PageHelper分页插件
PageHelper
前言
记录一下自己对PageHelper的学习,了解。
认识PageHelper
PageHelper是一款好用的开源免费的Mybatis第三方物理分页插件,虽然是个分页插件,但是PageHelper比我想象的要复杂许多,它做的很强大,也很彻底,强大到使用者可能并不需要这么多功能,彻底到一参可以两用。
安装
PageHelper的maven依赖及插件配置
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>4.1.6</version>
</dependency>
PageHelper除了本身的jar包外,它还依赖了一个叫jsqlparser的jar包,使用时,我们不需要单独指定jsqlparser的maven依赖,maven的间接依赖会帮我们引入。
- 在
mybatis配置文件中配置pageHelper分页插件
<plugins>
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper">
<property name="dialect" value="oracle"/>
<property name="offsetAsPageNum" value="false"/>
<property name="rowBoundsWithCount" value="false"/>
<property name="pageSizeZero" value="true"/>
<property name="reasonable" value="false"/>
<property name="supportMethodsArguments" value="false"/>
<property name="returnPageInfo" value="none"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
注意事项:
- plugins插件的配置在 settings(标签)之后 在environments之前
- settings中设置Mybatis的一些额外的运行参数 如是否开启延迟加载,动态代理使用CG-LIB,或JAVALIB等;
使用
1)、统计总数,(将SQL语句变为 select count(0) from xxx,只对简单SQL语句其效果,复杂SQL语句需要自己写)
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage(1,-1);
long count = page.getTotal();
2)、分页,pageNum - 第N页, pageSize - 每页M条数
A、只分页不统计(每次只执行分页语句)
PageHelper.startPage([pageNum],[pageSize]);
List<?> pagelist = queryForList( xxx.class, "queryAll" , param);
//pagelist就是分页之后的结果
B、分页并统计(每次执行2条语句,一条select count语句,一条分页语句)适用于查询分页时数据发生变动,需要将实时的变动信息反映到分页结果上
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage([pageNum],[pageSize],[iscount]);
List<?> pagelist = queryForList( xxx.class , "queryAll" , param);
long count = page.getTotal();
//也可以 List<?> pagelist = page.getList(); 获取分页后的结果集
3)、使用PageHelper查全部(不分页)
PageHelper.startPage(1,0);
List<?> alllist = queryForList( xxx.class , "queryAll" , param);
4)、PageHelper的其他API
String orderBy = PageHelper.getOrderBy(); //获取orderBy语句
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage(Object params);
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize);
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage(int pageNum, int pageSize, boolean isCount);
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize, orderBy);
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize, isCount, isReasonable); //isReasonable分页合理化,null时用默认配置
Page<?> page = PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize, isCount, isReasonable, isPageSizeZero); //isPageSizeZero是否支持PageSize为0,true且pageSize=0时返回全部结果,false时分页,null时用默认配置
相关默认值
//RowBounds参数offset作为PageNum使用 - 默认不使用
private boolean offsetAsPageNum = false;
//RowBounds是否进行count查询 - 默认不查询
private boolean rowBoundsWithCount = false;
//当设置为true的时候,如果pagesize设置为0(或RowBounds的limit=0),就不执行分页,返回全部结果
private boolean pageSizeZero = false;
//分页合理化
private boolean reasonable = false;
//是否支持接口参数来传递分页参数,默认false
private boolean supportMethodsArguments = false;
相关源码的分析
首先我们看下一官方给出的一些配置,以及对配置的解释:
<!-- com.github.pagehelper为PageHelper类所在包名 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper">
<property name="dialect" value="mysql" />
<!-- 该参数默认为false -->
<!-- 设置为true时,会将RowBounds第一个参数offset当成pageNum页码使用 -->
<!-- 和startPage中的pageNum效果一样 -->
<property name="offsetAsPageNum" value="false" />
<!-- 该参数默认为false -->
<!-- 设置为true时,使用RowBounds分页会进行count查询 -->
<property name="rowBoundsWithCount" value="true" />
<!-- 设置为true时,如果pageSize=0或者RowBounds.limit = 0就会查询出全部的结果 -->
<!-- (相当于没有执行分页查询,但是返回结果仍然是Page类型) <property name="pageSizeZero" value="true"/> -->
<!-- 3.3.0版本可用 - 分页参数合理化,默认false禁用 -->
<!-- 启用合理化时,如果pageNum<1会查询第一页,如果pageNum>pages会查询最后一页 -->
<!-- 禁用合理化时,如果pageNum<1或pageNum>pages会返回空数据 -->
<property name="reasonable" value="true" />
<!-- 3.5.0版本可用 - 为了支持startPage(Object params)方法 -->
<!-- 增加了一个`params`参数来配置参数映射,用于从Map或ServletRequest中取值 -->
<!-- 可以配置pageNum,pageSize,count,pageSizeZero,reasonable,不配置映射的用默认值 -->
<!-- 不理解该含义的前提下,不要随便复制该配置 <property name="params" value="pageNum=start;pageSize=limit;"/> -->
</plugin>
我们有必要配置的参数:
* dialect:标识是哪一种数据库,设计上必须。
* autoDialect:true or false,是否自动检测dialect。
* autoRuntimeDialect:true or false,多数据源时,是否自动检测dialect。
* closeConn:true or false,检测完dialect后,是否关闭Connection连接
上面这3个智能参数,不到万不得已,我们不应该在系统中使用,我们只需要一个dialect = mysql 或者 dialect = oracle就够了,如果系统中需要使用,还是得问问自己,是否真的非用不可。
上源码:
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public class PageHelper implements Interceptor {
//sql工具类
private SqlUtil sqlUtil;
//属性参数信息
private Properties properties;
//配置对象方式
private SqlUtilConfig sqlUtilConfig;
//自动获取dialect,如果没有setProperties或setSqlUtilConfig,也可以正常进行
private boolean autoDialect = true;
//运行时自动获取dialect
private boolean autoRuntimeDialect;
//多数据源时,获取jdbcurl后是否关闭数据源
private boolean closeConn = true;
//缓存
private Map<String, SqlUtil> urlSqlUtilMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, SqlUtil>();
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// ...
}
上面是官方源码以及源码所带的注释,我们再补充一下。
SqlUtil:数据库类型专用sql工具类,一个数据库url对应一个SqlUtil实例,SqlUtil内有一个Parser对象,如果是mysql,它是MysqlParser,如果是oracle,它是OracleParser,这个Parser对象是SqlUtil不同实例的主要存在价值。执行count查询、设置Parser对象、执行分页查询、保存Page分页对象等功能,均由SqlUtil来完成。
SqlUtilConfig:Spring Boot中使用,忽略。
autoRuntimeDialect:多个数据源切换时,比如mysql和oracle数据源同时存在,就不能简单指定dialect,这个时候就需要运行时自动检测当前的dialect。
Map<String, SqlUtil> urlSqlUtilMap:它就用来缓存autoRuntimeDialect自动检测结果的,key是数据库的url,value是SqlUtil。由于这种自动检测只需要执行1次,所以做了缓存。
ReentrantLock lock:这个lock对象是比较有意思的现象,urlSqlUtilMap明明是一个同步ConcurrentHashMap,又搞了一个lock出来同步ConcurrentHashMap做什么呢?是否是画蛇添足?在《Java并发编程实战》一书中有详细论述,简单的说,ConcurrentHashMap可以保证put或者remove方法一定是线程安全的,但它不能保证put、get、remove的组合操作是线程安全的,为了保证组合操作也是线程安全的,所以使用了lock。
com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper.java源码
// Mybatis拦截器方法
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
if (autoRuntimeDialect) {
// 多数据源
SqlUtil sqlUtil = getSqlUtil(invocation);
return sqlUtil.processPage(invocation);
} else {
// 单数据源
if (autoDialect) {
initSqlUtil(invocation);
}
// 指定了dialect
return sqlUtil.processPage(invocation);
}
}
public synchronized void initSqlUtil(Invocation invocation) {
if (this.sqlUtil == null) {
this.sqlUtil = getSqlUtil(invocation);
if (!autoRuntimeDialect) {
properties = null;
sqlUtilConfig = null;
}
autoDialect = false;
}
}
public void setProperties(Properties p) {
checkVersion();
//多数据源时,获取jdbcurl后是否关闭数据源
String closeConn = p.getProperty("closeConn");
//解决#97
if(StringUtil.isNotEmpty(closeConn)){
this.closeConn = Boolean.parseBoolean(closeConn);
}
//初始化SqlUtil的PARAMS
SqlUtil.setParams(p.getProperty("params"));
//数据库方言
String dialect = p.getProperty("dialect");
String runtimeDialect = p.getProperty("autoRuntimeDialect");
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(runtimeDialect) && runtimeDialect.equalsIgnoreCase("TRUE")) {
this.autoRuntimeDialect = true;
this.autoDialect = false;
this.properties = p;
} else if (StringUtil.isEmpty(dialect)) {
autoDialect = true;
this.properties = p;
} else {
autoDialect = false;
sqlUtil = new SqlUtil(dialect);
sqlUtil.setProperties(p);
}
}
public SqlUtil getSqlUtil(Invocation invocation) {
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
//改为对dataSource做缓存
DataSource dataSource = ms.getConfiguration().getEnvironment().getDataSource();
String url = getUrl(dataSource);
if (urlSqlUtilMap.containsKey(url)) {
return urlSqlUtilMap.get(url);
}
try {
lock.lock();
if (urlSqlUtilMap.containsKey(url)) {
return urlSqlUtilMap.get(url);
}
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(url)) {
throw new RuntimeException("无法自动获取jdbcUrl,请在分页插件中配置dialect参数!");
}
String dialect = Dialect.fromJdbcUrl(url);
if (dialect == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("无法自动获取数据库类型,请通过dialect参数指定!");
}
SqlUtil sqlUtil = new SqlUtil(dialect);
if (this.properties != null) {
sqlUtil.setProperties(properties);
} else if (this.sqlUtilConfig != null) {
sqlUtil.setSqlUtilConfig(this.sqlUtilConfig);
}
urlSqlUtilMap.put(url, sqlUtil);
return sqlUtil;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
autoRuntimeDialect:多数据源,会创建多个SqlUtil。
autoDialect:单数据源,只会创建1个SqlUtil。单数据源时,也可以当做多数据源来使用。
指定了dialect:只会创建1个SqlUtil。
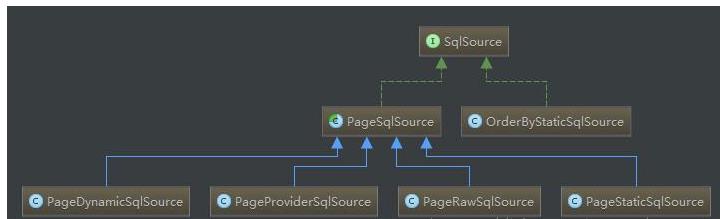
PageSqlSource类
public abstract class PageSqlSource implements SqlSource {
/**
* 获取正常的BoundSql
*
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
protected abstract BoundSql getDefaultBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
/**
* 获取Count查询的BoundSql
*
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
protected abstract BoundSql getCountBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
/**
* 获取分页查询的BoundSql
*
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
protected abstract BoundSql getPageBoundSql(Object parameterObject);
/**
* 获取BoundSql
*
* @param parameterObject
* @return
*/
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
Boolean count = getCount();
if (count == null) {
return getDefaultBoundSql(parameterObject);
} else if (count) {
return getCountBoundSql(parameterObject);
} else {
return getPageBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
}
}
getDefaultBoundSql:获取原始的未经改造的BoundSql。
getCountBoundSql:不需要写count查询,插件根据分页查询sql,智能的为你生成的count查询BoundSql。
getPageBoundSql:获取分页查询的BoundSql。
举例:
DefaultBoundSql:select stud_id as studId , name, email, dob, phone from students
CountBoundSql:select count(0) from students --由PageHelper智能完成
PageBoundSql:select stud_id as studId , name, email, dob, phone from students limit ?, ?
public class PageStaticSqlSource extends PageSqlSource {
private String sql;
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
private Configuration configuration;
private SqlSource original;
@Override
protected BoundSql getDefaultBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
String tempSql = sql;
String orderBy = PageHelper.getOrderBy();
if (orderBy != null) {
tempSql = OrderByParser.converToOrderBySql(sql, orderBy);
}
return new BoundSql(configuration, tempSql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
@Override
protected BoundSql getCountBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
// localParser指的就是MysqlParser或者OracleParser
// localParser.get().getCountSql(sql),可以根据原始的sql,生成一个count查询的sql
return new BoundSql(configuration, localParser.get().getCountSql(sql), parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
@Override
protected BoundSql getPageBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
String tempSql = sql;
String orderBy = PageHelper.getOrderBy();
if (orderBy != null) {
tempSql = OrderByParser.converToOrderBySql(sql, orderBy);
}
// getPageSql可以根据原始的sql,生成一个带有分页参数信息的sql,比如 limit ?, ?
tempSql = localParser.get().getPageSql(tempSql);
// 由于sql增加了分页参数的?号占位符,getPageParameterMapping()就是在原有List<ParameterMapping>基础上,增加两个分页参数对应的ParameterMapping对象,为分页参数赋值使用
return new BoundSql(configuration, tempSql, localParser.get().getPageParameterMapping(configuration, original.getBoundSql(parameterObject)), parameterObject);
}
}
假设List
其他PageSqlSource,原理和PageStaticSqlSource一模一样。
解析sql,并增加分页参数占位符,或者生成count查询的sql,都依靠Parser来完成。
com.github.pagehelper.parser.Parser源码
public class MysqlParser extends AbstractParser {
@Override
public String getPageSql(String sql) {
StringBuilder sqlBuilder = new StringBuilder(sql.length() + 14);
sqlBuilder.append(sql);
sqlBuilder.append(" limit ?,?");
return sqlBuilder.toString();
}
@Override
public Map<String, Object> setPageParameter(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql, Page<?> page) {
Map<String, Object> paramMap = super.setPageParameter(ms, parameterObject, boundSql, page);
paramMap.put(PAGEPARAMETER_FIRST, page.getStartRow());
paramMap.put(PAGEPARAMETER_SECOND, page.getPageSize());
return paramMap;
}
}
我们可以清楚的看到,MysqlParser是如何添加分页占位符和分页参数的。
public abstract class AbstractParser implements Parser, Constant {
public String getCountSql(final String sql) {
return sqlParser.getSmartCountSql(sql);
}
}
生成count sql,则是前文提到的jsqlparser工具包来完成的,是另外一个开源的sql解析工具包。
SqlUtil.doProcessPage()分页查询
// PageSqlSource装饰原SqlSource
public void processMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms) throws Throwable {
SqlSource sqlSource = ms.getSqlSource();
MetaObject msObject = SystemMetaObject.forObject(ms);
SqlSource pageSqlSource;
if (sqlSource instanceof StaticSqlSource) {
pageSqlSource = new PageStaticSqlSource((StaticSqlSource) sqlSource);
} else if (sqlSource instanceof RawSqlSource) {
pageSqlSource = new PageRawSqlSource((RawSqlSource) sqlSource);
} else if (sqlSource instanceof ProviderSqlSource) {
pageSqlSource = new PageProviderSqlSource((ProviderSqlSource) sqlSource);
} else if (sqlSource instanceof DynamicSqlSource) {
pageSqlSource = new PageDynamicSqlSource((DynamicSqlSource) sqlSource);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("无法处理该类型[" + sqlSource.getClass() + "]的SqlSource");
}
msObject.setValue("sqlSource", pageSqlSource);
//由于count查询需要修改返回值,因此这里要创建一个Count查询的MS
msCountMap.put(ms.getId(), MSUtils.newCountMappedStatement(ms));
}
// 执行分页查询
private Page doProcessPage(Invocation invocation, Page page, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//保存RowBounds状态
RowBounds rowBounds = (RowBounds) args[2];
//获取原始的ms
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) args[0];
//判断并处理为PageSqlSource
if (!isPageSqlSource(ms)) {
processMappedStatement(ms);
}
//设置当前的parser,后面每次使用前都会set,ThreadLocal的值不会产生不良影响
((PageSqlSource)ms.getSqlSource()).setParser(parser);
try {
//忽略RowBounds-否则会进行Mybatis自带的内存分页
args[2] = RowBounds.DEFAULT;
//如果只进行排序 或 pageSizeZero的判断
if (isQueryOnly(page)) {
return doQueryOnly(page, invocation);
}
//简单的通过total的值来判断是否进行count查询
if (page.isCount()) {
page.setCountSignal(Boolean.TRUE);
//替换MS
args[0] = msCountMap.get(ms.getId());
//查询总数
Object result = invocation.proceed();
//还原ms
args[0] = ms;
//设置总数
page.setTotal((Integer) ((List) result).get(0));
if (page.getTotal() == 0) {
return page;
}
} else {
page.setTotal(-1l);
}
//pageSize>0的时候执行分页查询,pageSize<=0的时候不执行相当于可能只返回了一个count
if (page.getPageSize() > 0 &&
((rowBounds == RowBounds.DEFAULT && page.getPageNum() > 0)
|| rowBounds != RowBounds.DEFAULT)) {
//将参数中的MappedStatement替换为新的qs
page.setCountSignal(null);
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(args[1]);
args[1] = parser.setPageParameter(ms, args[1], boundSql, page);
page.setCountSignal(Boolean.FALSE);
//执行分页查询
Object result = invocation.proceed();
//得到处理结果
page.addAll((List) result);
}
} finally {
((PageSqlSource)ms.getSqlSource()).removeParser();
}
//返回结果
return page;
}
源码中注意关键的四点即可:
1、msCountMap.put(ms.getId(), MSUtils.newCountMappedStatement(ms)),创建count查询的MappedStatement对象,并缓存于msCountMap。
2、如果count=true,则执行count查询,结果total值保存于page对象中,继续执行分页查询。
3、执行分页查询,将查询结果保存于page对象中,page是一个ArrayList对象。
4、args[2] = RowBounds.DEFAULT,改变Mybatis原有分页行为;
args[1] = parser.setPageParameter(ms, args[1], boundSql, page),改变原有参数列表(增加分页参数)。
PageHelper的两种使用方式
第一种、直接通过RowBounds参数完成分页查询 。
List<Student> list = studentMapper.find(new RowBounds(0, 10));
Page page = ((Page) list;
第二种、PageHelper.startPage()静态方法
//获取第1页,10条内容,默认查询总数count
PageHelper.startPage(1, 10);
//紧跟着的第一个select方法会被分页
List<Country> list = studentMapper.find();
Page page = ((Page) list;
注:返回结果list,已经是Page对象,Page对象是一个ArrayList。
原理:使用ThreadLocal来传递和保存Page对象,每次查询,都需要单独设置PageHelper.startPage()方法。
public class SqlUtil implements Constant {
private static final ThreadLocal<Page> LOCAL_PAGE = new ThreadLocal<Page>();
}
本文中经常提到的count查询,其实是PageHelper帮助我们生成的一个MappedStatement内存对象,它可以免去我们在XXXMapper.xml内单独声明一个sql count查询,我们只需要写一个sql分页业务查询即可。
PageHelper使用建议(性能最好):
1、明确指定dialect。2、明确编写sql分页业务和与它对应的count查询,别图省事。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号