2、反射-Method&父类
反射概述:
Reflection是Java被视为动态语言的关键
反射机制允许程序再执行期间借助于Reflection API取得任何类的内部信息
并直接操作任意对象内部的属性及方法
主要提供了功能:
1、再运行时任意构造一个类的对象
2、再运行时取任意一类所具有的成员变量和方法
3、再运行时调用任意一个对象的方法
4、生成动态代理
Class是对一个类的描述
1、类的属性:Field
2、类的方法:Method
3、类的构造器:Constrctor
public class Person { String name; private int age; //私有方法 private void test(){ } //共有的无参方法 public void test1(){ } //共有的带参方法 public void test2(String m){ System.out.println(m); } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("name:" + name); this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; } public Person() { } }
类的方法:Method
Method对应 类中的方法:
1、获取Method
2、获取类的方法的数组: getDeclaredMethods()
3、获取类指定的方法:getDeclaredMethod(String name,Class<?> ... parameterTypes)
获取私有的方法进行执行还需要添加一行代码:method.setAccessible(true)
4、执行方法:invoke(Object obj, Object ...arggs)
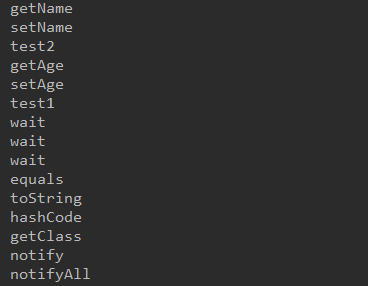
Class clazz = Class.forName("refelect.Person"); //1、得到clazz对应的类中的方法 //注意:私有的方法无法获取 Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); for (Method method : methods){ System.out.println(method.getName()); }
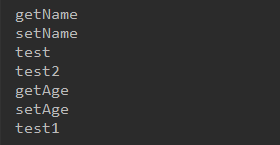
//2、获取所有的方法 //获取当前类的方法 Method[] declaredMethods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods(); for (Method method:declaredMethods){ System.out.println(method.getName()); }
//3、获取指定的方法,两个参数(1、方法名;2、参数(没有则不写)) Method setName = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class); System.out.println(setName.getName()); //获取私有的 Method test = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("test"); System.out.println(test.getName());

//4、执行方法 invoke(Object obj, Object... args) //参数1:要执行的对象 //参数2:传入的参数 Object o = clazz.newInstance(); setName.invoke(o,"MrChengs");

自定义的invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object obj,String methodName,Object ...args){ Class [] parameterTypes = new Class[args.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length ; i ++){ parameterTypes[i] = args[i].getClass(); } try { Method method = obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName,parameterTypes); return method.invoke(obj,args); }catch (Exception e){ } return null; }
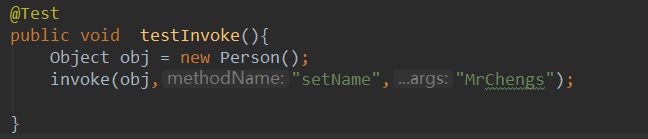
方法的重载--直接传入全类名
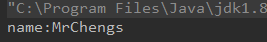
public Object invoke(String className,String methodName,Object ...args){ Object obj = null; try { obj = Class.forName(className).newInstance(); return invoke(obj, methodName, args); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return null; } public Object invoke(Object obj,String methodName,Object ...args){ Class [] parameterTypes = new Class[args.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length ; i ++){ parameterTypes[i] = args[i].getClass(); } try { Method method = obj.getClass().getDeclaredMethod(methodName,parameterTypes); return method.invoke(obj,args); }catch (Exception e){ } return null; } @Test public void testInvoke(){ Object obj = new Person(); Object invoke = invoke("refelect.Person", "setName", "MrChengs"); System.out.println(invoke); }
关于父类的问题
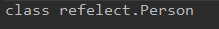
getSuperclass()
Class clazz = Class.forName("refelect.Student"); Class superclass = clazz.getSuperclass(); System.out.println(superclass);
public class Student extends Person { private void test3(String m){ System.out.println("Student test3"); System.out.println(m); } }
public class Person { private void test2(String m){ System.out.println("Person test2"); System.out.println(m); }
}
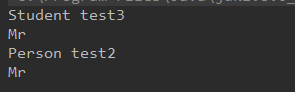
测试:
public Object invoke1(Object obj,String methodName,Object ...args){ Class [] parameterTypes = new Class[args.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length ; i ++){ parameterTypes[i] = args[i].getClass(); } try { Method method = getMethod(obj.getClass(),methodName,parameterTypes); method.setAccessible(true); return method.invoke(obj,args); }catch (Exception e){ } return null; } //获取父类中的方法 public Method getMethod(Class clazz,String methodName,Class ...para){ for (;clazz != Object.class;clazz = clazz.getSuperclass()){ try { Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod(methodName,para); return method; } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { } } return null; } @Test public void set(){ //执行自身类的方法 Object obj = new Student(); invoke1(obj,"test3","Mr"); //执行父类中的方法 invoke1(obj,"test2","Mr"); }