java高并发(已完结)
1,JUC简述
java.util.concurrent包

2,线程
2.1,线程和进程
进程:一个程序,例如一个浏览器、视频播放器
线程:一个进程包括多个线程(最少有一个main主线程),例如视频播放器有声音线程、图像线程等
一个java程序最少包含2个线程(一个main线程、一个GC线程,详情使用jsp -l查看GC线程)
(Thread、Runnable、Callable)
2.2,并发和并行
并发:多线程操作同一个资源(CPU一核心,分时复用)
并行:多核心同时执行(多个CPU核心互不干扰的执行任务)
并发编程的本质:充分利用CPU的资源
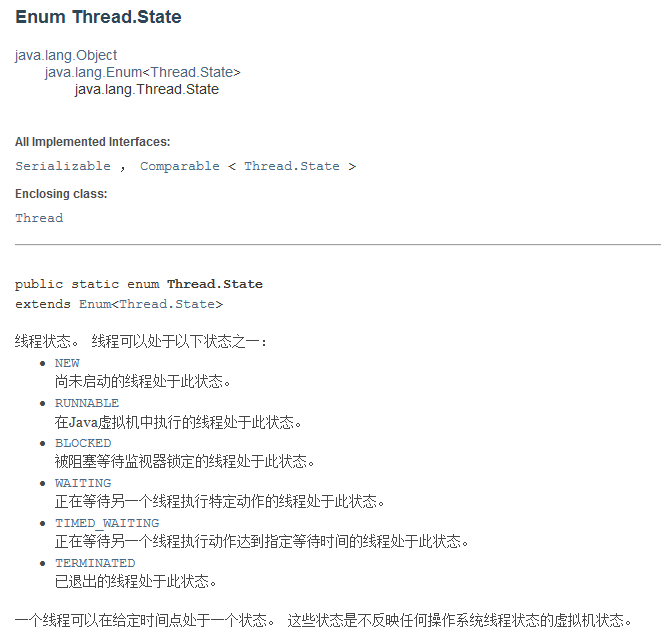
2.3,线程状态
线程有6个状态:
NEW(新创建未启动)、RUNNABLE(执行中)、BLOCKED(阻塞)、
WATING(一直等待中)、TIMED_WAITING(超时等待)、TERMINATED(终止)
2.4,wait/sleep区别
1,来自不同的类
wait来自object类,sleep来自于Thread类(一般使用JUC中的TimeUtil)
2,锁的释放
wait会释放锁,sleep不会释放锁(抱着锁睡觉)
3,使用的范围
wait必须在同步代码块中使用,sleep全局都可以用
4,是否需要捕获异常(需要重新确认)
wait不需要捕获异常、sleep需要捕获异常(idea也有提示)
3,锁(待完善)
传统的synchronized
public class LockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
new Thread(Tiket::getOne, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
class Tiket{
private static Integer sum = 10;
public static synchronized void getOne(){
if(sum>0){
sum --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+sum);
}else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>未买到车票");
}
}
}
Lock锁
public class LockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
new Thread(Tiket::getOne, String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
class Tiket{
private static Integer sum = 10;
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void getOne(){
lock.lock();
try {
if(sum>0){
sum --;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+sum);
}else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>未买到车票");
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
4,生产者和消费者问题(待完善)
单例模式、排序算法、生产者和消费者问题、死锁
package concurrent.seven;
/**
* @Author 59456
* @Date 2021/12/23
* @Descrip 判断等待、业务、通知
* @Version 1.0
*/
public class ProjectMain{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Data data = new Data();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
data.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
try {
data.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
// new Thread(()->{
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// try {
// data.increment();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
// },"C").start();
//
//
// new Thread(()->{
// for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
// try {
// data.decrement();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
// },"D").start();
}
}
class Data {
private int number = 0;
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
if(number!=0){
// 等待
this.wait();
}
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+number);
// 通知其他线程,+1完成
this.notify();
}
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
if(number==0){
// 等待
this.wait();
}
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+number);
// 通知其他线程,-1完成
this.notify();
}
}
问题存在,A、B、C、D 4个线程!虚假唤醒
5,8锁问题
package concurrent.ten;
/**
* @Author 59456
* @Date 2021/12/26
* @Descrip
* @Version 1.0
*/
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/***
* 8锁问题
* 1,两个synchronized多线程执行
* 发短信先
* 2,两个synchronized多线程执行,先调用的延时4s
* 发短信先,因为有锁的存在
* synchronized锁的是对象:方法的调用者,谁先拿到谁执行
* 3,有一个非synchronized的方法,没有锁的影响
* 你好先
* 4,2个对象phone1\phone2,不同的锁
* 打电话先
* 5,增加static静态方法1个对象,class模板锁
* 发短信
* 6,增加static静态方法2个对象,class模板锁
* 发短信
* 7,static的synchronized 和 普通的synchronized方法1个对象,两把锁互不影响
* 打电话
* 8,static的synchronized 和 普通的synchronized方法1个对象,两把锁互不影响
* 打电话
*/
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone1 = new Phone();
Phone phone2 = new Phone();
new Thread(()->{
phone1.sendMsg();
},"A").start();
// 休息1秒钟
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
new Thread(()->{
phone2.call();
},"B").start();
}
}
class Phone{
//
public static synchronized void sendMsg(){
// 休息1秒钟
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("发短信");
}
public synchronized void call(){
System.out.println("打电话");
}
public void hello(){
System.out.println("你好");
}
}
小结
new this 具体的一个对象
static class 唯一的一个模板
6,集合类不安全
List、Set、Map 不安全
package concurrent.Eleven;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @Author 59456
* @Date 2021/12/26
* @Descrip ConcurrentModificationException
* @Version 1.0
*/
/**
* 1,使用vector解决,本质就是synchronized(jdk1.0)
* 2,Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
* 3,new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
*/
public class ListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
// List<String> stringList = new Vector<>();
// List<String> stringList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
List<String> stringList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
stringList.add(UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0,5));
System.out.println(stringList);
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
stringList.forEach(e->{
System.out.println(e+"-A");
});
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
stringList.forEach(e->{
System.out.println(e+"-A");
});
}
}
补充知识(HashSet的底层是HashMap)
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
补充知识(HashMap 有两个参数初始容量、加载因子)
public HashMap() {
this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted
}
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
7,Callable
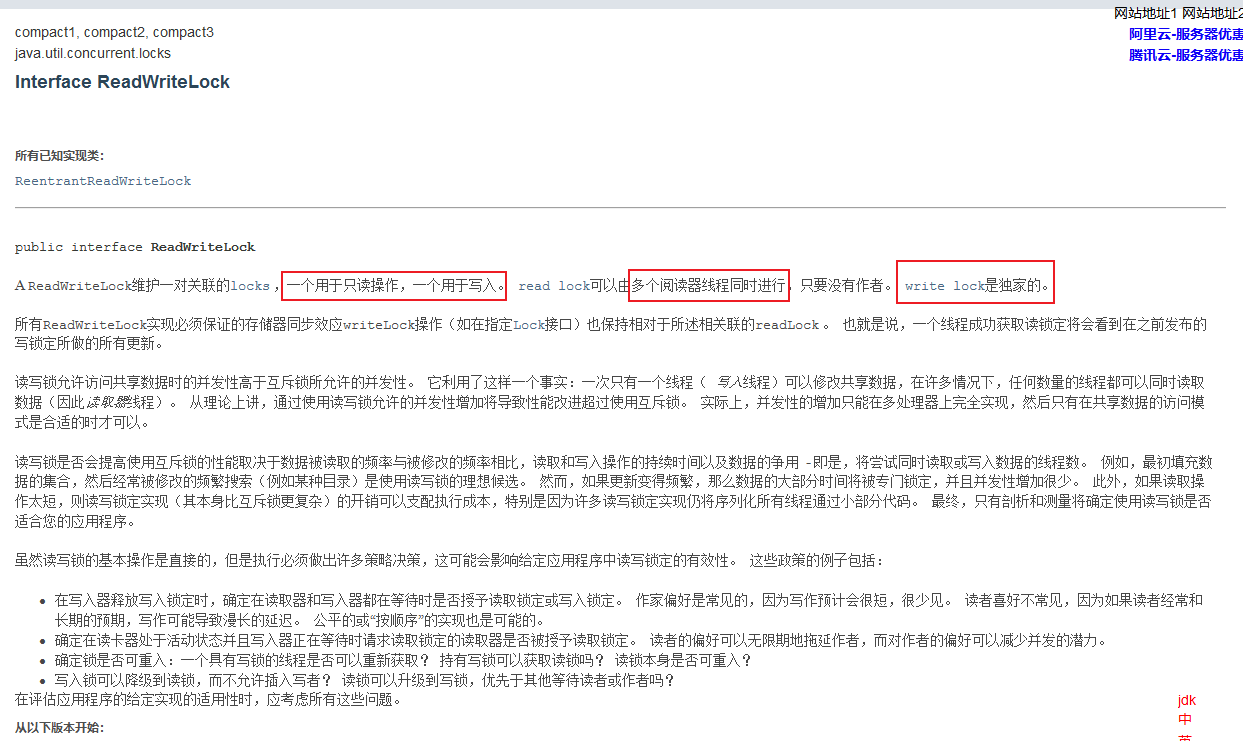
8,读写锁
10,阻塞队列
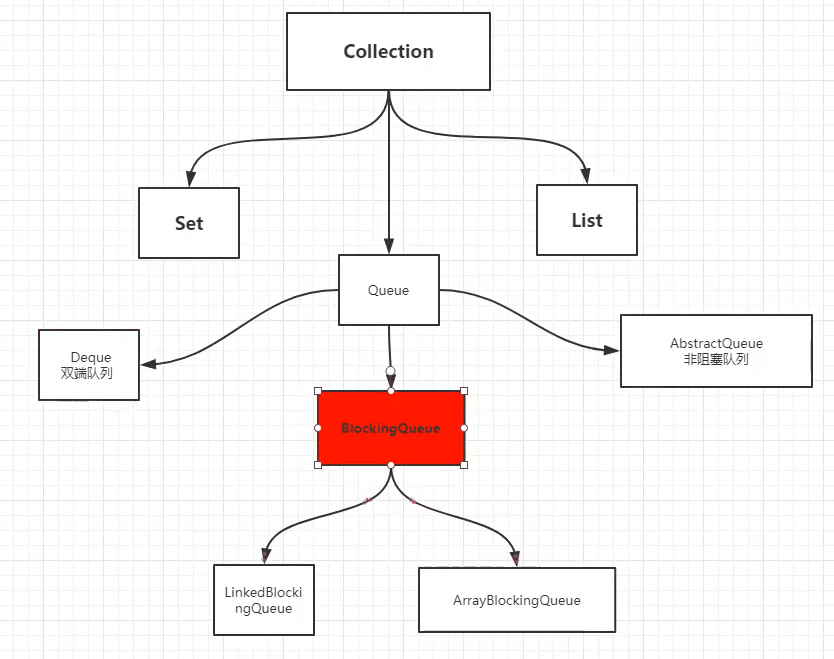
| 方式 | 抛出异常 | 有返回值 | 阻塞等待 | 超时等待 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 添加 | add | offer | put | offer |
| 移除 | remove | poll | take | poll |
| 检测队首元素 | element | peek |
11,线程池
池化技术(3大方法、7大参数、4种拒绝策略)
程序的运行需要占用系统的资源!优化资源的使用=》池化技术
线程池、连接池、内存池、对象池。。。
池化计划:事先准备好一些资源,有人需要使用就直接拿来使用,用完之后就“返还”
线程池的好处:1,降低资源的消耗;2,提高响应的速度;3,方便管理
线程可以复用,可以控制最大并发数、管理线程
阿里巴巴编码规约:线程池不允许使用Exectors创建

11.1,3大方法
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();// 单个线程
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);//固定线程大小
ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();//可伸缩的
三大方法的本质就是ThreadPoolExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,// 21亿
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
11.2,7大参数
// 本质
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,// 核心线程池大小
int maximumPoolSize,// 最大核心线程池大小
long keepAliveTime,// 超时了没有人调用就会释放
TimeUnit unit,// 超时单位
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,// 阻塞队列
ThreadFactory threadFactory,// 线程工厂,创建线程的,一般不会动
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {// 拒绝策略
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
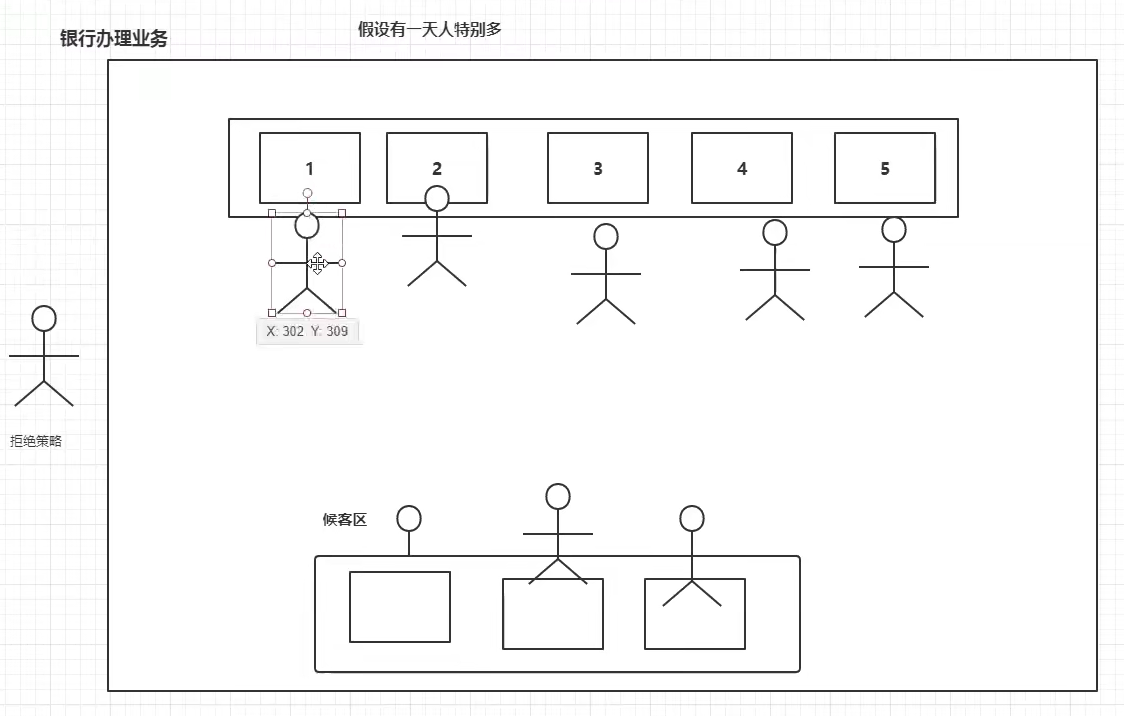
11.3,4种拒绝策略
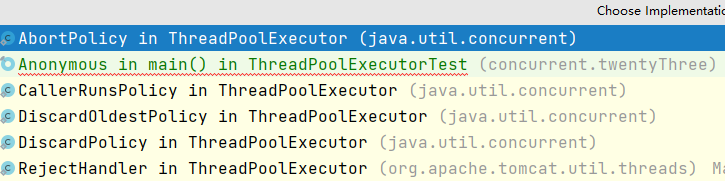
ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
2,// 核心线程池大小
5,// 最大核心线程池大小
3,// 超时了没有人调用就会释放
TimeUnit.SECONDS,// 超时单位
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3),// 阻塞队列
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),// 线程工厂,创建线程的,一般不会动
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());// 拒绝策略
最大承载值:最大核心线程池大小+阻塞队列个数
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
银行满了(休息区也满了),不能再进人了,抛出异常
超出最大承载值,直接报错
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy()
队列满了,丢掉任务,不会抛出异常(直接丢弃任务)
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()
队列满了,丢掉最早的任务,不会抛出异常(丢弃阻塞队列中靠最前的任务,并执行当前任务)
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
用调用者所在的线程来执行任务;
11.4,最大线程如何定义?
// 核心线程数也是基于性能考虑
// 估算平时的流量需要的线程数,设置核心线程数
/***
* cpu密集型:几核心cpu,就是几核,例如本机就是8核心
* int i = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
* IO密集型:判断程序中十分耗IO的线程,一般设置为2倍(防止阻塞)
* 例如需要15个线程处理数据,尽量设置30个线程池个数
*/
int i = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
12,四大函数式接口
lambda表达式、链式编程、函数式接口、Stream流式计算
函数式编程:有且只有一个方法的接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
// 非常多的FunctionalInterface
// 简化编程模型
// foreach(消费者类型的函数式接口)
Consumer、Function、Predicate、Supplier
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Function<T, R> {
/**
* Applies this function to the given argument.
*
* @param t the function argument
* @return the function result
*/
R apply(T t);
}
// 传入参数T,返回参数R
12.1,lambda表达式
Function、断定型接口Predicate、消费型接口Consumer、生产型接口Supplier
// 函数式Function
Function<String, String> function = e->"==>" + e;
System.out.println(function.apply("123456"));
System.out.println(function.apply("123"));
// 断定型接口Predicate
Predicate<String> predicate = "hello"::equals;
System.out.println(predicate.test("hello"));
System.out.println(predicate.test("12345"));
// 消费型接口Consumer
Consumer<String> consumer = System.out::println;
consumer.accept("hello");
consumer.accept("12345");
// 生产型接口Supplier
Supplier<String> stringSupplier = ()->"hello";
System.out.println(stringSupplier.get());
13,Stream流式计算
/**
* 1,ID必须是偶数
* 2,年龄大于23岁
* 3,用户名转换为大写
* 4,用户名倒序
* 5,只输出1个数据
*/
public class StreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User u1 = new User(1,"a",21);
User u2 = new User(2,"b",22);
User u3 = new User(3,"c",23);
User u4 = new User(4,"d",24);
User u5 = new User(5,"e",25);
List<User> userList = Arrays.asList(u1,u2,u3,u4,u5);
// userList.stream()
// .filter(u->u.getId()%2==0)
// .forEach(System.out::println);
// userList.stream()
// .filter(u->u.getAge()>23)
// .forEach(System.out::println);
// userList.stream()
// .map(u->{u.setName(u.getName().toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT));
// return u;
// })
// .forEach(System.out::println);
// userList.stream()
// .sorted((uu1,uu2)->uu2.getName().compareTo(uu1.getName()) )
// .forEach(System.out::println);
userList.stream()
.limit(1)
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
14,ForkJoin
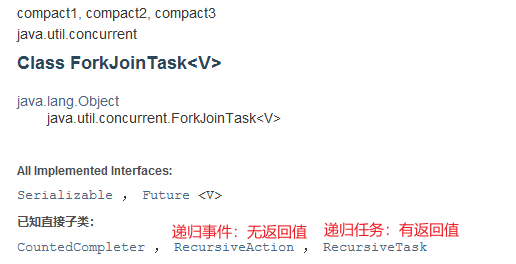
ForkJoin是什么?
ForkJoin在JDK1.7,并行执行任务,提高效率,大数据量(Map Reduce 把大任务拆分为小任务)
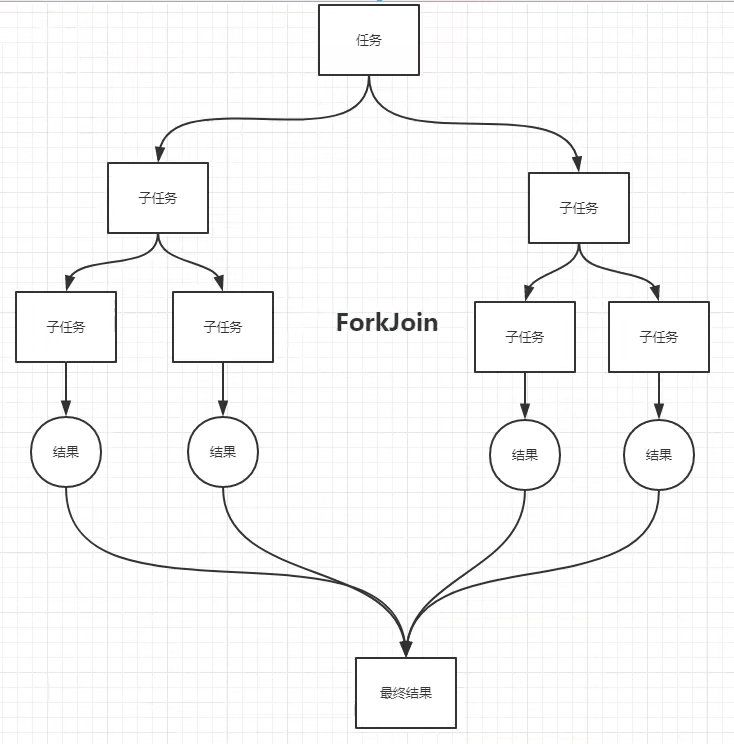
ForkJoin 工作窃取
A、B两个线程执行任务,B线程执行完后,A线程还有几个没有执行完;这时B线程会窃取A中未执行的任务进行执行。
这里面维护的都是双端队列
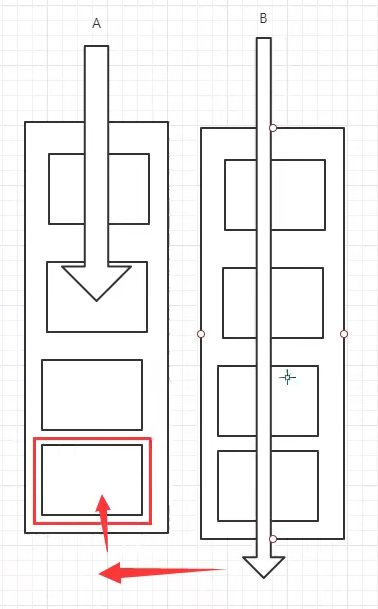

样例:0~10_0000_0000 => 求和
/**
* 3000 6000(forkJoin) 9000(Stream并行流)
* serial:data=>500000000500000000,time=>711
* forkJoin:data=>500000000500000000,time=>601
* LongStream:data=>500000000500000000,time=>387
*/
public class ForkJoinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
long start = 0L;
long end = 10_0000_0000L;
long startDate,endDate;
// 普通的串行求和计算
startDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
long sum = 0;//499999999500000000
for (long i = start; i <= end; i++) {
sum += i;
}
endDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("serial:data=>" + sum + ",time=>" + (endDate - startDate));
// forkJoin求和计算
startDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
ForkJoinTask<Long> task = new ForkJoinAdd(start, end);
ForkJoinTask<Long> submit = forkJoinPool.submit(task);
sum = submit.get();
endDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("forkJoin:data=>" + sum + ",time=>" + (endDate - startDate));
// stream并行流计算
startDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
sum = LongStream.rangeClosed(start, end).parallel().reduce(0, Long::sum);
endDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("LongStream:data=>" + sum + ",time=>" + (endDate - startDate));
}
}
/**
* 1,forkJoinPool 通过这个执行
* 2,计算任务forkJoinPool.excutor(forkJoinTask)
* 3,计算类要继承forkJoinTask
*/
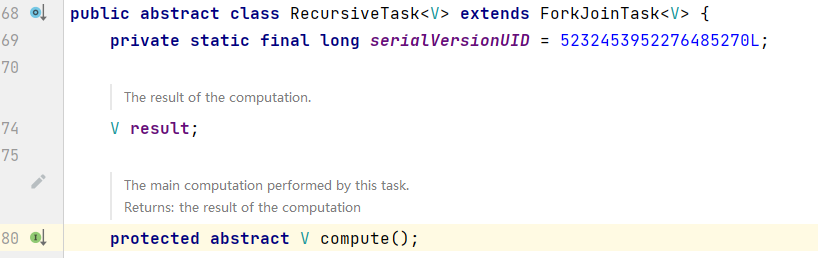
class ForkJoinAdd extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
private Long start;
private Long end;
private Long temp = 10_0000L;
public ForkJoinAdd(Long start, Long end) {
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
/**
* The main computation performed by this task.
*
* @return the result of the computation
*/
@Override
protected Long compute() {
if((end-start)<temp){
long sum = 0L;
for (long i = start; i <= end; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}else {
long middle = (start + end) / 2;// 中间值
ForkJoinAdd task1 = new ForkJoinAdd(start, middle);
task1.fork(); // 拆分任务,把任务压入线程
ForkJoinAdd task2 = new ForkJoinAdd(middle + 1, end);
task2.fork();
return task1.join() + task2.join();
}
}
}
15,异步回调
Future
public class FutureTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("one");
});
System.out.println("second");
// 当需要取未来的返回值时,就会阻塞main线程,直到获取到数据
System.out.println(completableFuture.get());
}
}
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
int sqrt = 10/0;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("one");
return 1024;
});
Integer result = completableFuture.whenComplete((t,u)->{
System.out.println("t=>" + t); // 正常的返回结果
System.out.println("u=>" + u); // 错误信息
}) .exceptionally((e)->{
e.printStackTrace();
return 233;
}).get();
System.out.println("result:"+result);
16,JMM
java memory model
线程A中的内存区块生命周期:
1,主内存锁住(lock),单个线程内存独占!!!
2,从主内存中读取(read)数据
3,加载(load)到线程A的工作内存中
4,执行引擎使用(User)工作内存的数据
5,将执行后的数据(assign)赋值到工作内存
6,将工作内存中的数据传输(store)到主内存
7,将接收到的工作内存数据回写(write)到主内存
8,将主内存的锁释放
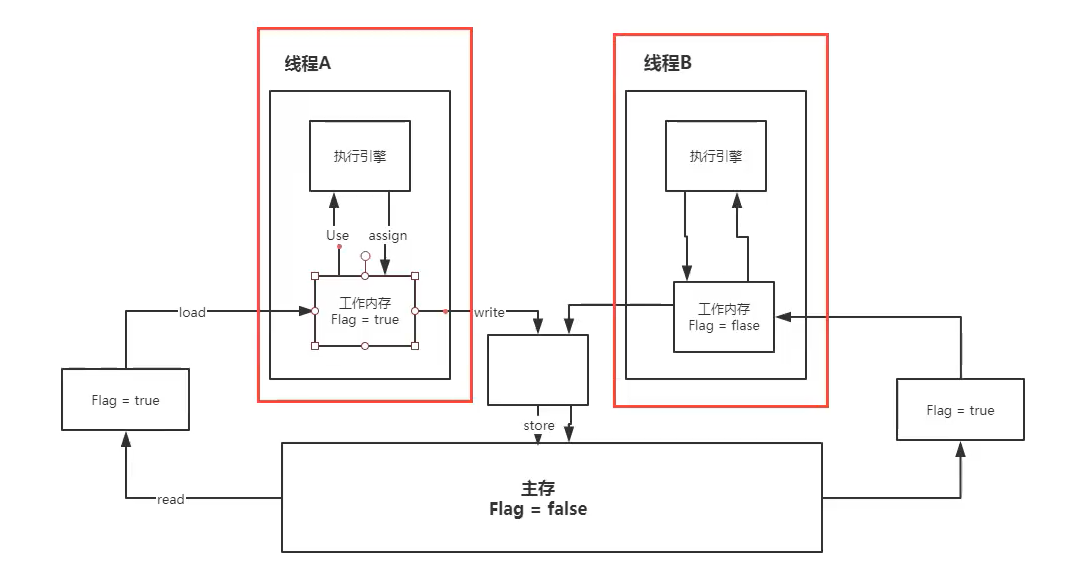
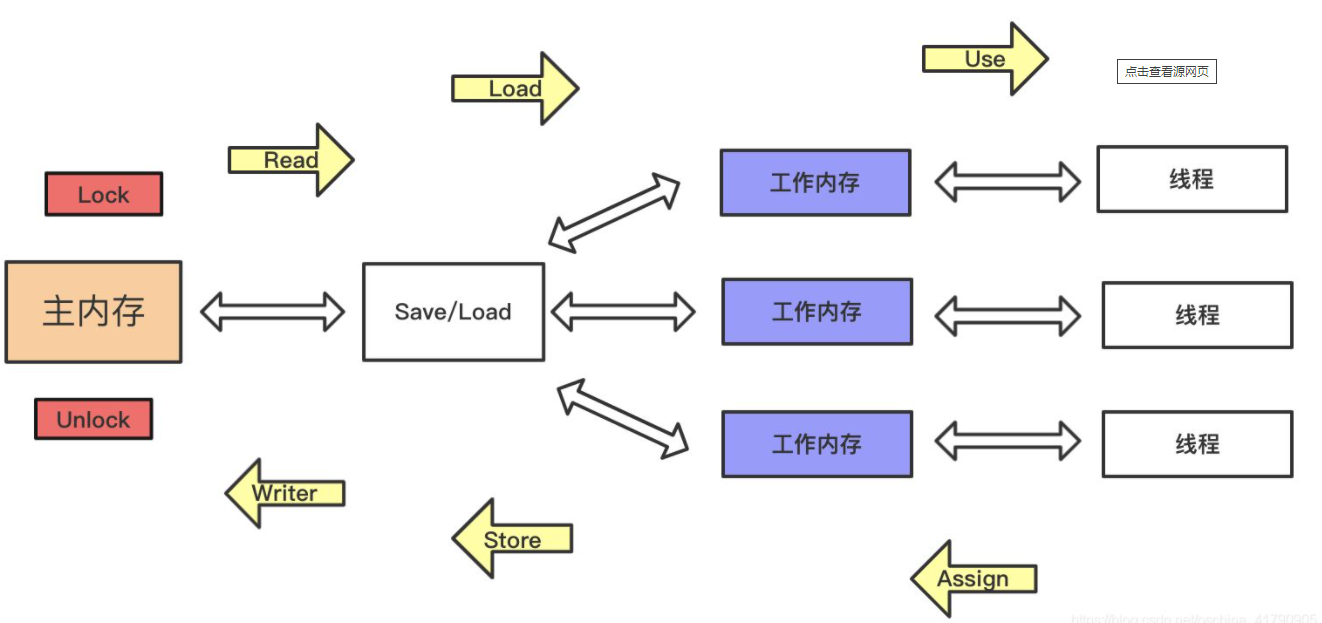
备注:
lock(锁定):作用于主内存的变量,把一个变量标识为一条线程独占状态。
unlock(解锁):作用于主内存变量,把一个处于锁定状态的变量释放出来,释放后的变量才可以被其他线程锁定。
read(读取):作用于主内存变量,把一个变量值从主内存传输到线程的工作内存中,以便随后的load动作使用
load(载入):作用于工作内存的变量,它把read操作从主内存中得到的变量值放入工作内存的变量副本中。
use(使用):作用于工作内存的变量,把工作内存中的一个变量值传递给执行引擎,每当虚拟机遇到一个需要使用变量的值的字节码指令时将会执行这个操作。
assign(赋值):作用于工作内存的变量,它把一个从执行引擎接收到的值赋值给工作内存的变量,每当虚拟机遇到一个给变量赋值的字节码指令时执行这个操作。
store(存储):作用于工作内存的变量,把工作内存中的一个变量的值传送到主内存中,以便随后的write的操作。
write(写入):作用于主内存的变量,它把store操作从工作内存中一个变量的值传送到主内存的变量中。
17,Volatile
Volatile是Java虚拟机提供轻量级的同步机制
1,保证可见性;
// private static Integer count = 0;
private static volatile Integer count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("recursive in! ");
while (count==0){
}
System.out.println("recursive out! ");
}).start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
count ++;
System.out.println("counting! ");
System.out.println("main thread =>" + count);
}
2,不保证原子性;
原子性:不可分割(最小粒度、例如普朗克常量)
线程A执行的时候,不被打扰,要么执行成功,要么执行失败(lock、synchronized保证原子性)
private static volatile Integer sum = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
add();
}).start();
}
// TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
while (Thread.activeCount()>2){
// 1条GC线程,1条主线程
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println("sum=>"+sum);
}
public static void add(){
sum ++;
}
//输出sum=>1981
如果不加lock和synchronized如何保证原子性?使用原子类解决
private static volatile AtomicInteger sum = new AtomicInteger(0);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 2000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
add();
}).start();
}
// TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
while (Thread.activeCount()>2){
// 1条GC线程,1条主线程
Thread.yield();
}
System.out.println("sum=>"+sum);
}
public static void add(){
sum.getAndIncrement();
}
和操作系统挂钩,在内存中修改值!Unsafe很特殊native方法!
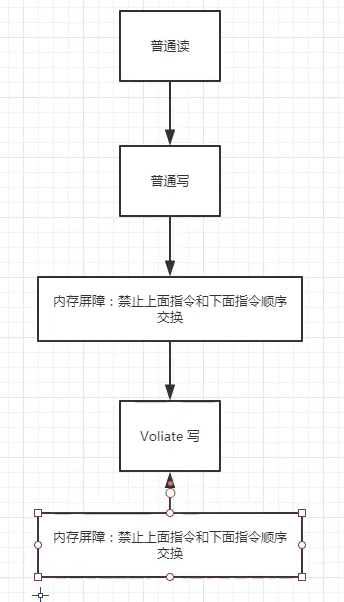
3,禁止指令重排
程序源码被编译器优化后的重排执行顺序!!!
可能进行重排的地方:1,编译器优化重排;2,指令并行重排;3,内存系统也会重排
进行指令重排的前提是要考虑数据之间的依赖性关系
内存屏障,CPU指令集:1,保证特定的操作执行顺序;2,保证某些变量的内存可见性()
18,单例模式
饿汉式、DCL懒汉式、Cglib类加器
饿汉式
public class Hungry {
private Hungry() {
}
/**
* 系统启动后,就直接初始化对象(static)
* 缺点:这个单例有可能系统并没有使用!浪费内存
*/
private final Hungry hungry = new Hungry();
public Hungry getInstance() {
return hungry;
}
}
普通懒汉式
public class LazyMan {
private LazyMan() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private static LazyMan lazyMan;
/**
* 单线程下,没有问题,但是高并发时GG
* @return
*/
public static LazyMan getInstance(){
if(lazyMan==null){
lazyMan = new LazyMan();
}
return lazyMan;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
LazyMan.getInstance();
},String.valueOf(i)).start();
}
}
}
DCL懒汉式(double lock)
public class LazyMan {
private static boolean reflectFlag = false;
// 3重检测!
private LazyMan() {
synchronized (LazyMan.class){
if(reflectFlag == false){
reflectFlag = true;
}else {
throw new RuntimeException("反射破坏单例被我禁止!");
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "ok");
}
private static volatile LazyMan lazyMan;
/**
* 单线程下,没有问题,但是高并发时GG
* DCL懒汉模式可以在高并发时没有并发问题,但是原子性无法保证
* @return
*/
public static LazyMan getInstance(){
if(lazyMan==null){
synchronized (LazyMan.class){
if(lazyMan==null){
lazyMan = new LazyMan();// 不是原子性操作
/**
* 1,分配内存空间A
* 2,执行构造方法,初始化对象
* 3,把这个对象指向这个内存空间A
*/
}
}
}
return lazyMan;
}
/* 还是可以被破坏掉 */
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Constructor<LazyMan> constructor = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
Field reflectFlag = LazyMan.class.getDeclaredField("reflectFlag");
reflectFlag.setAccessible(true);
LazyMan lazyMan1 = constructor.newInstance(null);
reflectFlag.set(lazyMan1,false);
LazyMan lazyMan2 = constructor.newInstance(null);
reflectFlag.set(lazyMan2,false);
System.out.println(lazyMan1);
System.out.println(lazyMan2);
}
备注:java并发DCL问题(待)
查看constructor.newInstance,只有枚举不能使用反射破坏单例
@CallerSensitive
public T newInstance(Object ... initargs)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException
{
if (!override) {
if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
checkAccess(caller, clazz, null, modifiers);
}
}
if ((clazz.getModifiers() & Modifier.ENUM) != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot reflectively create enum objects");
ConstructorAccessor ca = constructorAccessor; // read volatile
if (ca == null) {
ca = acquireConstructorAccessor();
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T inst = (T) ca.newInstance(initargs);
return inst;
}
测试样例:
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EnumSingle instance0 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
// Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle.<init>()
EnumSingle instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(null);
System.out.println(instance0);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}
直接使用javap命令
// javap -p .\EnumSingle.class
Compiled from "EnumSingle.java"
public final class concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle extends java.lang.Enum<concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle> {
public static final concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle INSTANCE;
private static final concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle[] $VALUES;
public static concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle[] values();
public static concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle valueOf(java.lang.String);
private concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle();
public concurrent.thirteenThree.EnumSingle getInstance();
public static void main(java.lang.String[]) throws java.lang.Exception;
static {};
}
使用jad.exe反编译工具查看代码
package concurrent.thirteenThree;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public final class EnumSingle extends Enum
{
public static EnumSingle[] values()
{
return (EnumSingle[])$VALUES.clone();
}
public static EnumSingle valueOf(String name)
{
return (EnumSingle)Enum.valueOf(concurrent/thirteenThree/EnumSingle, name);
}
private EnumSingle(String s, int i)
{
super(s, i);
}
public EnumSingle getInstance()
{
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String args[])
throws Exception
{
EnumSingle instance0 = INSTANCE;
Constructor declaredConstructor = concurrent/thirteenThree/EnumSingle.getDeclaredConstructor(null);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
EnumSingle instance1 = (EnumSingle)declaredConstructor.newInstance(null);
System.out.println(instance0);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
public static final EnumSingle INSTANCE;
private static final EnumSingle $VALUES[];
static
{
INSTANCE = new EnumSingle("INSTANCE", 0);
$VALUES = (new EnumSingle[] {
INSTANCE
});
}
}
// 确实使用的private EnumSingle(String s, int i) 有参构造器
public enum EnumSingle {
INSTANCE;
public EnumSingle getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
EnumSingle instance0 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE;
Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class);
declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true);
//Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Cannot reflectively create enum objects
EnumSingle instance1 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(null);
System.out.println(instance0);
System.out.println(instance1);
}
}
19,CAS
什么是CAS
public class CasTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2021);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
// 期望=>更新 CAS是CPU的并发原语
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021,2022);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
// 与期望值不符合=>不更新
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021,2022);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
}
}
atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();
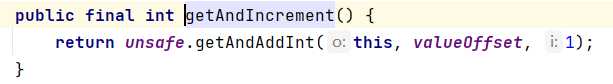
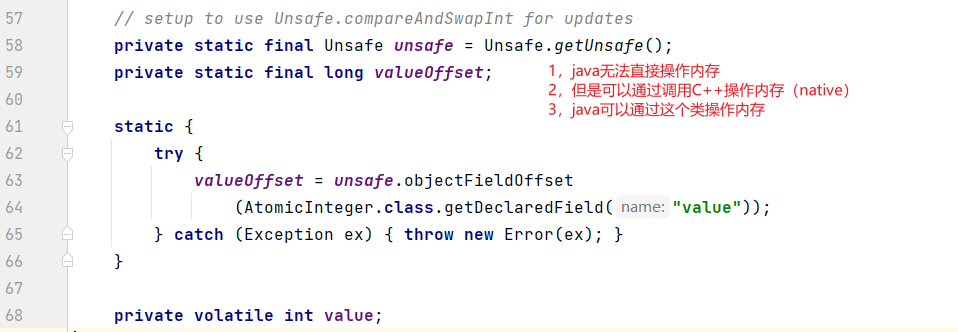
native compareAndSwapInt 内存操作效率很高(同时也是一个自旋锁)
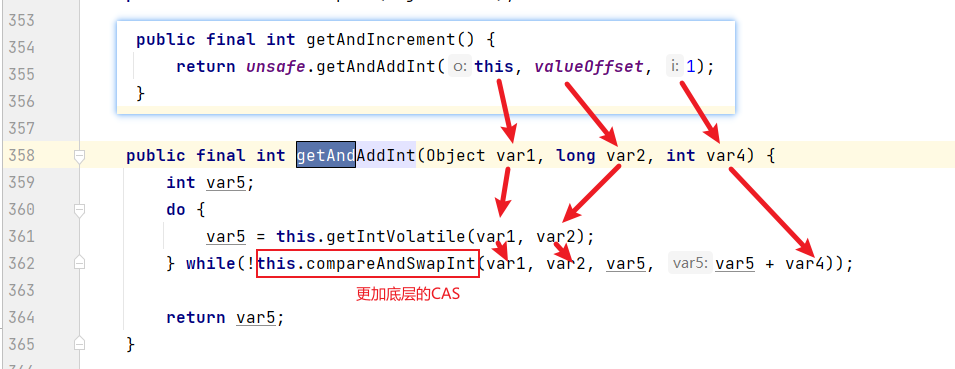
CAS:比较当前工作内存中的值与主内存中的值,如果这个值是期望的,那么就执行操作,如果不是就一直循环
缺点:
1,循环耗时;2,一次性只能保证一个共享变量的原子性;3,ABA问题
CAS:ABA问题(狸猫换太子)
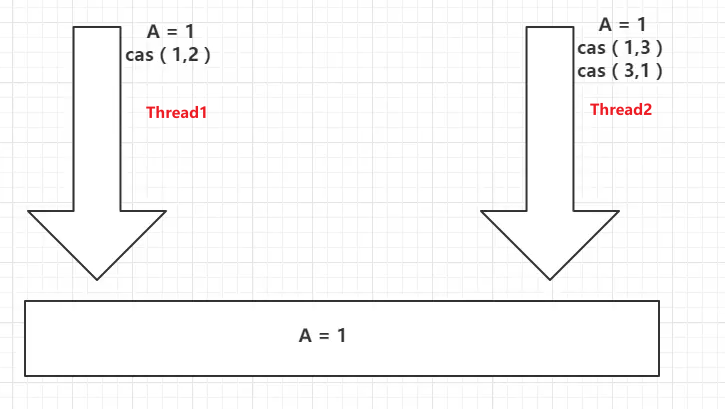
线程1,2分别操作主内存中的数据A,线程2操作2次将数据由1变为3,再立马变为1;但是线程1没有感知到主内存的数据变化!!!
样例:
public class CasTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(2021);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+atomicInteger.get());
// 期望=>更新 CAS是CPU的并发原语
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021,2022);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+atomicInteger.get());
new Thread(()->{
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2022, 2021);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+atomicInteger.get());
}).start();
// 与期望值不符合=>不更新
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
atomicInteger.compareAndSet(2021,2022);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+atomicInteger.get());
}
}
/*
输出:
main=>2021
main=>2022
Thread-0=>2021
main=>2022
*/
20,原子引用
带版本号的原子操作!使用乐观锁解决
Integer使用对象缓存机制,默认范围时-128~127,推荐使用静态工厂方法valueOf获取对象实例,而不是new,因为valueOf使用缓存,而new一定是创建新对象分配新的内存空间!

public class CasTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// AtomicStampedReference 如果泛型是一个包装类,注意对象的引用问题【阿里巴巴编码规范中也有该描述】
AtomicStampedReference atomicStampedReference = new AtomicStampedReference(100,1);
new Thread(()->{
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=stamp>"+stamp+";value=>"+atomicStampedReference.get(new int[]{stamp}));
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(
100,
101,
atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),
atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=stamp>"+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+";value=>"+atomicStampedReference.get(new int[]{stamp}));
},"a").start();
new Thread(()->{
int stamp = atomicStampedReference.getStamp();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=stamp>"+stamp+";value=>"+atomicStampedReference.get(new int[]{stamp}));
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+atomicStampedReference.compareAndSet(
101,
102,
atomicStampedReference.getStamp(),
atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+1));
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+
"=stamp>"+atomicStampedReference.getStamp()+
";value=>"+atomicStampedReference.get(new int[]{stamp}));
},"b").start();
}
}
/*
输出:
a=stamp>1;value=>100
b=stamp>1;value=>100
a=>true
a=stamp>2;value=>101
b=>true
b=stamp>3;value=>102
*/
21,各种锁的理解
21.1,公平锁、非公平锁
公平锁:不可插队
非公平锁:可插队,(默认使用的都是非公平锁)
public ReentrantLock() {// 默认
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {// 多态,公平锁
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
21.2,可重入锁
也叫递归锁,拿到锁A后也自动获取到锁B、锁C
注意:锁必须配对(加锁、解锁需要配对)否则会出现死锁!
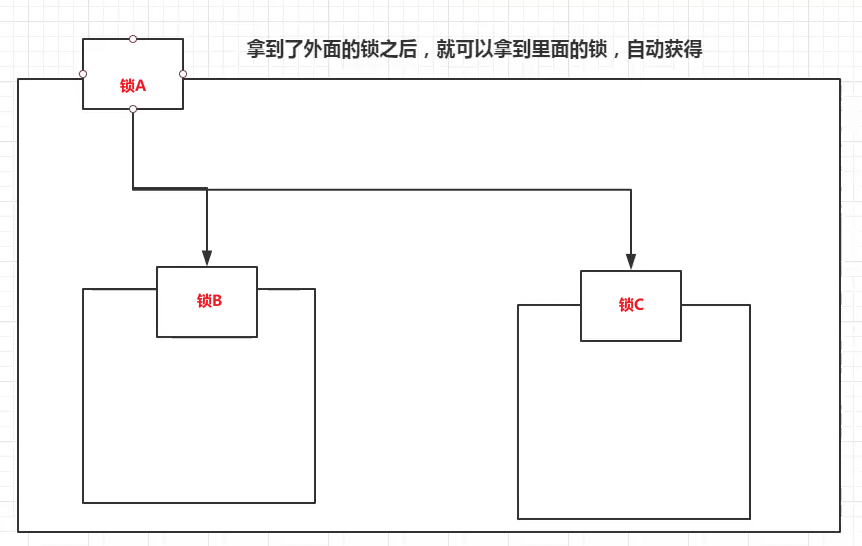
synchronized版本可重入锁样例:
public class ReentrantLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone phone = new Phone();
new Thread(phone::sms,"A").start();
new Thread(phone::sms,"B").start();
}
}
class Phone{
public synchronized void sms(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+"发短信");
call();
}
public synchronized void call(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+"打电话");
}
}
/*
A=>发短信
A=>打电话
B=>发短信
B=>打电话
*/
ReentrantLock版本可重入锁样例:
public class ReentrantLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone2 phone = new Phone2();
new Thread(phone::sms,"A").start();
new Thread(phone::sms,"B").start();
}
}
class Phone2{
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void sms(){
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+"发短信");
call();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void call(){
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+"打电话");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
/*
A=>发短信
A=>打电话
B=>发短信
B=>打电话
*/
21.3,自旋锁
经典的自旋锁atomicInteger.getAndIncrement()

本质就是获取不到锁,就自旋等待直到获取到锁为止!!!
使用CAS自定义自旋锁
public class SpinLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpinLock spinLock = new SpinLock();
new Thread(()->{
spinLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>业务逻辑块开始执行");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
spinLock.unlock();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
spinLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>业务逻辑块开始执行");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
spinLock.unlock();
}
},"B").start();
}
}
class SpinLock{
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference();
public void lock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
long timeStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+"=>lock自旋开始,尝试获取锁!");
while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)) {
}
long timeEnd = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+"=>lock=>自旋结束,获取到锁! 耗时=>"+ (timeEnd-timeStart));
}
public void unlock(){
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread.getName()+"=>unlock完成!");
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread,null);
}
}
/*
A=>lock自旋开始,尝试获取锁!
A=>lock=>自旋结束,获取到锁! 耗时=>0
A=>业务逻辑块开始执行
B=>lock自旋开始,尝试获取锁!
A=>unlock完成!
B=>lock=>自旋结束,获取到锁! 耗时=>5005
B=>业务逻辑块开始执行
B=>unlock完成!
*/
21.4,死锁
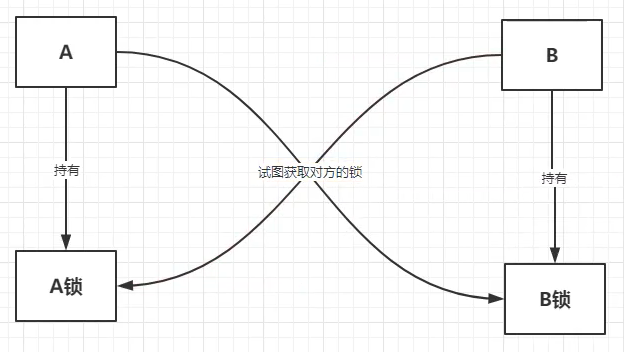
A已经获取到自己的锁,并尝试获取B的锁!但同时,B也已经获取到自己的锁并尝试获取A的锁!(循环等待)
死锁样例:
public class DeadLockTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String lockA = "A";
String lockB = "B";
new Thread(new DemoThread(lockA,lockB)).start();
new Thread(new DemoThread(lockB,lockA)).start();
}
}
class DemoThread implements Runnable{
private String lockA;
private String lockB;
public DemoThread(String lockA, String lockB) {
this.lockA = lockA;
this.lockB = lockB;
}
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized(lockA){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock:"+lockA+"=>get:"+lockB);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lockB){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "lock:"+lockB+"=>get:"+lockA);
}
}
}
}
排查死锁!
jdk bin目录下
1,使用jps -l 查看进程号信息
2,使用jstack查看堆栈信息找到死锁问题
PS E:\2_项目\activeclub\SpringBootHelloWorld\target\test-classes\concurrent\thirteenThree> jstack 50232
2022-01-08
Full thread dump Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (25.251-b08 mixed mode):
"DestroyJavaVM" #16 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002b82800 nid=0x9348 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Thread-1" #15 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000001f4ae800 nid=0xc640 waiting for monitor entry [0x000000002016f000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at concurrent.thirteenEight.DemoThread.run(DeadLockTest.java:39)
- waiting to lock <0x000000076ba8d098> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0x000000076ba8d0c8> (a java.lang.String)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"Thread-0" #14 prio=5 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000001f4ae000 nid=0x7980 waiting for monitor entry [0x000000002006f000]
java.lang.Thread.State: BLOCKED (on object monitor)
at concurrent.thirteenEight.DemoThread.run(DeadLockTest.java:39)
- waiting to lock <0x000000076ba8d0c8> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0x000000076ba8d098> (a java.lang.String)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"Service Thread" #13 daemon prio=9 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000001f291000 nid=0xc7a8 runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C1 CompilerThread3" #12 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001f210800 nid=0xb19c waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread2" #11 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001f20e000 nid=0xbc1c waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread1" #10 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001f20d000 nid=0xc478 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"C2 CompilerThread0" #9 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001f20c800 nid=0xc474 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"JDWP Command Reader" #8 daemon prio=10 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000001e6b1000 nid=0xac44 runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"JDWP Event Helper Thread" #7 daemon prio=10 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000001e6af800 nid=0x3840 runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"JDWP Transport Listener: dt_socket" #6 daemon prio=10 os_prio=0 tid=0x000000001e6a4000 nid=0xc628 runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Attach Listener" #5 daemon prio=5 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001e643800 nid=0x30a0 waiting on condition [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Signal Dispatcher" #4 daemon prio=9 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001e69b000 nid=0xaa14 runnable [0x0000000000000000]
java.lang.Thread.State: RUNNABLE
"Finalizer" #3 daemon prio=8 os_prio=1 tid=0x000000001c824000 nid=0xba5c in Object.wait() [0x000000001ebff000]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0x000000076b588ee0> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:144)
- locked <0x000000076b588ee0> (a java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue.remove(ReferenceQueue.java:165)
at java.lang.ref.Finalizer$FinalizerThread.run(Finalizer.java:216)
"Reference Handler" #2 daemon prio=10 os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001e620800 nid=0x9e24 in Object.wait() [0x000000001eaff000]
java.lang.Thread.State: WAITING (on object monitor)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Native Method)
- waiting on <0x000000076b586c00> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
at java.lang.Object.wait(Object.java:502)
at java.lang.ref.Reference.tryHandlePending(Reference.java:191)
- locked <0x000000076b586c00> (a java.lang.ref.Reference$Lock)
at java.lang.ref.Reference$ReferenceHandler.run(Reference.java:153)
"VM Thread" os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001c816800 nid=0x1a58 runnable
"GC task thread#0 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002b9f000 nid=0xc3e8 runnable
"GC task thread#1 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002ba0800 nid=0xbac0 runnable
"GC task thread#2 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002ba2000 nid=0xaac0 runnable
"GC task thread#3 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002ba3800 nid=0xa6b8 runnable
"GC task thread#4 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002ba7000 nid=0xb688 runnable
"GC task thread#5 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002ba8000 nid=0xbd2c runnable
"GC task thread#6 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bab800 nid=0xbff4 runnable
"GC task thread#7 (ParallelGC)" os_prio=0 tid=0x0000000002bac800 nid=0x8d10 runnable
"VM Periodic Task Thread" os_prio=2 tid=0x000000001f32d000 nid=0xc584 waiting on condition
JNI global references: 1523
Found one Java-level deadlock:
=============================
"Thread-1":
waiting to lock monitor 0x000000001c823af8 (object 0x000000076ba8d098, a java.lang.String),
which is held by "Thread-0"
"Thread-0":
waiting to lock monitor 0x000000001c81fa58 (object 0x000000076ba8d0c8, a java.lang.String),
which is held by "Thread-1"
Java stack information for the threads listed above:
===================================================
"Thread-1":
at concurrent.thirteenEight.DemoThread.run(DeadLockTest.java:39)
- waiting to lock <0x000000076ba8d098> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0x000000076ba8d0c8> (a java.lang.String)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
"Thread-0":
at concurrent.thirteenEight.DemoThread.run(DeadLockTest.java:39)
- waiting to lock <0x000000076ba8d0c8> (a java.lang.String)
- locked <0x000000076ba8d098> (a java.lang.String)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
Found 1 deadlock.
工作中排查问题:1,日志;2,堆栈信息jstack



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端