数据结构-最大堆、最小堆【手动实现】
0,堆的简介
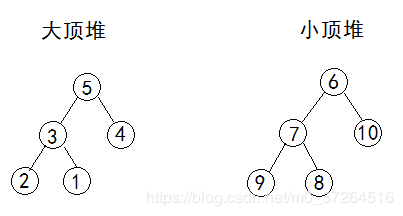
数据结构中的堆是一种特殊的二叉树,不同于 Java 内存模型中的堆。
堆必须符合以下两个条件:
- 是一棵完全二叉树。
- 任意一个节点的值都大于(或小于)左右子节点的值。
从第一点可以知道,堆适合用数组来存储。
第二点中,若父节点都大于等于左右子节点,则被称为大顶堆,反之则为小顶堆。

图-最大堆及其存储方式
0.1节点的父、子节点关系
一个节点【根节点除外】的父节点地址为其地址的二分之一,它的左子节点地址为其地址值的2倍,右子节点地址为其地址2倍加1。
例如:现在有个节点的地址为3,其数值为5;那么它的父节点地址为3/2=1,父节点的数值为13;左子节点地址为3*2=6,左子节点数值为6;右子节点地址为3*2+1=7,这个最大堆中没有其右节点数据。
0.2节点的存储、删除操作
添加新元素的时候,一般先存放到数组的尾部,之后在通过向上重排序的操作,来进行堆化【满足堆数据结构的调整】
删除元素时【一般默认删除第一个根节点】,现将数组的最后一个元素放到根节点的位置,之后通过向下重排序的操作,来进行堆化处理。
1,堆的实现
主要实现功能:①添加元素-add();②输出极值并清除-poll();③输出极值不清除-peek();
上面的功能都是是显示的函数,隐形函数有:①扩容dilatate();②向上重排序reSortUp();③向下重排序reSortDown();
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.Solution1; public class Heap { private static final int CAPACITY=16; private static final boolean TYPE=true; private static int[] nums; private int capacity=16; int size=0; private boolean type=true;//true由小到大,false由大到小 public Heap(){ this(CAPACITY); } public Heap(int capacity){ this(capacity,TYPE); } public Heap(boolean type){ this(CAPACITY,type); } public Heap(int capacity,boolean type){ this.capacity=capacity; this.type=type; nums=new int[capacity]; } //数据添加 public void add(int num){ if(size+1>=capacity){ dilatate(); } nums[size+1]=num; reSortUp(size+1); size++; } private void reSortUp(int index){ if(type){//由小到大 while (index!=1){ if(nums[index/2]>nums[index]){ int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[index/2]; nums[index/2]=temp; index/=2; }else if(nums[index/2]==nums[index]){ // throw new IllegalArgumentException("数据结构-堆不接受重复数据输入"); break; }else { return; } } }else {//由大到小 while (index!=1){ if(nums[index/2]<nums[index]){ int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[index/2]; nums[index/2]=temp; index/=2; }else if(nums[index/2]==nums[index]){ // throw new IllegalArgumentException("数据结构-堆不接受重复数据输入"); break; }else { return; } } } } //数据输出,并且清楚该数据 public int poll() throws Exception { if(size>0){ int temp=nums[1]; nums[1]=nums[size]; reSortDown(); size--; return temp; }else { throw new Exception("数据为空"); } } private void reSortDown(){ int index=1; int L,R; if(type){//由小到大 while (index<size){ L=index*2; R=L+1; if(R<=size){ boolean flag=nums[L]<nums[R]; int min=(flag?nums[L]:nums[R]); if(nums[index]>min){ if(flag){ int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[L]; nums[L]=temp; index=L; }else { int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[R]; nums[R]=temp; index=R; } }else { return; } }else if(L<=size){ if(nums[index]>nums[L]){ int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[L]; nums[L]=temp; } return; }else { return; } } }else {//由大到小 while (index<size){ L=index*2; R=L+1; if(R<size){ boolean flag=nums[L]<nums[R]; int max=(flag?nums[R]:nums[L]); if(nums[index]<max){ if(flag){ int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[R]; nums[R]=temp; index=R; }else { int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[L]; nums[L]=temp; index=L; } }else { return; } }else if(L<size){ if(nums[index]<nums[L]){ int temp=nums[index]; nums[index]=nums[L]; nums[L]=temp; } return; }else { return; } } } } //数据输出,不清除该数据 public int peek() throws Exception { if(size>0){ return nums[0]; }else { throw new Exception("数据为空"); } } //数据扩容,二倍扩容 private void dilatate(){ capacity=capacity<<1; int[] pre=new int[capacity]; for(int i=1;i<=size;i++){ pre[i]=nums[i]; } nums=pre; } } class Client{ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Heap heap=new Heap(4,true); // Heap heap=new Heap(4,false); heap.add(5); heap.add(3); heap.add(3); heap.add(7); heap.add(1); heap.add(0); heap.add(8); heap.add(8); int len=heap.size; for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ System.out.print(heap.poll()+","); } } } /* 0,1,3,5,7,8, 8,7,5,3,1,0, */
2,堆的应用
3.1 堆排序
利用堆这种数据结构,来进行数组排序,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
3.2 Java容器中的优先队列
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue=new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
3.3 求动态集合中位数
有若干个数据,求其中位数,并且数据还在不断的输入【两个堆数据即可很好的解决问题,一个最大堆,一个最小堆】
3.4 60百分位的数
这个问题是上面的问题的扩展,本质上也是使用两个对数据结构即可。但是需要控制两个堆中元素个数的比例!

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号