深入理解printf
printf的流程
- 将内存中的数据拷贝到stdout中
- 将stdout拷贝到FO文件对象中(文件对象帮助与硬件进行交互,输出到屏幕上)
- 清理stdout
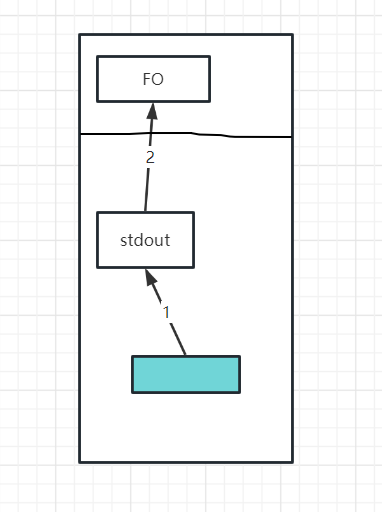
在Linux中,若printf的格式化字符串未添加 \n ,则只会将内存中的数据拷贝到stdout,待程序结束清理stdout才会输出到屏幕。
#include <47func.h>
void* threadFunc(void* arg)
{
//printf("child");
printf("child");
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid,NULL,threadFunc,NULL);
sleep(1);
printf("man thread\n");
exit(0);
}
main线程通过pthread_create函数创建出子线程后,父子线程并发运行,但main线程中在printf之前添加了sleep函数,所以子线程一定会先运行printf函数,但是由于子线程的printf函数输出的字符串中未加入 \n ,故会首先将child字符串放入stdout中,待main线程中sleep函数运行结束后,同main线程中的printf一起输出。


