CS224D Lecture 4 札记
咳咳,又到了博文时间,这一课的内容相对较少,所以就相对较快的来总结来博文啦,哈哈哈
废话不多说了,开始写吧,这一课的内容主要有三个部分,第一部分是window classification,第二部分是关于softmax的求梯度的tips,第三部分是Neuron Network 的一个简单介绍。
在这堂课开始的时候老师讲了一句话很经典,特此抄录下来:The large context you get, the more order of the words you ignore. The less you know whether that word was actually in a position of a adv adj or noun. 你的context选取的越大,越多的单词顺序就会被忽略,越不可能知道这个单词是adj, adv还是noun。
Classification intuition
这一部分简要的介绍了如何进行分类,一个简单的办法就是用softmax进行分类
W是softmax的weight matrix用来进行分类。分子的y代表ground truth的index,分母是将所有可能的class的值相加,最后求得一个概率。俺们的目标当然是使得这个概率越大越好啦,所以构造cost function或者loss function是这样的
我们使用到了极大似然估计(maximize likelihood estimation)就是假定所有事件发生是IID的,然后这些事件同时发生的概率就是它们各自概率的乘积,我们的目标就是求得使这个概率最大的参数,这里取log然后求和,利用到了log求和就是其parameters求积的性质。前面加了个符号,显然我们是要求使其最小的Weight Matrix。
之后又讲了一边上一堂课的内容Loosing generalization by re-training word vectors就是要不要更新word vectors呢?
slide里写得很好:If you only have a small training data set, don't train the word vectors. If you have a very large dataset, it may work better to train word vectors to the task.
原因上一节课就讲过了,就不再赘述了。
Side note
课上讲了几个术语,让人不是那么迷惑。
1. Word vector matrix L is also called lookup table.
2. Word vectors = word embeddings = word representations他们大概都是同一个意思哦!
Window Classification
这下终于到了本课的其中一个重点了。为什么需要window classification呢?因为不用window classificaiton容易出现ambiguity这种问题呀!
那么这东西怎么实现的呢?Instead of classifying a single word, just classify a word together with its context window of neighboring words.
给center word定义一个label然后连接所有他周围的word vector使其形成一个更长的vector。
然后怎么进行window Classification呢老样子还是用我们熟悉的softmax只是这时候的word vector不再仅仅是center word vector并且要concatenating all word vectors surrounding it。
具体怎么做呢?slides里给出了tips,但我还是觉得推的太简单所以我又手推了一遍。
一下是推导过程:
我tip 2推倒的不太对,课上的意思是使用chain rule,很简单,不用多说了。
https://www.math.hmc.edu/calculus/tutorials/multichainrule/

上面的链接详细的讲了chain rule,课上tip2要相加的原因是f_1, f_2 ....f_n相当于上面图中的x, y变量。整个函数和所有f都相关,所以要最后相加。
tip 4推出delta怎么得来的。
最后推了一个对softmax weights W求导的计算方法。
Basic neural networks
A single neuron简单的说就是多个softmax的组合。
多加几个out layers就使得结构更复杂,能力也更强。
再增加一个或多个hidden layers就更牛逼了,slides讲的很详细,UFLDL上讲得也挺好,链接,就不赘述了。
Intuition of back-propagation
课上推荐的那个四页的论文简直就是糊弄人嘛,其实就是个BP的科普,实质性的内容很少。里面比较经典的句子我摘抄下来了:
The procedure repeatedly adjusts the weights of the connections in the network so as to minimize a measure of the difference between the actual output vector of the net and the desired output vector.
Connections within a layer or from higher to lower layers are forbidden, but connections can skip intermediate layers.
如果想稍微详细了解BP的话还是看UFLDL上的简介吧!链接
BP的思路就是从output layer往最前一层倒推,for each node i in
layer l, we would like to compute an "error term" 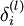 that
measures how much that node was "responsible" for any errors in our output.
that
measures how much that node was "responsible" for any errors in our output.
给每一层每一个edge计算responsible for any errors in our output,好无辜的edges
从最上一层说起,他的思路就是,如果你这个edge输入的z大,那么你对error的贡献也就大,计算responsible就是将error对每一个edge的z求导,这样就把最后一层的edges上的responsibles求出来了。
下一层的responsible呢,就是先把所有上层的responsibles求weights average其中weights就是edges上的W_ij然后再乘上f'(z)
然后就是J(W,b;x,y)对W_ij求导啦,也很简单使用chain rule其中要注意的一点就是这一层的x向量就是之前一层的a向量,不然怎么老感觉答案不对(- -)。
然后下面的公式是使用简洁的matrix表示方法很好看,也很简洁。
最后下面的pseudo-code很有借鉴意义,在自己code的时候可以参考着写。
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号