ErrorProperties getErrorProperties() { return this.errorProperties; } }
1.3 实例
1.3.1 浏览器
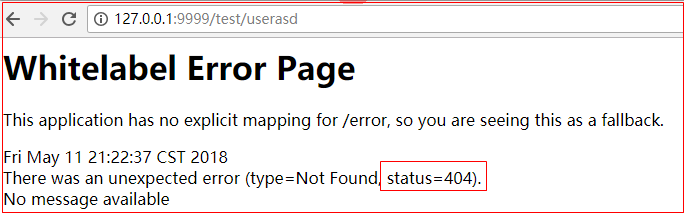
利用浏览器请求一个不存在的url
1.3.2 postman
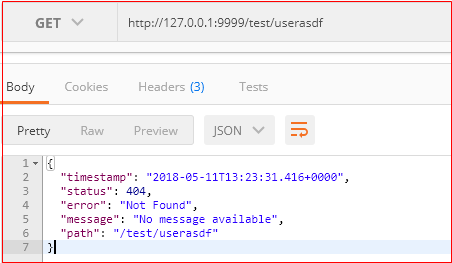
利用postman请求一个不存在的url
1.4 修改默认的HTML页面
如果是浏览器发送的请求出现异常后,跳转到 /error 请求后会根据错误编号返回对应的HTML文档,例如:404.html、500.html
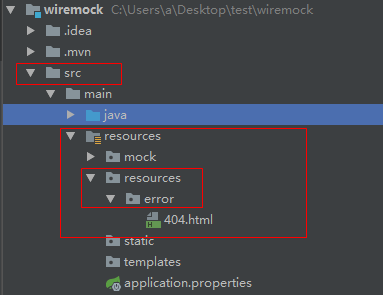
技巧01:我们可以重写这些404.html等文档,直接在 src/main/resources 路径下创建一个 resources/error 文件夹,形如:

<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <h2>你所访问的资源不存在</h2> </body> </html>
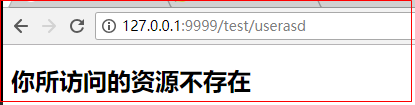
技巧02:在到 error 文件夹内部创建 404.html 等异常HTML文件即可,重启项目后利用浏览器访问一个不存在的url就会返回自定义的那个404.html文档,例如:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号