shiro密码的比对,密码的MD5加密,MD5盐值加密,多个Relme
有具体问题的可以参考之前的关于shiro的博文,关于shiro的博文均是一次工程的内容
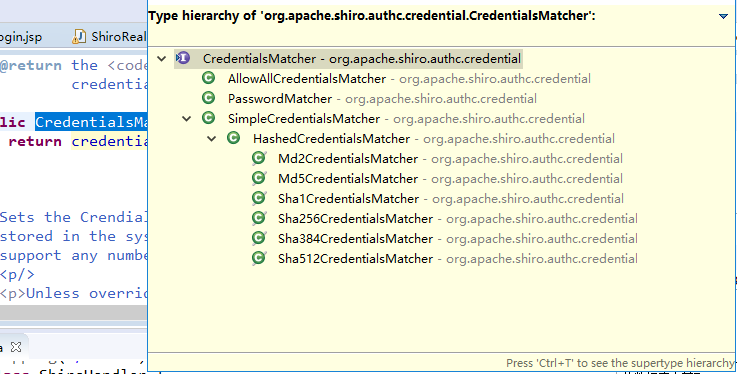
密码的比对
通过AuthenticatingRealm的CredentialsMatcher方法
密码的加密,主要是在CredentialsMatcher的....
密码的MD5加密
数据表中保存的密码,不应该是明文的,而且不能反推得到密码
1.如何把一个字符串加密成MD5
使用其提供的接口实现
2.替换当前的Realm的CredentialsMatcher属性,直接使用HashedCredentialsMatcher对象,
并且设置加密算法
applicatonContext.xml文件中
<!--
3.配置Realm
3.1直接实现Realm接口的bean
-->
<bean id="jdbcRealm" class="com.MrChengs.shiro.realms.ShiroRealm">
<property name="credentialsMatcher">
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher">
<!-- 加密的方法 -->
<property name="hashAlgorithmName" value="MD5"></property>
<!-- 指定加密的次数 -->
<property name="hashIterations" value="20"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
看源码:
public SimpleHash(String algorithmName, Object source, Object salt, int hashIterations) throws CodecException, UnknownAlgorithmException { if (!StringUtils.hasText(algorithmName)) { throw new NullPointerException("algorithmName argument cannot be null or empty."); } this.algorithmName = algorithmName; this.iterations = Math.max(DEFAULT_ITERATIONS, hashIterations); ByteSource saltBytes = null; if (salt != null) { saltBytes = convertSaltToBytes(salt); this.salt = saltBytes; } ByteSource sourceBytes = convertSourceToBytes(source); hash(sourceBytes, saltBytes, hashIterations); }
测试加密:
public static void main(String[] args) { String hash="MD5"; Object cred = "123456"; Object salt = null; int hashInter = 1024; //加密的类 System.out.println(new SimpleHash(hash, cred, salt, hashInter)); }
fc1709d0a95a6be30bc5926fdb7f22f4
MD5盐值加密
假设两个人原始密码一致,这样也会更加安全
所以此时需要使用到盐值
步骤:
在doGetAuthenticationInfo的方法返回值创建SimpleAuthenticationInfo对象的时候
使用SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, credentialsSalt, realmName);
//盐值 ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username);
使用ByteSource.Util.bytes()来计算盐值
盐值需要唯一一般使用随机字符串或userid
使用 new SimpleHash(algorithmName, source, salt, hashIterations)计算盐值解密后的盐值
此时放置的不在是明文的密码
ShiroRealm.java
//6.根据用户的情况来构建AuthenticationInfo并且返回 //以下信息是从数据库中获取的 //principal:认证的实体信息,可以是username,也可以是数据表对应的实体对象 Object principal = username; //credentials:密码 Object credentials = null; if("user".equals(username)){ //计算后user密码为123456的盐值 credentials = "2044dc18864ca3bc408359a0fb13c2a7"; }else if("admin".equals(username)){ //计算和admin密码为123456的盐值 credentials = "30beaf2a87d54ebe889cfccc076247ad"; } //realmName:当前realm对象为name,调用父类的getName()方法即可 String realmName = getName(); //盐值 ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username); SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = null;//new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, realmName); info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, credentialsSalt, realmName); return info; }
盐值的计算:
public static void main(String[] args) { String hash="MD5"; Object cred = "123456"; Object salt = "admin"; int hashInter = 20; //加密的类 System.out.println(new SimpleHash(hash, cred, salt, hashInter)); //new SimpleHash(algorithmName, source, salt, hashIterations) }
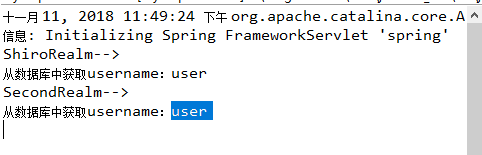
在测试中,只有用户名为user/admin 密码为123456才能成功登陆
多Realm
创建新的类
SecondRealm。java
public class SecondRealm extends AuthenticatingRealm { @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken arg0) throws AuthenticationException { System.out.println("SecondRealm-->"); //1.把AuthenticationToken转为UsernamePasswordToken UsernamePasswordToken upToken = (UsernamePasswordToken) arg0; //2.从UsernamePasswordToken获取username String username = upToken.getUsername(); //3.调用数据库的方法,从数据库查询username对应的用户记录 System.out.println("从数据库中获取username:" + username); //4.若用户不存在可以抛出异常 UnKnownAccountException异常 if("unknow".equals(username)){ throw new UnknownAccountException("username 不存在"); } //5.根据用户信息的清空决定是否需要抛出其他的异常 if("monster".equals(username)){ throw new LockedAccountException("用户被锁定"); } //6.根据用户的情况来构建AuthenticationInfo并且返回 //以下信息是从数据库中获取的 //principal:认证的实体信息,可以是username,也可以是数据表对应的实体对象 Object principal = username; //credentials:密码 Object credentials = null; if("user".equals(username)){ credentials = "6e3be0247455b9298f47eac8e57a07214ef84115"; }else if("admin".equals(username)){ credentials = "ff9633d047eaaf9861984ed86e5f73f904647716"; } //realmName:当前realm对象为name,调用父类的getName()方法即可 String realmName = getName(); //盐值 ByteSource credentialsSalt = ByteSource.Util.bytes(username); SimpleAuthenticationInfo info = null;//new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, realmName); info = new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(principal, credentials, credentialsSalt, realmName); return info; } public static void main(String[] args) { String hash="SHA1"; Object cred = "123456"; Object salt = "user"; int hashInter = 20; //加密的类 System.out.println(new SimpleHash(hash, cred, salt, hashInter)); //new SimpleHash(algorithmName, source, salt, hashIterations) } }
加密方式是SHA1
在applicationContext.xml
需要注释一个
<!--
1.配置SecurityManager
-->
<bean id="securityManager" class="org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager">
<property name="cacheManager" ref="cacheManager"/>
<!-- 此时这个属性需要注释使用下面的属性配置
<property name="realm" ref="jdbcRealm"/>
-->
<property name="authenticator" ref="autheniicator"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 认证器 -->
<bean id="autheniicator" class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator">
<property name="realms">
<list>
<ref bean="jdbcRealm"/>
<ref bean="SecondRealm"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!--
3.配置Realm
3.1直接实现Realm接口的bean
-->
<bean id="jdbcRealm" class="com.MrChengs.shiro.realms.ShiroRealm">
<property name="credentialsMatcher">
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher">
<!-- 加密的方法 -->
<property name="hashAlgorithmName" value="MD5"></property>
<!-- 指定加密的次数 -->
<property name="hashIterations" value="20"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="SecondRealm" class="com.MrChengs.shiro.realms.SecondRealm">
<property name="credentialsMatcher">
<bean class="org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.HashedCredentialsMatcher">
<!-- 加密的方法 -->
<property name="hashAlgorithmName" value="SHA1"></property>
<!-- 指定加密的次数 -->
<property name="hashIterations" value="20"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
执行的顺序和list的顺序有关
<bean id="autheniicator" class="org.apache.shiro.authc.pam.ModularRealmAuthenticator"> <property name="realms"> <list> <ref bean="jdbcRealm"/> <ref bean="SecondRealm"/> </list> </property> </bean>