1-MySQL - 用户管理
用户名@白名单
MySQL支持用户名@白名单的方式连接,有以下几种方式:
| 链接方式 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
wordpress@'10.0.0.%' |
只允许10网段连接 | 常用 |
wordpress@'%' |
所有地址 | |
wordpress@'10.0.0.200' |
只允许某一个地址链接 | |
wordpress@'localhost' |
只允许本地连接 | |
wordpress@'db03' |
只允许别名是db03连接 |
|
wordpress@'10.0.0.5%' |
只允许IP地址末尾51~59的连接 |
|
wordpress@'10.0.0/255.255.254.0' |
只允许254这个网段的连接 |
白名单用户管理操作:
mysql> create user zhangkai@'localhost' identified by '123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select user,host from mysql.user;
+---------------+-----------+
| user | host |
+---------------+-----------+
| mysql.session | localhost |
| mysql.sys | localhost |
| root | localhost |
| zhangkai | localhost |
+---------------+-----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> alter user zhangkai@'localhost' identified by '1234';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> drop user zhangkai@'localhost';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select user,host from mysql.user;
+---------------+-----------+
| user | host |
+---------------+-----------+
| mysql.session | localhost |
| mysql.sys | localhost |
| root | localhost |
+---------------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
上面示例演示了白名单用户的增删改查的操作。不过这个白名单用户仅能用来登录到MySQL,权限有限!
常用的权限:
ALL:
SELECT,INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, CREATE, DROP, RELOAD, SHUTDOWN,
PROCESS, FILE, REFERENCES, INDEX, ALTER, SHOW DATABASES, SUPER,
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLES, LOCK TABLES, EXECUTE, REPLICATION SLAVE,
REPLICATION CLIENT, CREATE VIEW, SHOW VIEW, CREATE ROUTINE, ALTER ROUTINE,
CREATE USER, EVENT, TRIGGER, CREATE TABLESPACE
ALL : 以上所有权限,一般是普通管理员拥有的
with grant option:超级管理员才具备的,给别的用户授权的功能
创建用户并授权:
mysql> grant all on database_name.* to zhangkai@'localhost' identified by '123';
-- grant:授权命令
-- all:权限
-- on:为什么对象设置权限
-- wordpress.*:wordpress库下的所有表;需要注意的是,wordpress库如果不存在,该语句也能执行
-- zhangkai@'localhost':指定的用户
-- 修改权限还是使用grant命令来做,grant命令可以反复使用
一般的,应用用户的权限应该是有限的,常用的也就是select insert update delete。
PS:在MySQL8.0之后,grant命令有了新特性:
- 创建用户和授权分开
grant命令不再支持创建用户,也不支持修改密码- 授权之前,必须要创建用户
也就是,以后创建用户和授权操作要分开来做。
create user zhangkai@'%' identified by 'zhangkai1234';
grant all on *.* to zhangkai@'%';
另外,权限范围有几种写法:
| 权限 | 描述 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
*.* |
所有库下的所有表,使用与管理员用户 | |
wordpress.* |
指定库下的所有表,适用于开发和应用用户 | |
wordpress.t1 |
指定库下的指定表,用的不多 |
那么,如何查看用户的权限信息和如何回收权限呢?
-- 查看用户权限
show grants for zhangkai@'localhost';
-- 回收权限
revoke delete,drop on database@table from zhangkai@'localhost';
关于查看用户权限,需要补充一些内容。
- 之前提过,使用
create user root@'%' identified by '123'创建的用户,仅能用来登录MySQL,别的啥也干不了。
mysql> show grants for root@'192.168.85.%';
+---------------------------------------------+
| Grants for root@192.168.85.% |
+---------------------------------------------+
| GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'root'@'192.168.85.%' |
+---------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
正如上例的关键字USAGE表示该用户只有登录MySQL权限。想要别的权限,需要自己用有grant权限的账号为该账号授权,因为这个账号此时也没有授权这个权限。
- 关于
WITH GRANT OPTION,当你查看权限时,发现账号拥有ALL权限外,还有WITH GRANT OPTION权限。
mysql> show grants for root@'localhost';
+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for root@localhost |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION |
| GRANT PROXY ON ''@'' TO 'root'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION |
+---------------------------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
WITH GRANT OPTION表示该用户可以将自己拥有的权限授权给别人。
注意,如果在授权时没有加WITH GRANT OPTION参数,就表示该账户的权限只能自己用,而不能赋予别人,所以你在授权时要考虑好加不加WITH GRANT OPTION参数。
grant all on *.* to root@'%' identified by '123';
grant all on *.* to root@'%' identified by '123' with grant option;
也就是,上面两条命令你要事情况而选择。
修改密码
虽然上面已经提到了修改密码,但这里也单独把修改密码说下。
修改密码命令:
-- 将本地的root用户的密码修改为 123
alter user root@'localhost' identified by '123';
本地管理员用户密码忘记了
解决思路是:
- 关闭MySQL服务
mysqld_safe模式启动,即关闭MySQL的用户密码验证模块,也就是不加载授权表,然后禁止远程连接,仅能通过本地socket链接- 无密码登登录到MySQL
- 修改密码
- 重启MySQL
linux参考下面的方式1;Windows的参考方式2。
方式1
这个流程是Linux中演示的。
流程:
[root@cs mysql]# systemctl stop mysqld
[root@cs mysql]# mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
[root@cs mysql]# mysql
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 3
Server version: 5.7.20 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> alter user root@'localhost' identified by '123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> exit;
Bye
[root@cs mysql]# pkill mysqld
[root@cs mysql]# systemctl start mysqld
相关参数解释:
--skip-grant-tables:关闭授权表,这样就可以无验证登录了。--skip-networking:关闭TCP/IP,该参数的目的是只能本地通过socket连接登录,保证修改密码时的安全性。&是后台执行。- 至于在修改密码前的
flush privileges操作是因为修改密码还是要使用授权表,但是由于mysqld_safe模式启动授权表没有从磁盘加载到内存,所以直接执行alter命令会失败,所以要使用flush privileges命令将授权表加载到内存中,才能修改密码成功。修改的flush privileges让其新密码立即生效。
方式2
win10 + mysql.5.7.20
这里用Windows演示。并且你的MySQL是有配置文件的。
1. 修改配置文件
其实还是关闭授权表登录,然后修改密码,然后再开启授权表那一套。
[mysqld]
skip-grant-tables=1
2. 重启MySQL服务
net stop mysql57
net start mysql57
3. 无密码登录到MySQL,然后修改密码
# 无密码登录
mysql -u root -p
# 修改密码
update mysql.user set authentication_string = password('123'),password_last_changed=now() where user='root';
flush privileges;
# 或者使用下面的命令修改也一样
alter user root@'localhost' identified by '123';
flush privileges;
4. 退出客户端,并删除配置文件中的skip-grant-tables=1选项
[mysqld]
# skip-grant-tables=1
5. 然后在重启MySQL服务即可
net stop mysql57
net start mysql57
mac系统密码找回
套路参考方式1,也是关闭授权表那一套。但命令可能稍有不同,这里做个记录。
接下来的所有操作都在终端中完成。
- 首先关闭MySQL服务:
sudo mysql.server stop
mysqld_safe模式启动,即关闭MySQL的用户密码验证模块,也就是不加载授权表,然后禁止远程连接,仅能通过本地socket链接:
sudo mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking &
- 无密码登登录到MySQL:
# 3.1 终端输入mysql登录进去
mysql
# 3.2 再把授权表加载到内存中,后续才能修改密码
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 3.3 修改密码
mysql> alter user root@'localhost' identified by '123';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 3.4 再次刷新
mysql> flush privileges;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
# 3.5 退出,此时密码修改完毕了
mysql> exit;
Bye
- 杀掉
mysqld_safe模式启动的MySQL服务。
sudo pkill mysqld
- 重新启动MySQL服务。
sudo mysql.server start
- 使用新密码登录:
$ mysql -uroot -p123
mysql: [Warning] World-writable config file '/usr/local/mysql/etc/my.cnf' is ignored.
mysql: [Warning] Using a password on the command line interface can be insecure.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 8
Server version: 5.7.31 MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show databases;
ok了。
常见报错
ERROR 1133 (42000): Can't find any matching row in the user table
mariadb5.5.68
一般的,我们在MySQL上,创建用户和授权基本上就三步就行了:
create user zhangkai@'%' identified by '123';
grant all on t1.* to zhangkai@'%';
flush privileges;
然后,这个用户就创建成功了。
但是有次用的是mariadb,在这个过程中,遇到了报错。
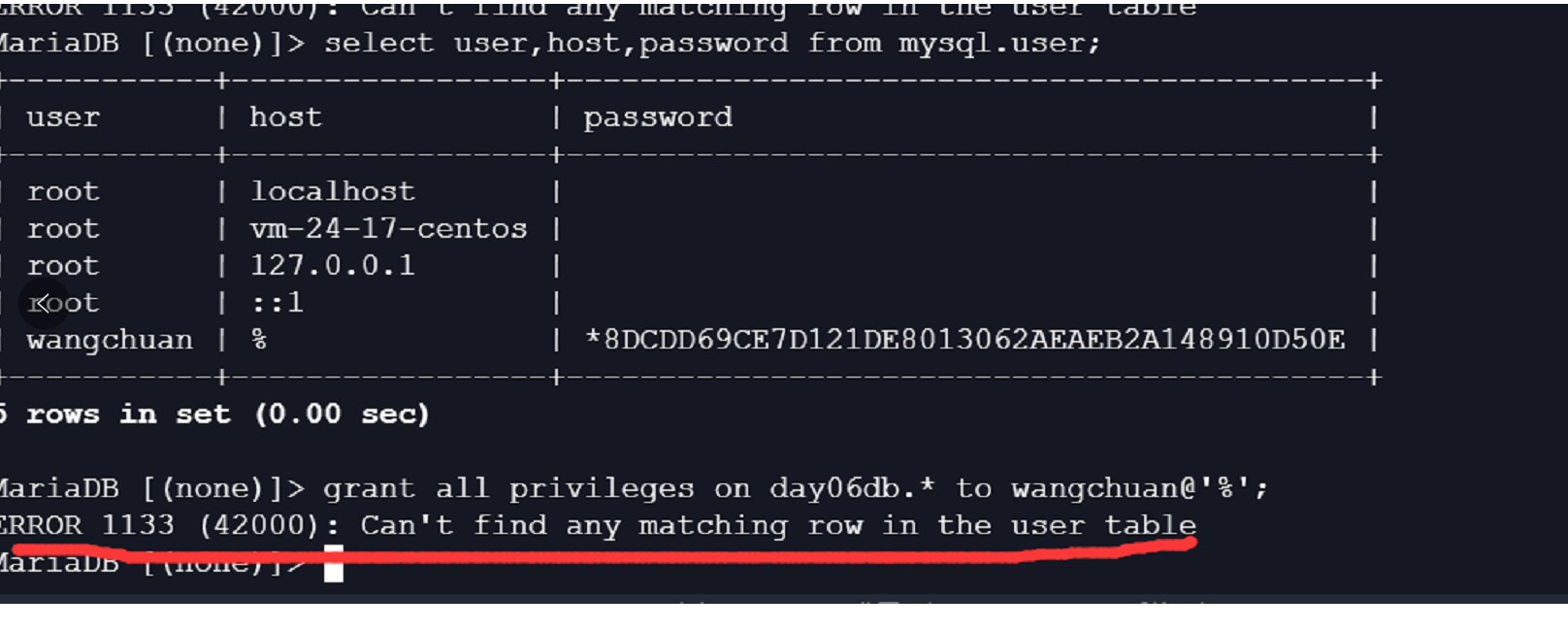
首先根据这截图,要授权的账号wangchuan@'%'是存在user表中的。但授权时失败了。
这个问题产生的原因创建账号成功,也就是写入了user表中,这也是user表能查出来的原因。
但是并没有及时写入权限表(grant table),才导致的授权失败。
那么解决方案也是有的,来看正确的执行命令:
insert into mysql.user(user,host,password) values('wangchuan','%',password('qwe123'));
flush privileges;
grant all on t1.* to wangchuan@'%';
flush privileges;
一步一刷新,就没问题了。
再来进一步扩展说点其他的,这个报错是因是insert into命令造成的,insert into只是将用户写入到mysql.user表中,但此时该用户还没有生效,就执行grant命令当然失败了,所以我们才在解决方案中,一步一刷新,让插入的用户及时生效。
另外,mysql5.7之后,mysql.user表中就没有了password字段,而是改成了authentication_string,但就算改成了authentication_string,执行也会报错,因为mysql.user表中还有其它字段没有默认值(如ssl_cipher)你也要处理这些问题。
总之啊,后续不建议使用insert into 命令,因为这个命令在mysql5.6及以下使用还行,高版本你就要自己调整了,有点麻烦,所以mysql5.7以上都用create user 命令就行了,简单省事儿。
欢迎斧正,that's all,see also:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号