8、集合--LinkedList的测试以及相关方法的源码分析
LinkedList测试
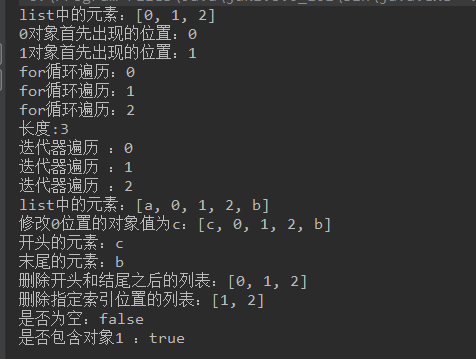
public static void main(String[] args) { List list = new LinkedList(); //添加元素 list.add(1); list.add(2); //在指定位置添加元素 list.add(0,0); System.out.println("list中的元素:" + list); //对象首次出现的位置 System.out.println("0对象首先出现的位置:"+list.indexOf(0)); //对象最后出现的位置 System.out.println("1对象首先出现的位置:"+list.lastIndexOf(1)); //for循环遍历 for (int i = 0;i < list.size();i++){ System.out.println("for循环遍历:" + list.get(i)); } //返回列表的长度 System.out.println("长度:" + list.size()); //迭代器遍历 Iterator it = list.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()){ System.out.println("迭代器遍历 :" + it.next() ); } //将对象添加在集合的开头 ((LinkedList) list).addFirst("a"); //将对象添加在集合的末尾 ((LinkedList) list).addLast("b"); System.out.println("list中的元素:" + list); //修改指定位置的对象 list.set(0,"c"); System.out.println("修改0位置的对象值为c:" + list); //获取集合中开头的元素 System.out.println("开头的元素:" + ((LinkedList) list).getFirst()); //获取集合中末尾的元素 System.out.println("末尾的元素:" + ((LinkedList) list).getLast()); //删除列表开头的元素 ((LinkedList) list).removeFirst();//删除的是a //删除列表末尾的元素 ((LinkedList) list).removeLast();//删除的是b System.out.println("删除开头和结尾之后的列表:" + list); //删除指定索引的位置 list.remove(0); System.out.println("删除指定索引位置的列表:" + list); //判断列表是否为空 System.out.println("是否为空:" + list.isEmpty()); //是否包含对象1 System.out.println("是否包含对象1 :" + list.contains(1)); //清空集合 list.clear(); }
相关底层的方法实现:
1、new对象之后List list = new LinkedList();
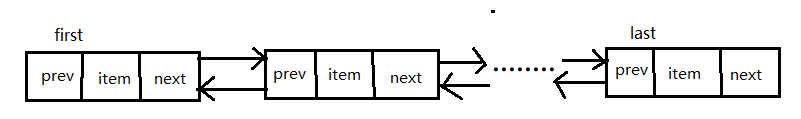
可以看作是一个双向的链表每个节点都有first节点和last节点
方法都是通过移动节点指向来实现的
//集合元素数量
transient int size = 0; //链表头节点 transient Node<E> first; //链表为节点 transient Node<E> last;
protected transient int modCount = 0;
public LinkedList() { }
private static class Node<E> {
E item;//元素值
Node<E> next;//后置节点
Node<E> prev;//前置节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
2、add(E e)方法
public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; }
调用linkLast()方法:
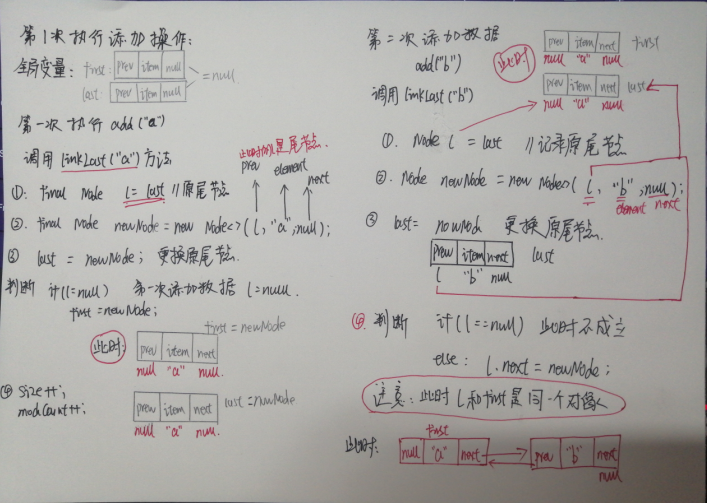
void linkLast(E e) {q final Node<E> l = last;//记录原来尾部节点 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);//以原尾部节点为新节点的前置节点 last = newNode;//更新尾部节点 if (l == null)//若原链表为空链表、需要额外更新头节点 first = newNode; else//否则更新原尾节点的后置节点为现在的尾节点 l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } }
3、indexOf(Object o):o元素首先出现的位置
首先定义一个索引值index=0;用于返回元素第一次出现的位置
判断传入的对象o是否为null
①、如果为null
使用for循环进行遍历
从起始节点first开始
然后判断Node类的item属性是否等于null
如果等于null则返回index
否则index++
②、如果传入的对象o不为null
直接进行遍历链表
使用equals()方法进行判断元素o和item属性值是否相同
如果等于则返回index
否则index ++
③、如果这个对象不存在
此时直接返回-1
此时在循环中使用x=x.next向下循环遍历
public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) {//如果目标对象是null for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else {//遍历链表 for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; }
4、lastIndexOf(Object o):判断元素最后一次出现的所以位置
此时定义index所引值大小size,从链表的最后面开始遍历,即尾节点开始遍历
判断传入的元素o是否为空:
①、如果传入的元素o为null
此时循环中定义的Node对象x=last即尾节点
首先将index--
在去判断x.item 是否等于null,然后返回index
遍历是使用x = x.prev只想前置节点
②、如果不为null
则首先让index--
然后使用equals()方法进行数据的对比
如果比对相同则返回index
③、如果这个元素o不存在则返回-1
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) { int index = size; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (x.item == null) return index; } } else { for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) { index--; if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; } } return -1; }
5、size()方法:返回链表的长度
此时直接返回size的值
public int size() { return size; }
6、get(int index)方法:获取指定索引位置的值
checkElementIndex(index)方法检测index是否越界
具体的实现在isElementIndex(int index)进行返回
public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; }
private void checkElementIndex(int index) { if (!isElementIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }
private boolean isElementIndex(int index) { return index >= 0 && index < size; }
Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
最后返回node(int index)方法
进行查找指定位置的Node类的实例
7、addFirst(E e):在链表的第一个位置添加元素o
public void addFirst(E e) { linkFirst(e); }
private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); first = newNode; if (f == null) last = newNode; else f.prev = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
首先定义一个Node的实例 f 并且只想first(即只想首链)
在新建一个Node的实现newNode,用于创建新的实例,且next指向f
再把newNode的值赋值给first(首节点)
判断此时的f是否为空(首节点是否为null)
①、如果为空:则将newNode赋值给last
②、不为空:则将原首节点的prev指向新的节点newNode
8、addLast(E e):将对象添加在集合的末尾
public void addLast(E e) { linkLast(e); }
void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; }
首相定义Node的实例 l 指向尾节点
在定义一个新的实例newNode,且prev属性指向l(即last尾节点)
此时在将newNode赋值非尾节点last
判断l是否为空:尾节点是否为空
①、如果为空:则把newNode赋值非first首节点
②、不为空:则将尾节点l的next属性指向新建的节点newNode
9、set(int index,E element):修改指定位置的元素值
①、调用checkElementIndex()方法去检验index是否合法
②、调用node(int index)方法去找指定位置上的node节点
③、将旧值保存在oldValue上,在进行将要改的值element赋值给找到的节点
④、返回旧值oldValue
public E set(int index, E element) { checkElementIndex(index); Node<E> x = node(index); E oldVal = x.item; x.item = element; return oldVal; }
private void checkElementIndex(int index) { if (!isElementIndex(index)) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); }
Node<E> node(int index) { if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } }
10、getFirst():获取集合中开头的元素
public E getFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return f.item; }
首相定义一个Node实例f指向链表的首节点first、
在进行判断首节点是否为null
最后返回首节点的item属性值
11、getLast():获取集合中末尾的元素
public E getLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return l.item; }
与getFirst()方法类似
12、removeFirst():删除列表开头的元素
public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); }
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { // assert f == first && f != null; final E element = f.item; final Node<E> next = f.next; f.item = null; f.next = null; // help GC first = next; if (next == null) last = null; else next.prev = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
首先定义一个Node实例f指向首节点first
在进行判断f是否为空
最后调用unlinkFirst()方法
定义一个值element用于保存首节点中的值(f.item)
在定义一个Node的实例next作为临时变量来保存第二个节点(first.next)
然后将first的item和next值均赋值为null
最后将first重新指向next的临时变量
判断临时变量next是否为空:
为空:将尾节点置为null
不为空:将临时节点的prev的属性值置为空
13、removeLast():删除列表末尾的元素
public E removeLast() { final Node<E> l = last; if (l == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkLast(l); }
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) { // assert l == last && l != null; final E element = l.item; final Node<E> prev = l.prev; l.item = null; l.prev = null; // help GC last = prev; if (prev == null) first = null; else prev.next = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
和removeFirst()类似
14、remove(int index):删除指定索引的位置
public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); }
E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
思想:
找到指定位置上的节点之后假设为A
A的前置节点为A1,A的后置节点为A2
此时将A1.next 指向 A2
同时将A节点置为null
15、remove(Object o):删除元素o
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; }
E unlink(Node<E> x) { // assert x != null; final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; }
思想:首先判断该元素o是否为空在进行遍历链表
unlink()方法的思想同上
16、isEmpty():集合是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; }
即判断size()是否为0
17、contaions(Object o):判断集合中是否包含元素o
public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) != -1; }
public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; }
此时的思想是:
查找元素第一次出现的位置进行返回
18、clear():清空集合
public void clear() { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; }
即从头遍历集合
同时将item、next、prev三个属性值都置为0
最后将size的值置为0
以上是对LinkedList底层一些方法实现的分析
更多的实现可以看底层源码



