python | 小游戏 开局托儿所 自动化脚本 pyautogui
小游戏开局托儿所自动化脚本 pyautogui
纯sb游戏,我脚本都不是总能上100分。当然,跟我算法不是最优肯定也有关系。
别玩这游戏,纯浪费时间。
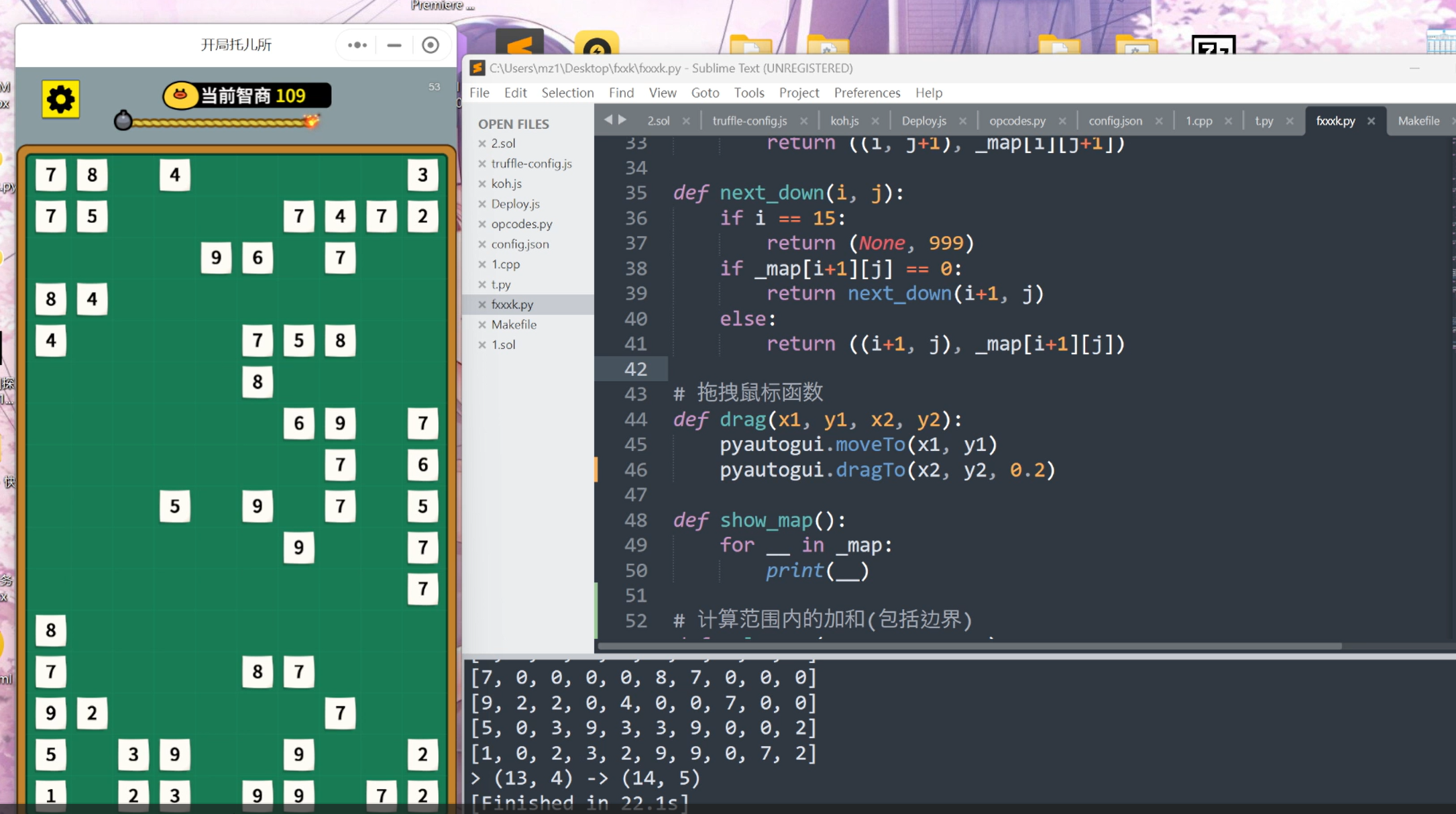
好久不写这种带算法的代码了,调了半天。
import pyautogui
def like(boxa, boxb):
if abs(boxa.top-boxb.top) < 10 and abs(boxa.left-boxb.left) < 10:
# print(boxa, boxb)
return True
return False
def loc2xy(locbox):
if locbox.left - zeroloc[0] > 0:
d_x = (locbox.left - zeroloc[0]) // 60
else:
d_x = 0
if (locbox.top - zeroloc[1]) > 0:
d_y = (locbox.top - zeroloc[1]) // 60
else:
d_y = 0
return (d_x, d_y)
def xy2loc(x, y):
# print((zeroloc[0]+60*y, zeroloc[1]+60*x))
return (zeroloc[0]+62*y, zeroloc[1]+62*x)
# sb csdn 别偷我代码
# 返回右边一个非0位置 和数值
def next_right(i, j):
if j == 9:
return (None, 999)
if _map[i][j+1] == 0:
return next_right(i, j+1)
else:
return ((i, j+1), _map[i][j+1])
def next_down(i, j):
if i == 15:
return (None, 999)
if _map[i+1][j] == 0:
return next_down(i+1, j)
else:
return ((i+1, j), _map[i+1][j])
# 拖拽鼠标函数
def drag(x1, y1, x2, y2):
pyautogui.moveTo(x1, y1)
pyautogui.dragTo(x2, y2, 0.2)
def show_map():
for __ in _map:
print(__)
# 计算范围内的加和(包括边界)
def calc_map(x1, y1, x2, y2):
_sum = 0
for i in range(x1, x2+1):
for j in range(y1, y2+1):
_sum += _map[i][j]
return _sum
# 清零区域
def clean_map(x1, y1, x2, y2):
for i in range(x1, x2+1):
for j in range(y1, y2+1):
_map[i][j] = 0
locations = []
real_locs = []
setloc = pyautogui.locateOnScreen(f'img/set.png', confidence=0.9)
zeroloc = (setloc.left, setloc.top+127)
print(zeroloc)
for i in range(1, 10):
locations.append(pyautogui.locateAllOnScreen(f'img/{i}.png', confidence=0.9))
# 除去相同的
length = 0
for _ in range(9):
a = []
locs = list(locations[_])
for i in range(len(locs)):
ok = True
for j in range(i+1, len(locs)):
if like(locs[i], locs[j]):
ok = False
break
if ok:
a.append(locs[i])
length += len(a)
real_locs.append(a)
# print(real_locs)
print(length)
# assert length == 160
print('ok')
# 整理地图 10*16
_map = [[0 for j in range(10)] for i in range(16)]
for i in range(len(real_locs)):
for loc in real_locs[i]:
x, y = loc2xy(loc)
_map[y][x] = i+1
show_map()
change = True
while change == True: # 循环直到没有可以消除的
change = False
for i in range(16):
for j in range(10):
row_list = [(i,j)]
count = _map[i][j] # 求和
tmp, num = next_right(i, j) # 横向相加
while tmp is not None:
count += num
row_list.append(tmp)
if count > 10:
break
elif count == 10: # 横向消除
loc1 = xy2loc(i,j)
loc2 = xy2loc(tmp[0], tmp[1])
drag(loc1[0], loc1[1], loc2[0]+45, loc2[1]+45)
change = True
# 清除数据
for _loc in row_list:
_map[_loc[0]][_loc[1]] = 0
# print(((i,j),(tmp[0],tmp[1])))
# show_map()
else:
tmp, num = next_right(tmp[0], tmp[1])
column_list = [(i,j)]
count = _map[i][j] # 求和
tmp, num = next_down(i, j) # 竖向相加
while tmp is not None:
count += num
column_list.append(tmp)
if count > 10:
break
elif count == 10: # 竖向消除
loc1 = xy2loc(i,j)
loc2 = xy2loc(tmp[0], tmp[1])
drag(loc1[0], loc1[1], loc2[0]+45, loc2[1]+45)
change = True
# 清除数据
for _loc in column_list:
_map[_loc[0]][_loc[1]] = 0
# print(((i,j),(tmp[0],tmp[1])))
# show_map()
else:
tmp, num = next_down(tmp[0], tmp[1])
# 斜向消除只需要遍历到最大column和row
# print((i,j))
row_max = row_list.pop()
column_max = column_list.pop()
j_max = row_max[1]
i_max = column_max[0]
# print((i_max, j_max))
# show_map()
# print(calc_map(i,j,i_max,j_max))
# print('-------------')
for i_index in range(i, i_max):
for j_index in range(j, j_max):
_tmp_sum = calc_map(i, j, i_index, j_index)
if _tmp_sum == 10:
show_map()
print(f'> {(i,j)} -> {(i_index, j_index)}')
loc1 = xy2loc(i,j)
loc2 = xy2loc(i_index, j_index)
drag(loc1[0], loc1[1], loc2[0]+45, loc2[1]+45)
change = True
clean_map(i, j, i_index, j_index)
# elif _tmp_sum > 10:
# break
本文来自博客园,作者:Mz1,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mz1-rc/p/17962922
如果有问题可以在下方评论或者email:mzi_mzi@163.com
分类:
python






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 【杭电多校比赛记录】2025“钉耙编程”中国大学生算法设计春季联赛(1)
2023-01-13 re | [NPUCTF2020]EzReverse