10-RabbitMQ-整合SpringBoot
RabbitMQ整个SpringBoot
SpringBoot因其配置简单、快速开发,已经成为热门的开发之一
消息中间件的工作过程可以用生产者消费者模型来表示.即,生产者不断的向消息队列发送信息
而消费者从消息队列中消费信息.具体过程如下:
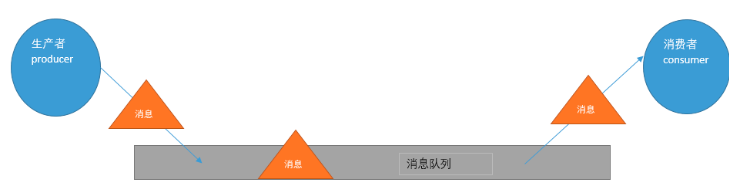
从上图可看出,对于消息队列来说,生产者,消息队列,消费者是最重要的三个概念
生产者发消息到消息队列中去,消费者监听指定的消息队列,并且当消息队列收到消息之后,
接收消息队列传来的消息,并且给予相应的处理.消息队列常用于分布式系统之间互相信息的传递.
使用SpringBoot进行整合RabbitMQ
1.pom文件的引入
这是操作RabbitMQ的starter必须要进行引入的
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.配置文件进行基础的配置
spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/user spring.rabbitmq.port=5672 spring.rabbitmq.password=user spring.rabbitmq.username=user spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168.43.157
RabbitMQ的模式
1、direct模式
配置Queue(消息队列).那注意由于采用的是Direct模式,需要在配置Queue的时候,指定一个键
使其和交换机绑定.
DirectQueue.java
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class DirectQueue { //若队列不存在则进行创建队列
//返回的是队列名字 @Bean public Queue queue(){ return new Queue("direct_queue"); } }
消息生产者
Sender.java
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Sender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; public void send(){ String msg = "direct_queue"; User user = new User(); user.setName("MrChegns"); user.setAge(12); amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("direct_queue",user); } }
此时发送的消息是一个User类型的对象
对于发送对象需要实现序列化接口
User.java
package com.cr.rabbitmqs.direct; import java.io.Serializable; public class User implements Serializable { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public User(String name, int age) {this.name = name; this.age = age; } public User() { } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } }
消费者
Receive.java
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Receive { //对队列进行监听
//同时可以监听多个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "direct_queue") public void listen(User msg){ System.out.println(msg); } }
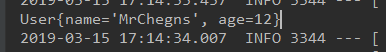
测试:
@Autowired private Sender sender; @Test public void test1(){ sender.send(); }
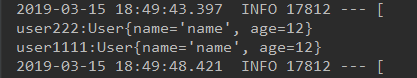
得到的结果i:
2、topic模式
首先我们看发送端,我们需要配置队列Queue,再配置交换机(Exchange)
再把队列按照相应的规则绑定到交换机上
Topic.java
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding; import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class Topic { //创建队列 @Bean(name = "message") public Queue Aqueue(){ return new Queue("message.topic"); } @Bean(name = "message1") public Queue BQueue(){ return new Queue("message.topics"); } //交换机 //若不存在则进行创建交换机 @Bean public TopicExchange exchange(){ return new TopicExchange("topic_exchange"); } //交换机和队列进行绑定 @Bean Binding bindingExchangeTopic(@Qualifier("message")Queue message,TopicExchange exchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(message).to(exchange).with("message.topic"); } @Bean Binding bindingExchangeTopics(@Qualifier("message1")Queue message,TopicExchange exchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(message).to(exchange).with("message.#"); } }
消费者
Receive1.java
import com.cr.rabbitmqs.direct.User; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Receive1 { @RabbitListener(queues = "message.topic") public void tes(User user){ System.out.println( "user1111:" + user); } }
Receive2.java
import com.cr.rabbitmqs.direct.User; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class Receive2 { @RabbitListener(queues = "message.topics") public void tes(User user){ System.out.println("user222:" + user); } }
消息生产者:
TopicSend.java
import com.cr.rabbitmqs.direct.User; import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class TopicSend { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; //发送消息 public void send(){ User user = new User("name",12); amqpTemplate.convertSendAndReceive("topic_exchange","message.dev",user); } //发送消息 public void send1(){
User user = new User("name",12);
amqpTemplate.convertSendAndReceive("topic_exchange","message.topic",user );
}
}
在开发中这种模式的使用还是相对比较多的,此时测试的是两种方法
一个方法所有的队列都可以进行获取
一个方法只有一个队列可以获取到消息
测试:
@Autowired private TopicSend topicSend; @Test public void ttt(){ topicSend.send(); }
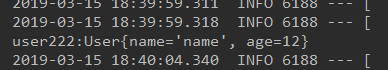
测试:
@Autowired private TopicSend topicSend; @Test public void ttt(){ topicSend.send1(); }
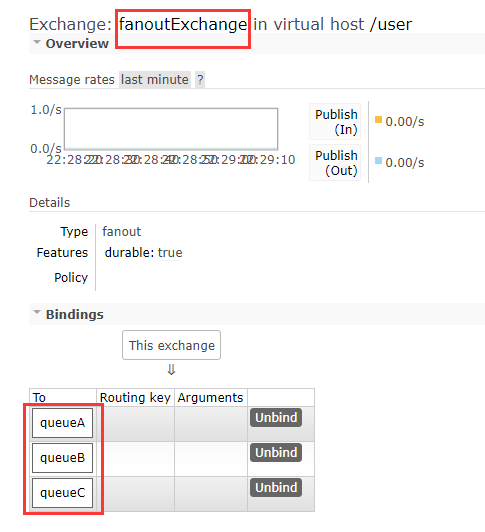
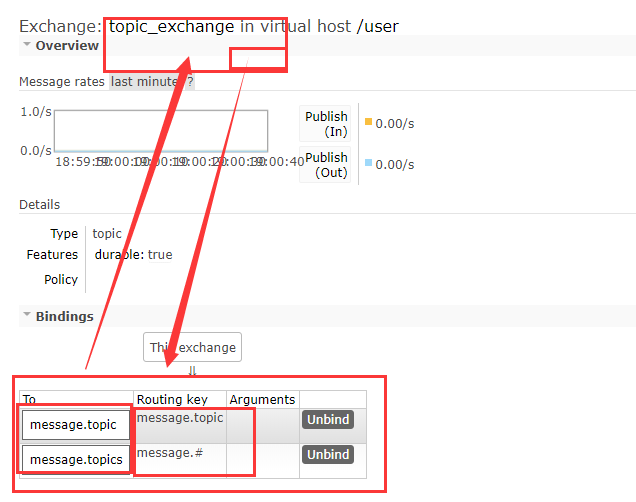
后台查看交换机和队列的绑定关系以机相关的路由键
3、fanout
那前面已经介绍过了,Fanout Exchange形式又叫广播形式,因此我们发送到路由器的消息会使
得绑定到该路由器的每一个Queue接收到消息,这个时候就算指定了Key,或者规则(即上文中
convertAndSend方法的参数2),也会被忽略!那么直接上代码,发送端配置如下:
Fanout.java
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding; import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class Fanout { //队列 //如果队列不存在会自动创建队列 @Bean public Queue queueA(){ return new Queue("queueA"); } @Bean public Queue queueB(){ return new Queue("queueB"); } @Bean public Queue queueC(){ return new Queue("queueC"); } //交换机 //如果交换机不存在会自动创建队列 @Bean public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){ return new FanoutExchange("fanoutExchange"); } //将交换机和队列进行绑定 @Bean Binding bindingExchangequeueA(Queue queueA,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queueA).to(fanoutExchange); } @Bean Binding bindingExchangequeueB(Queue queueB,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queueB).to(fanoutExchange); } @Bean Binding bindingExchangequeueC(Queue queueC,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){ return BindingBuilder.bind(queueC).to(fanoutExchange); } }
消费者:
FanoutReceive.java
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component //监听器 @RabbitListener(queues = "queueA") public class FanoutReceive { //监听的方法 @RabbitHandler public void listen(String msg){ System.out.println("queueA" + msg); } }

FanoutSender.java
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class FanoutSender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; //发送消息 public void send(){ String msg = "test fanout...."; //发送消息:参数依次是 交换机名字--路由键(此时设置路由键没有作用)--消息 amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","",msg); } }
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest public class BpptandrabbitmqApplicationTests { //测试fanout @Autowired private FanoutSender fanoutSender; @Test public void fanout() { fanoutSender.send(); } }
此时3个队列都能接收到消息
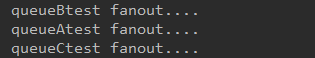
交换机、队列以及路由键