2、Android-UI(布局待完成)
2.3、布局
实现界面的整齐摆放各种控件需要使用布局来完成
布局是一种可用于放置很多控件的容器
可以按照一定的规律调整内部的控件位置
布局的内部不仅可以放置控件还可以放置布局

1、线性布局
LinearLayout又称线性布局,是一种常常用到的布局
会将所包含的控件再线性方向上一次排列
垂直方向上排列的
之前的代码种排列都是垂直排列
是因为再android:orientation属性制指定了排列的方向上vertical
如果指定:horizontal控件就会在水平方向上进行排列
默认不指定就是水平方向horizontal
如果使用horizontal则内部的控件宽度就不能指定为match_parent单独一个控件就会占用水平方向
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/button_first" android:textAllCaps="false" android:text="to first"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/button_second" android:text="to second"/> </LinearLayout>
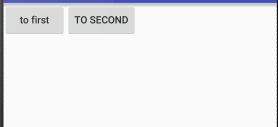
android:layout_gravity:
用于指定控件再布局中的对其方式,取值和android:gravity差不多
注意:
当LinerLayout的排列方向是horizontal是,只有垂直方向上的对齐方式才会生效,因为此水平方向上的对齐方式长度是不固定的
没添加一个控件、水平方向的长度都会改变,因而无法指定该方向上的对齐方式
即:水平---垂直生效 垂直---水平生效
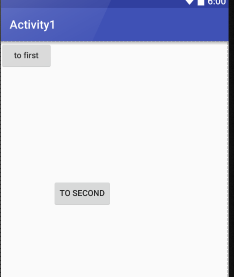
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/button_first" android:textAllCaps="false" android:text="to first" android:layout_gravity="top" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/button_second" android:layout_gravity="center" android:text="to second"/>
</LinerLayout>
结果如下图:
LinerLayout是水平方向的
我们只能指定垂直方向上的排列方向
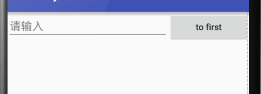
android:layout_weight:
允许开发者使用比列方式来指定控件的大小
再手机适配方面可以起到非常重要的作用
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit_test1"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:hint="请输入"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<Button
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button_first"
android:textAllCaps="false"
android:text="to first"
android:layout_gravity="top"
/>
这里的EditView和Button的宽度都设置成了0dp
再设置android:layout_weight属性,此时的控件不再由android:width指定
这里设置成0dp是一种规范化的写法
dp是Android种用于指定控件大小、间距等属性的单位
这里也会根据android:layout_weight的值来等分屏幕的宽度
原理:
LinerLayout下所有指定的layout_wight的值相加
再根据每个控件的值进行求比例
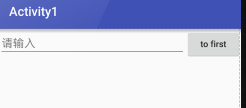
<EditText android:id="@+id/edit_test1" android:layout_weight="2" android:hint="请输入" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/button_first" android:textAllCaps="false" android:text="to first" android:layout_gravity="top" />
此时只有EditText种执行属性
Button的属性设置为刚好包裹住元素
EditText会沾满被Button使用之后的屏幕空间
2、相对布局
RelativeLayout又称为相对布局
可以通过相对定位的方式让控件出现在任何位置
新建布局文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:text="btn1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true"/> <Button android:text="btn2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true"/> <Button android:text="btn3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true"/> <Button android:text="btn4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"/> <Button android:text="btn5" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"/> </RelativeLayout>
效果:

这里使用到如下的属性进行布局设置
android:layout_alignParentLeft:和父布局的左对齐
android:layout_alignParentTop:和父布局的上对齐
android:layout_alignParentRight:和父布局的右对齐
android:layout_alignParentBottom:和父布局的下对齐
android:layout_centerInParent:和父布局的居中显示
相对于父布局来说
之前的都是相对于父布局进行定位的
还可以相对控件进行定位
将代码进行修改:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:text="btn1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/btn3" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/btn3" android:id="@+id/btn1"/> <Button android:text="btn2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_above="@+id/btn3" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btn3" android:id="@+id/btn2"/> <Button android:text="btn3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:id="@+id/btn3"/> <Button android:text="btn4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/btn3" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/btn3" android:id="@+id/btn4"/> <Button android:text="btn5" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/btn3" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btn3" android:id="@+id/btn5"/> </RelativeLayout>
效果:
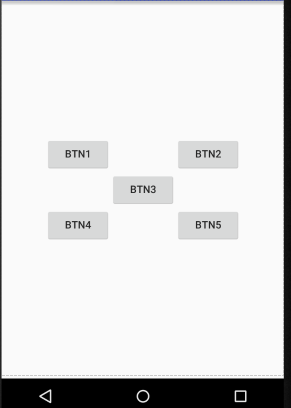
这里使用到的属性:
android:layout_above:让一个控件位于一个控件的上方
android:layout_below:让一个控件位于一个控件的下方
android:layout_toLeftOf:让一个控件位于一个控件的左侧
android:layout_toRightOf:让一个控件位于一个控件的右侧
再次使用属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:text="btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/btn3"
android:id="@+id/btn1"/>
<Button
android:text="btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/btn3"
android:id="@+id/btn2"/>
<Button
android:text="btn3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:id="@+id/btn3"/>
<Button
android:text="btn4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/btn3"
android:id="@+id/btn4"/>
<Button
android:text="btn5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/btn3"
android:id="@+id/btn5"/>
</RelativeLayout>
这里使用到如下属性:
android:layout_alignLeft:让一个控件的左边缘和零一控件的左边缘对齐(该控件默认位于父布局的上边)
android:layout_alignRight让一个控件的右边缘和另一控件的右边缘对齐(该控件默认位于父布局的上边)
同时还可以使用layout_alignTop和layout_alignBottom

3、帧布局(FrameLayout )
FrameLayout成为帧布局
应用的场景也相对比较少
所有的控件都默认摆放在布局的左上角
都会从左上角开始进行占用空间
新建文件:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView android:text="TextView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/text_view"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image_view" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/> </FrameLayout>
效果:

当没有准备图片资源时,可以使用下方的代码进行引用
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
上述的使用场景比较小,但是可以使用的
效果种可以发现 :
ImageView是在TextView之后添加的
但是此时的图片压在文字的上面
还可以进行修改布局中的对齐方式使用:android:gravity属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:text="TextView" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/text_view" android:layout_gravity="left"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/image_view" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher" android:layout_gravity="right"/> </FrameLayout>
效果:

4、表格布局(TableLayout)
遇到排列整齐的情况就可以使用表格布局进行排列
可以使布局排列整齐
TableLayout的属性:
android:collapseColumns:设置需要被隐藏的列的序号
android:shrinkColumns:设置允许被收缩的列的列序号
android:stretchColumns:设置运行被拉伸的列的列序号
以上这三个属性的列号都是从0开始算的,比如shrinkColunmns = "2",对应的是第三列!
android:layout_column="2":表示的就是跳过第二个,直接显示到第三个格子处,从1开始算的!
android:layout_span="4":表示合并4个单元格,也就说这个组件占4个单元格
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:stretchColumns="2"> <TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="0" android:text="btn1"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="1" android:text="btn2"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="3" android:text="btn3"/> </TableRow> <TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="1" android:text="btn4"/> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="2" android:text="btn5"/> </TableRow> <TableRow> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_column="2" android:text="btn6"/> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
效果:

5、网格布局GridLayout
作为android 4.0 后新增的一个布局
①跟LinearLayout(线性布局)一样,他可以设置容器中组件的对齐方式
②容器中的组件可以跨多行也可以跨多列(相比TableLayout直接放组件,占一行相比较)
常用属性:
设置组件的排列方式: android:orientation=""
设置组件的对齐方式: android:layout_gravity=""
设置网格布局的行列:
设置有多少行:android:rowCount="4" //设置网格布局有4行
设置有多少列:android:columnCount="4" //设置网格布局有4列
设置控件再几行几列(都是从0开始算)
组件在第几行:android:layout_row = "2" //设置组件位于第3行
组件在第几列:android:layout_column = "2" //设置该组件位于第3列
设置组件横向/纵向占几行几列
横跨几行:android:layout_rowSpan = "2" //纵向横跨2行
横跨几列:android:layout_columnSpan = "3" //横向横跨3列
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:columnCount="4" android:orientation="horizontal" > <Button android:layout_column="3" android:text="/"/> <Button android:text="1"/> <Button android:text="2"/> <Button android:text="3"/> <Button android:text="*"/> <Button android:text="4"/> <Button android:text="5"/> <Button android:text="6"/> <Button android:text="-" android:id="@+id/btn_sub"/> <Button android:text="7"/> <Button android:text="8"/> <Button android:text="9"/> <Button android:layout_rowSpan="3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="145dp" android:text="+"/> <Button android:text="0" android:layout_gravity="fill" android:layout_columnSpan="2"/> <Button android:text="00"/> <Button android:text="=" android:layout_columnSpan="3" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_width="265dp"/> </GridLayout>

6、绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout)
通过指定x、y的坐标来控制组件再布局种的位置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button android:text="123" android:layout_x="40dp" android:layout_y="40dp" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </AbsoluteLayout>

极少使用此布局
7、百分比布局
前三张布局种只有LinerLayout支持使用layout_weigh属性来指定按比例指定控件大小功能
其余两种不支持
如果使用RelativeLayout来实现两个按钮评分布局的宽度效果是比较困难的
Android引入一种百分比布局来解决这个问题
再这个布局中可以不使用warp_content、match_parent来指定控件的大小
允许直接指定控件再布局中所占的百分比实现
再FrameLayout、RalativeLayout种进行功能的扩展
提供了PercentFrameLayout、PercentRelativeLayout
待完成(............)




