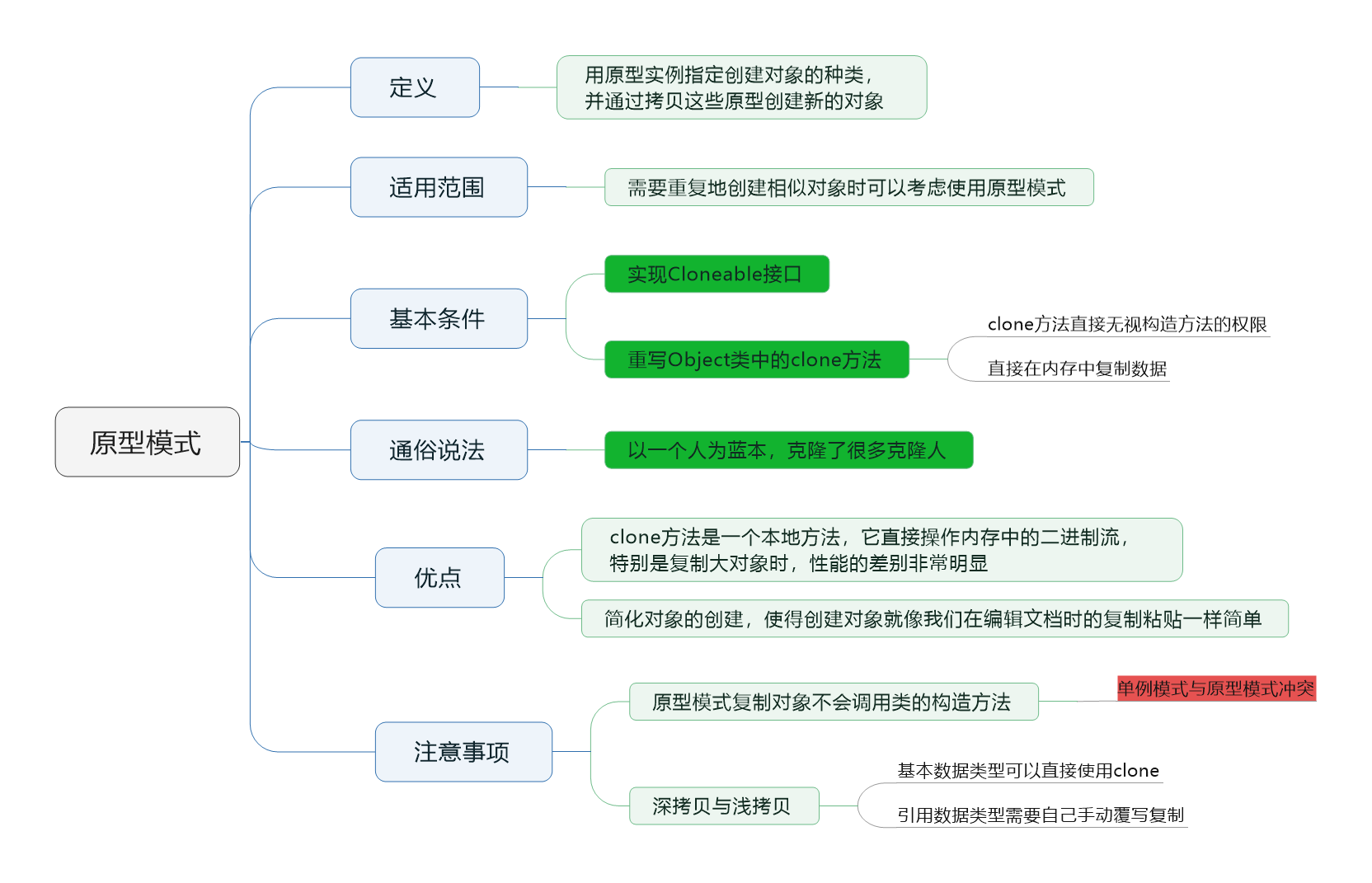
原型模式(思维导图)
图1 原型模式【点击查看大图】
1,原型对象
public class Prototype implements Cloneable{ public Prototype clone(){ Prototype prototype=null; try{ prototype=(Prototype)super.clone(); }catch (CloneNotSupportedException e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return prototype; } } class ConcretePrototype extends Prototype { private int num= (int) (Math.random()*100); public void show() { System.out.println("原型模式实现类-"+num); } }
2,测试验证
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { ConcretePrototype cp=new ConcretePrototype(); for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ ConcretePrototype clonecp=(ConcretePrototype) cp.clone(); clonecp.show(); } } }
3,关于原型模式与单例模式冲突的原因
首先:单例模式是只能产生一个实例化对象,构造方法私有化,不能通过普通的方法进行实例化。
如果想要获取新的实例化对象,要怎么办呢?
①直接跳过无视私有化构造:反射机制
②我压根不新建立一个实例化对象,跳过私有化构造,我直接进行开辟新空间的数据深拷贝:原型模式【必须实现Cloneable方法】
以上两种方法都可以无视单例模式,获取多个实例化对象。
探究未知是最大乐趣