SeaweedFS在.net core下的实践方案(续一)
前言
我们之前已经完成了SeaweedFS在.net core下的使用了,但是说实话,还是不够,于是,我的目光盯住了IApplicationBuilder的扩展方法UseStaticFiles
这个可是好东西啊,我们访问资源的静态文件映射,你懂我的意思吧,对这里下手~
前戏
开工之前,我们转到定义看看
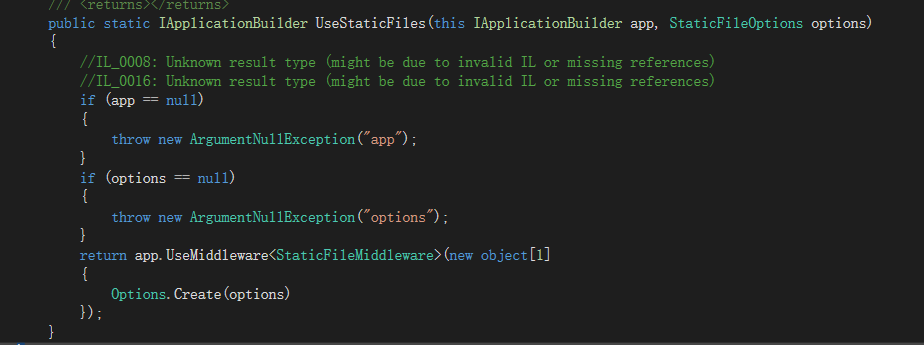
StaticFileOptions,这个就是我们自定义乱嗨的前提
它有两个,我们DIY需要用到的参数
RequestPath、FileProvider
顾名思义,前者是访问路径的前置地址
RequestPath的值是wwwroot,那么我们访问
http://url/wwwroot/XX.后缀 才会触发这个,而且,一定要是带后缀的才触发
后者是,前置地址触发的基础上才调用的
我们给他安排一下
实现
因为核心参数FileProvider类型为IFileProvider,所以,我们写一个实现类吧
public class SeaweedFSFileProvider : IFileProvider { public IDirectoryContents GetDirectoryContents(string subpath) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string subpath) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public IChangeToken Watch(string filter) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }
我们现在需要用到的是GetFileInfo这个方法,另外两个,并不会触发(严谨一点说,GetDirectoryContents,我们访问无论是资源目录路径,还是完整的资源路径,都不会触发)
比如我们wwwroot这个文件夹是资源路径
无论是
http://url/wwwroot/ 还是 http://url/wwwroot,都不触发
这个也没触发~
emmmmm,可能研究太浅了,这两个接口方法是给其他实现类提供的定制化功能?比如FileServer?
GetFileInfo方法的返回值是IFileInfo
这个接口,触发文件返回的顺序是
Exists属性->Length属性->LastModified属性->Exists属性->PhysicalPath属性->CreateReadStream方法
我们写一个实现
public class SeaweedFSFileInfo : IFileInfo { public bool Exists { get; set; } public long Length => new MemoryStream(Context).Length; public string PhysicalPath { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public DateTimeOffset LastModified { get; } public bool IsDirectory => false; private byte[] Context { get; } public SeaweedFSFileInfo() { } public SeaweedFSFileInfo(string physicalPath, byte[] context) { Context = context; PhysicalPath = physicalPath; Name = Path.GetFileName(PhysicalPath); LastModified = DateTimeOffset.Now; Exists = true; } public Stream CreateReadStream() { return new MemoryStream(Context); } }
我们修改一下SeaweedFSFileProvider,这里注入一个IFileService
因为我们希望整个SeaweedFSFileProvider他只依赖于IFileService,而不过多依赖SeaweedFS的实现,不会让代码简洁性受损
public class SeaweedFSFileProvider : IFileProvider { private IFileService Service { get; } public SeaweedFSFileProvider(IFileService service) { Service = service; } public IDirectoryContents GetDirectoryContents(string subpath) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string subpath) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public IChangeToken Watch(string filter) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }
我们转到接口IFileService,写一个接口
public interface IFileService { Task<SeaweedFSDirAssignModel> GetUploadFileUrlAsync(); Task<SeaweedFSUploadResponse> UploadFileAsync(string url,byte[] context); IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string subpath); }
再转到实现类
增加这个实现
public IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string subpath) { throw new NotImplementedException(); }
我们去外层的SeaweedFSFileProvider修改一下
public class SeaweedFSFileProvider : IFileProvider { private IFileService Service { get; } public SeaweedFSFileProvider(IFileService service) { Service = service; } public IDirectoryContents GetDirectoryContents(string subpath) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } public IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string subpath) { return Service.GetFileInfo(subpath); } public IChangeToken Watch(string filter) { throw new NotImplementedException(); } }
这样IFileService 里面变成什么样,都跟这层没关系了
我们定义一个IFileInfoFactory
public interface IFileInfoFactory { bool Contains(string filepath); IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string filepath); IFileInfo AddFileInfo(string filepath, byte[] context); IFileInfo AddNotExists(string filepath); }
再写一个默认实现
public class FileInfoFactory: IFileInfoFactory { private List<IFileInfo> FileInfo { get; } = new List<IFileInfo>(); public bool Contains(string filepath) { return FileInfo.Any(file => file.PhysicalPath.Equals(filepath)); } public IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string filepath) { return FileInfo.FirstOrDefault(file => file.PhysicalPath.Equals(filepath)); } public IFileInfo AddFileInfo(string filepath,byte[] context) { var info = new SeaweedFSFileInfo(filepath, context); FileInfo.Add(info); return info; } public IFileInfo AddNotExists(string filepath) { var info = new SeaweedFSFileInfo(); FileInfo.Add(info); return info; } }
我们修改一下
SeaweedFSService的默认实现,增加一个注入IFileInfoFactory
private IFileInfoFactory FileInfoFactory { get; } public SeaweedFSService(IOptions<SeaweedFSServiceConfiguration> options, IFileInfoFactory fileInfoFactory) { Configuration = options.Value; FileInfoFactory = fileInfoFactory; }
我们实现一下
GetFileInfo方法
public IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string subpath) { using (var client = HttpClientFactory.Create()) { var path = subpath.Replace(Path.GetExtension(subpath), ""); var splits = path.Split("/".ToCharArray(), StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); if (splits.Length == 0) { return FileInfoFactory.AddNotExists(subpath); } else { var fid = $"{splits[0]},{splits[1]}"; var response = client.GetAsync($"http://{Configuration.BaseUrl}/{fid}") .GetAwaiter() .GetResult(); if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound) { return FileInfoFactory.AddNotExists(subpath); } else { var context = response.Content; var bytes = context.ReadAsByteArrayAsync() .GetAwaiter() .GetResult(); if (FileInfoFactory.Contains(subpath)) { return FileInfoFactory.GetFileInfo(subpath); } else { return FileInfoFactory.AddFileInfo(subpath, bytes); } } } } }
这个时候,我们测试一下
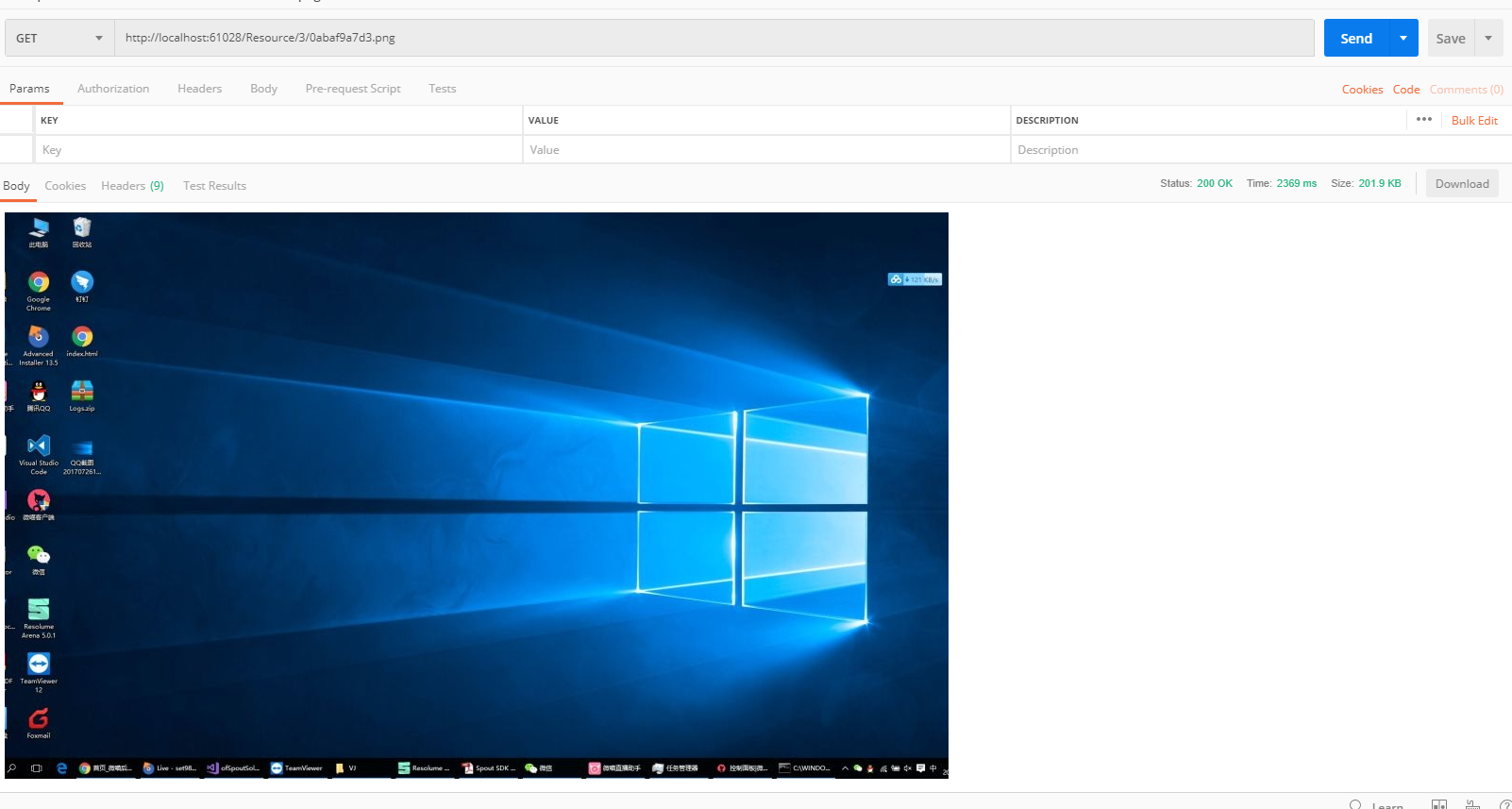
大功告成,撒花
优化
但是我们可能场景是这个文件上传了,就不再修改了,修改后文件,变成新路径,这样,文件就始终是静态的,那么这样反复http请求就没意义了
所以,我们修改一下
private SeaweedFSServiceConfiguration Configuration { get; } private IFileInfoFactory FileInfoFactory { get; } private IDistributedCache Cache { get; } public SeaweedFSService(IOptions<SeaweedFSServiceConfiguration> options, IFileInfoFactory fileInfoFactory, IDistributedCache cache) { Configuration = options.Value; FileInfoFactory = fileInfoFactory; Cache = cache; }
增加了一个分布式缓存
我们就找这个缓存,能不能找到,还能找到,就说明已经缓存了这个文件信息,就不再走http
修改一下GetFileInfo
public IFileInfo GetFileInfo(string subpath) { var key = $"Distributed_Files_{subpath}"; var contextBytes = Cache.Get(key); if (contextBytes != null && FileInfoFactory.Contains(subpath)) { return FileInfoFactory.GetFileInfo(subpath); } else { using (var client = HttpClientFactory.Create()) { var path = subpath.Replace(Path.GetExtension(subpath), ""); var splits = path.Split("/".ToCharArray(), StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries); Cache.Set(key, new byte[] { }); if (splits.Length == 0) { return FileInfoFactory.AddNotExists(subpath); } else { var fid = $"{splits[0]},{splits[1]}"; var response = client.GetAsync($"http://{Configuration.BaseUrl}/{fid}") .GetAwaiter() .GetResult(); if (response.StatusCode == HttpStatusCode.NotFound) { return FileInfoFactory.AddNotExists(subpath); } else { var context = response.Content; var bytes = context.ReadAsByteArrayAsync() .GetAwaiter() .GetResult(); if (FileInfoFactory.Contains(subpath)) { return FileInfoFactory.GetFileInfo(subpath); } else { return FileInfoFactory.AddFileInfo(subpath, bytes); } } } } } }
这样访问的地址,缓存没失效之前,并且在文件缓存里面,就不再走http请求了
附
我们附上入口的代码
ConfigureServices方法内增加
services.AddDistributedMemoryCache();
这样就启用了默认的分布式缓存接口,后期要替换的实现,只用更换这里的具体实现就好了,我们不依赖具体实现
Configure方法内增加代码
using (var services = app.ApplicationServices.CreateScope()) { var fileService = services.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IFileService>(); app.UseStaticFiles( new StaticFileOptions { RequestPath = "/Resource", FileProvider = new SeaweedFSFileProvider(fileService) } ); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号