5、反射-动态代理
创建动态代理
1、Proxy提供用于创建动态代理类和代理对象的静态方法,他是所有动态代理类的父类
2、Proxy提供了两个方法来创建动态代理类和动态代理实例
需求
代码执行之前
代码执行之后都需要进行代码的打印
interface ArithmeticCalcular { public int add(int a,int b); public int sub(int a , int b); }
public class ArithmeticCalcularImpl implements ArithmeticCalcular { @Override public int add(int a, int b) { System.out.println("方法执行之前add"); int res = a + b; System.out.println("add: " + res); return res; } @Override public int sub(int a, int b) { System.out.println("方法执行之前sub"); int res = a -b ; System.out.println("sub:" + res); return res; } }
这里会发现再方法中的代码很多都是重复的
public static void main(String[] args) { ArithmeticCalcular add = new ArithmeticCalcularImpl(); add.add(1,2); }
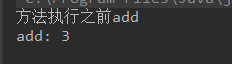
此时可以发现如果日志文件过多,很多代码会重用,而且同样的代码需要多次使用(甚至超过程序代码)
此时可以使用动态代理
代理设计的原理:
使用一个代理将对象包装起来
然后使用该代理对象取代原始对象
任何对象的调用都有通过代理对象
代理对象决定是否可以及时将方法调用转到原始对象上
public class ArithmeticCalcularImpl1 implements ArithmeticCalcular { @Override public int add(int a, int b) { int res = a + b; return res; } @Override public int sub(int a, int b) { int res = a -b ; return res; } }
/* newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h) ClassLoader:由动态代理产生的对象由那个类加载器进行加载(通常情况下和被代理对象使用一样的类加载器) interfaces:由动态代理产生的对象必须实现的接口的Class数组 InvocationHandler:当具体调用代理对象方法时,将产生什么具体行为 */ ArithmeticCalcular arithmeticCalcular = new ArithmeticCalcularImpl1(); ArithmeticCalcular proxy = (ArithmeticCalcular) Proxy.newProxyInstance(arithmeticCalcular.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{ArithmeticCalcular.class}, new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("invoke.."); return 0; } }); int add = proxy.add(2, 4); System.out.println(add);
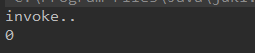
此时的返回值0就是InvocationHandler中的返回值
final ArithmeticCalcular arithmeticCalcular = new ArithmeticCalcularImpl1();
ArithmeticCalcular proxy =
(ArithmeticCalcular) Proxy.newProxyInstance(arithmeticCalcular.getClass().getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{ArithmeticCalcular.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//proxy:
//method:正在被调用的方法
//args:调用方法传入的参数
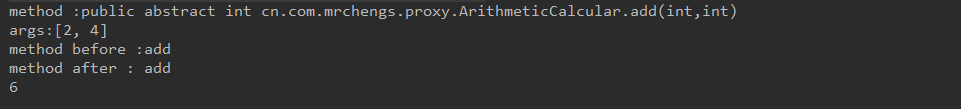
System.out.println("method :" + method);
//method :public abstract int cn.com.mrchengs.proxy.ArithmeticCalcular.add(int,int)
System.out.println("args:" + Arrays.asList(args));
//args:[2, 4]
//日志前置
System.out.println("method before :" + method.getName());
//method before :add
//调用被代理类的目标方法
Object invoke = method.invoke(arithmeticCalcular, args);
//日志后置
System.out.println("method after : " + method.getName());
//method after : add
return invoke;
}
});
int add = proxy.add(2, 4);
System.out.println(add);
再次更新一下
ArithmeticCalcularImpl1 arithmeticCalcular = new ArithmeticCalcularImpl1(); ArithmeticCalcular proxy = (ArithmeticCalcular) Proxy.newProxyInstance(arithmeticCalcular.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{arithmeticCalcular.getClass().getInterfaces().getClass()}, new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { //proxy: //method:正在被调用的方法 //args:调用方法传入的参数 System.out.println("method :" + method); //method :public abstract int cn.com.mrchengs.proxy.ArithmeticCalcular.add(int,int) System.out.println("args:" + Arrays.asList(args)); //args:[2, 4] //日志前置 System.out.println("method before :" + method.getName()); //method before :add //调用被代理类的目标方法 Object invoke = method.invoke(arithmeticCalcular, args); //日志后置 System.out.println("method after : " + method.getName()); //method after : add return invoke; } }); int add = proxy.add(2, 4); System.out.println(add);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号