【字符串算法】——重拾KMP与AC自动机
——这两个玩意是好久以前学习的,现在大都忘记了,重新回忆一遍。
对于一个字符串S(文本串),我们拥有几个子串(模式串),如何去求出这些子串在S中位置?
这时候就要用到KMP算法。
简要构成就不叙述了,直接讲原理:
eg:
如下两个串,上为文本串(S),下为模式串(T),我们从头开始匹配。
S:abcabdabd
T:abcabc
到了某一位发现不一样:
S:abcabdabd
T:abcabc
那么我们就将模式串右移,因为ab两个字母是重复的。
S:abcabdabd
T: abcabc
继续匹配……
这个右移的过程是通过next数组实现的,它用来确定失配后变化的位置。
求next数组的方式:
很简单,不赘述了。
1 void nextst() 2 { 3 int j=0,k=-1; 4 nexts[0]=-1; 5 while(j<s2.length()){ 6 if(k==-1||s2[j]==s2[k]){ 7 nexts[++j]=++k; 8 } 9 else k=nexts[k]; 10 } 11 }
细心发现,这就是个模式串自匹配。
剩下的没啥好说的。我懒。
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=1e6+10; 4 string s1; 5 string s2; 6 int nexts[maxn]; 7 void nextst() 8 { 9 int j=0,k=-1; 10 nexts[0]=-1; 11 while(j<s2.length()){ 12 if(k==-1||s2[j]==s2[k]){ 13 nexts[++j]=++k; 14 } 15 else k=nexts[k]; 16 } 17 } 18 void kmp(){ 19 int i=0,j=0; 20 while(j<=s2.length()){ 21 if(j==s2.length()){ 22 cout<<i-s2.length()+1<<endl; 23 j=nexts[j]; 24 } 25 if(i>=s1.length()) break; 26 while(j>=0&&s1[i]!=s2[j]) j=nexts[j]; 27 i++; 28 j++; 29 } 30 } 31 int main(){ 32 cin>>s1>>s2; 33 nextst(); 34 kmp(); 35 for(int i=1;i<=s2.length();i++){ 36 cout<<nexts[i]<<" "; 37 } 38 cout<<endl; 39 return 0; 40 }
AC自动机,顾名思义,就是可以帮助你AC problem的东西借用OIWIKI上的一句话:
AC 自动机利用一个 fail 指针来辅助多模式串的匹配。
我认为这句话基本可以概括AC自动机的特点和功能,如果还有其他细节的话,就是:
AC 自动机是 以 TRIE 的结构为基础 ,结合 KMP 的思想 建立的。
我们来看啥是TRIE树:
没啥好看的,就是一棵由字符构成的树,每个节点都是一个字符,节点的儿子是其他字符,大概长这样:
(网上找的图)
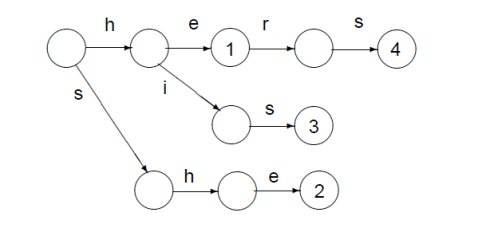
这张图就是he she is hers(意义不明)
接着有个叫fail指针的东西,类似于next数组,也是用来找匹配的。
如何构建?
这里引用一下OIWIKI上讲的:
我只会写普通版的模板,找空学一下优化:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 const int maxn=1e6+10; 4 int n,cnt=1,rt=1; 5 struct trie{ 6 int ch[27]; 7 int end; 8 int next; 9 }zh[maxn]; 10 void ins(const string &s){ 11 int o=rt; 12 for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ 13 int &t = zh[o].ch[s[i]-'a']; 14 if (!t) t = ++cnt; 15 o = t; 16 } 17 zh[o].end++; 18 } 19 void failed(){ 20 queue<int> a; 21 zh[rt].next=rt; 22 a.push(rt); 23 while(!a.empty()){ 24 int t=a.front(); 25 a.pop(); 26 for(int i=0;i<26;i++){ 27 if(zh[t].ch[i]){ 28 int fat=zh[t].next; 29 while(!zh[fat].ch[i]&&fat!=rt){ 30 fat=zh[fat].next; 31 } 32 zh[zh[t].ch[i]].next=(zh[fat].ch[i]&&t!=rt)?zh[fat].ch[i]:fat; 33 a.push(zh[t].ch[i]); 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 int sear(const string &s){ 39 int o=rt,res=0; 40 for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){ 41 if(zh[o].ch[s[i]-'a']) o=zh[o].ch[s[i]-'a']; 42 else{ 43 o=zh[o].next; //zh[o].next 44 while(!zh[o].ch[s[i]-'a']&&o!=rt){ 45 o=zh[o].next; 46 } 47 o=(zh[o].ch[s[i]-'a'])?zh[o].ch[s[i]-'a']:o; 48 } 49 for(int t=o;t!=rt&&zh[t].end!=-1;t=zh[t].next){ 50 res+=zh[t].end; 51 zh[t].end=-1; 52 } 53 } 54 return res; 55 } 56 int main(){ 57 cin>>n; 58 for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ 59 string s; 60 cin>>s; 61 ins(s); 62 } 63 failed(); 64 string t; 65 cin>>t; 66 cout<<sear(t)<<endl; 67 return 0; 68 }
那么回忆就暂时到此结束了,以后会找空更新这个页面的。
——抓住了时间,却不会利用的人,终究也逃不过失败的命运。


