数据结构:队列
数据结构:队列
先入先出的数据结构
说明
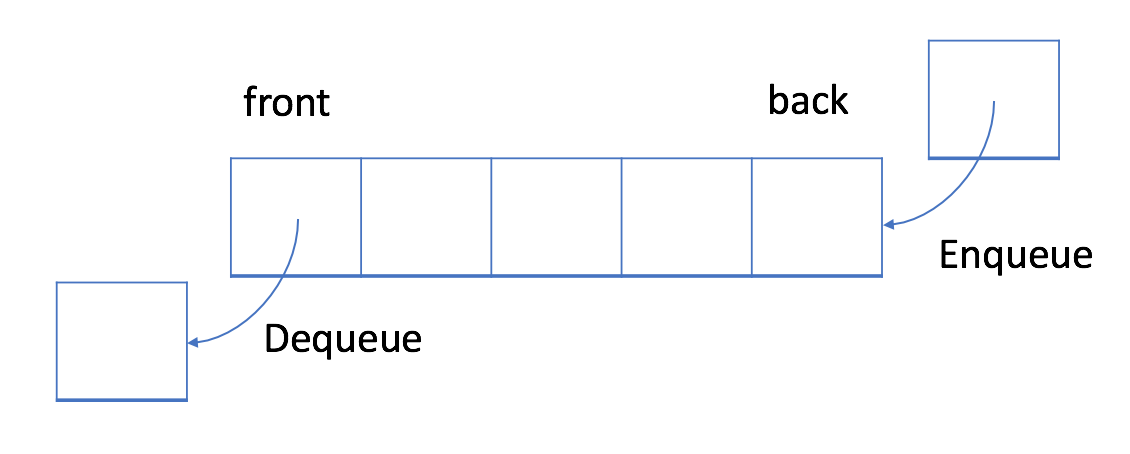
在先入先出数据结构中,将首先处理队列中的第一个元素,即front所指的位置元素。
如上图所示,队列是典型的 FIFO 数据结构。插入(insert)操作也称作入队(enqueue),新元素始终被添加在队列的末尾。 删除(delete)操作也被称为出队(dequeue)。 你只能移除第一个元素。
示例
入队操作

出队操作
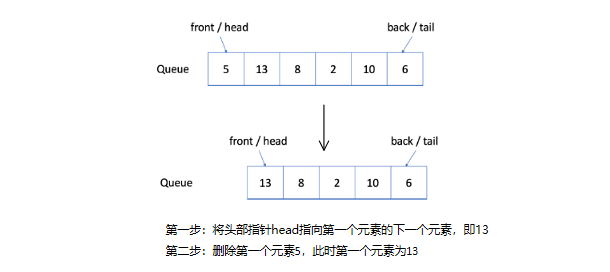
队列实现
为了实现队列,我们可以使用动态数组和指向队列头部的索引。
如上所述,队列应支持两种操作:入队和出队。入队会向队列追加一个新元素,而出队会删除第一个元素。 所以我们需要一个索引来指出起点。
// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
class MyQueue {
// store elements
private List<Integer> data;
// a pointer to indicate the start position
private int p_start;
public MyQueue() {
data = new ArrayList<Integer>();
p_start = 0;
}
/** Insert an element into the queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int x) {
data.add(x);
return true;
};
/** Delete an element from the queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return false;
}
p_start++;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
return data.get(p_start);
}
/** Checks whether the queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return p_start >= data.size();
}
};
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyQueue q = new MyQueue();
q.enQueue(5);
q.enQueue(3);
if (q.isEmpty() == false) {
System.out.println(q.Front());
}
q.deQueue();
if (q.isEmpty() == false) {
System.out.println(q.Front());
}
q.deQueue();
if (q.isEmpty() == false) {
System.out.println(q.Front());
}
}
}
上面的实现很简单,但在某些情况下效率很低。 随着起始指针的移动,浪费了越来越多的空间。 当我们有空间限制时,这将是难以接受的。

如果我们出队了一个元素,此时第一个位置将空出来,这个空间的浪费我们可以使用循环队列来解决。
循环队列
说明
循环队列是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则并且队尾被连接在队首之后以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
循环队列的一个好处是我们可以利用这个队列之前用过的空间。在一个普通队列里,一旦一个队列满了,我们就不能插入下一个元素,即使在队列前面仍有空间。但是使用循环队列,我们能使用这些空间去存储新的值。
实现
class MyCircularQueue {
private int[] data;
private int head;
private int tail;
private int size;
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the queue to be k. */
public MyCircularQueue(int k) {
data = new int[k];
head = -1;
tail = -1;
size = k;
}
/** Insert an element into the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if (isFull() == true) {
return false;
}
if (isEmpty() == true) {
head = 0;
}
tail = (tail + 1) % size;
data[tail] = value;
return true;
}
/** Delete an element from the circular queue. Return true if the operation is successful. */
public boolean deQueue() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return false;
}
if (head == tail) {
head = -1;
tail = -1;
return true;
}
head = (head + 1) % size;
return true;
}
/** Get the front item from the queue. */
public int Front() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return -1;
}
return data[head];
}
/** Get the last item from the queue. */
public int Rear() {
if (isEmpty() == true) {
return -1;
}
return data[tail];
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is empty or not. */
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head == -1;
}
/** Checks whether the circular queue is full or not. */
public boolean isFull() {
return ((tail + 1) % size) == head;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularQueue obj = new MyCircularQueue(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.enQueue(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.deQueue();
* int param_3 = obj.Front();
* int param_4 = obj.Rear();
* boolean param_5 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_6 = obj.isFull();
*/
队列用法
除基本Collection操作外,队列还提供额外的插入,提取和检查操作。这些方法中的每一种都以两种形式存在:一种在操作失败时抛出异常,另一种返回特殊值(null或false,具体取决于操作)。后一种形式的插入操作专门用于容量限制的队列 实现; 在大多数实现中,插入操作不会失败。

// "static void main" must be defined in a public class.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. Initialize a queue.
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList();
// 2. Get the first element - return null if queue is empty.
System.out.println("The first element is: " + q.peek());
// 3. Push new element.
q.offer(5);
q.offer(13);
q.offer(8);
q.offer(6);
// 4. Pop an element.
q.poll();
// 5. Get the first element.
System.out.println("The first element is: " + q.peek());
// 7. Get the size of the queue.
System.out.println("The size is: " + q.size());
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号