9、NIO--阻塞式
使用NIO完成网络通信的三个核心:
1、通道(Channel):负责连接
java.nio.channels.Channel接口:
SelectableChannel抽象类:有一下几个实现类
SocketChannel TCP
ServerSocketChannel TCP
DategramChannel UDP
Pipe.SinkChannel
Pipe.SourceChannel
2、缓冲区(Buffer):负责数据的存取
3、选择器(Selector):式SelectableChannel的多路复用器,用于监控SelectableChannel的IO状况
代码实例:
//服务端 @Test public void server() throws IOException{ //1、获取异常 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2、绑定连接 serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8081)); //3、获取客户端连接的通道 SocketChannel sockChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); //4、分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //5、接收客户端的数据保存到本地 FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:\\aaa.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE,StandardOpenOption.READ); while(sockChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); outChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } serverSocketChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); sockChannel.close(); }
//客户端 @Test public void client(){ //1、获取通道 SocketChannel socketChannel = null; FileChannel inChannel = null; try { socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8081)); //2、分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //3、读取本地文件,并且发送 inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:\\a.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); socketChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { socketChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } try { inChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
先开启服务端在开启客户端:

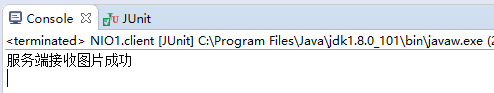
阻塞式测试:(服务端给客户端回复响应信息)
@Test public void server() throws IOException{ //1、获取异常 ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2、绑定连接 serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8081)); //3、获取客户端连接的通道 SocketChannel sockChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept(); //4、分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //5、接收客户端的数据保存到本地 FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:\\aaaa.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE,StandardOpenOption.READ); while(sockChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); outChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } //发送反馈信息 buf.put("服务端接收图片成功".getBytes()); buf.flip(); sockChannel.write(buf); serverSocketChannel.close(); outChannel.close(); sockChannel.close(); }
客户端:
//客户端 @Test public void client(){ //1、获取通道 SocketChannel socketChannel = null; FileChannel inChannel = null; try { socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8081)); //2、分配指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //3、读取本地文件,并且发送 inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:\\a.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); socketChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } //接收服务端的反馈 int len = 0; while((len = socketChannel.read(buf)) != -1){ buf.flip(); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len)); buf.clear(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally { try { socketChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } try { inChannel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
此时运行服务端和客户端
会发现处于阻塞状态
并无相关的信息进行打印


此时的解决方案:客户端告诉服务端我已经发送数据完成:
在客户端中进行添加代码:
//3、读取本地文件,并且发送 inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:\\a.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ); while(inChannel.read(buf) != -1){ buf.flip(); socketChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); } //告诉服务端数据已发送 socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
此时是可以接收到服务端的反馈信息
非阻塞式
服务端:
//服务端 @Test public void server() throws IOException{ //1、获取通道 ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); //2、切换非阻塞模式 ssChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3、绑定连接 ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8081)); //4、获取选择器 Selector selector = Selector.open(); //5、将通道注册到选择器上,指定监听事件 //SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT:接收 ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //6、轮询式的获取选择器上已经准备就绪的事件 while(selector.select() > 0){ //7、获取当前选择器中所有注册的“悬着键” Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); //8、迭代获取 while(it.hasNext()){ //9、获取准备就绪的事件 SelectionKey sk = it.next(); //10、判断是什么事件准备就绪 if(sk.isAcceptable()){ //接收就绪就获取客户端的连接 SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); //切换非阻塞模式 sChannel.configureBlocking(false); //将该通道注册到选择器上 sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); }else if(sk.isReadable()){ //判断是都是读就绪状态 SocketChannel sChannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel(); //读取数据 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); int len = 0; while((len = sChannel.read(buf)) > 0){ buf.flip(); System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len)); buf.clear(); } } } //取消选择键 SelectionKey sk = it.next(); it.remove(); } }
客户端:
//客户端 @Test public void client() throws IOException{ //1、获取通道 SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8081)); //2、切换非阻塞模式 sChannel.configureBlocking(false); //3、指定大小的缓冲区 ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //4、发送数据给服务端 buf.put(new Date().toString().getBytes()); buf.flip(); sChannel.write(buf); buf.clear(); //5、关闭通道 sChannel.close(); }
先运行服务端在运行客户端:
选择器
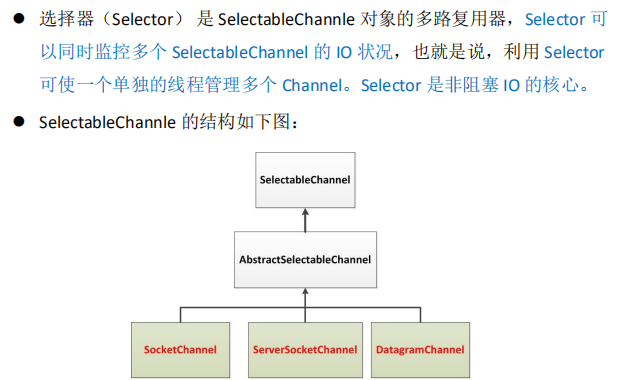
选择器的应用


SelectionKey
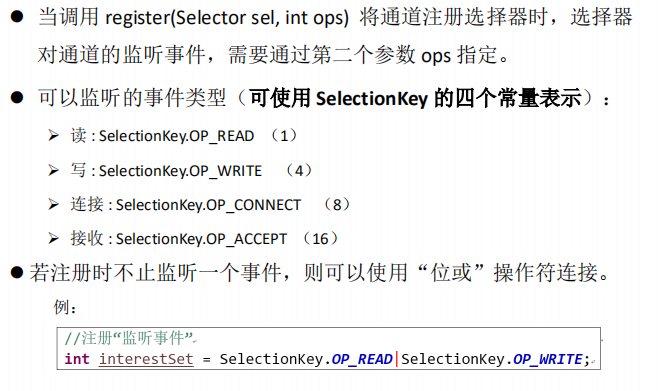

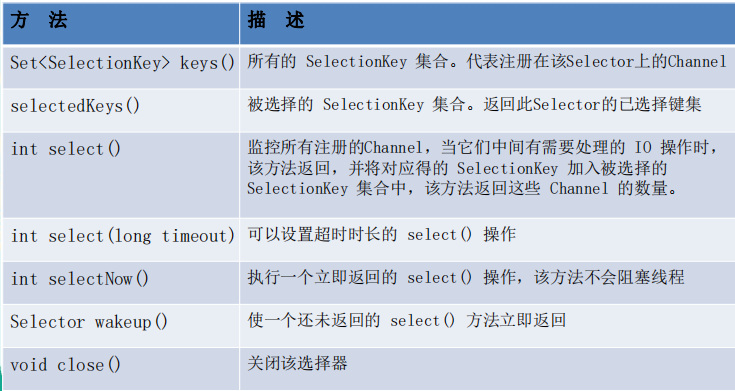
Selector的常用方法
SocketChannel






