英语语法笔记整理
①原文正在更新中:https://www.cnblogs.com/MrFlySand/p/17631957.html
②内容:高中英语、专升本英语、四级英语
③QQ交流群:https://pd.qq.com/s/c01padly
④更新日期:2024年3月1日16:48:21
⑤视频讲解:【小蓝书专升本终极语法】
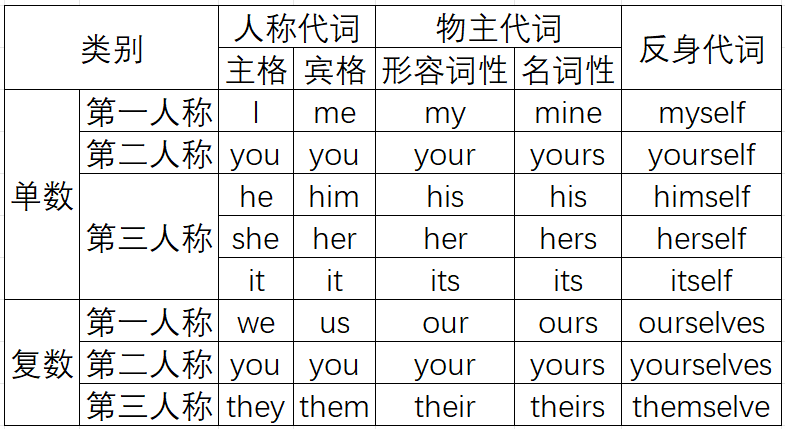
词汇
形容词:修饰名词或代词
敏捷的 quick (使用“的”)
绚丽的 gorgeous
勇敢的 courageous
高的 high
优雅的 graceful
副词:修饰动词、形容词
Hit hard 用力地打(使用“地”)
very graceful非常优雅
介词(preposition):介词后面一定用名词
- 常用介词(重点):
at(在) / on(在...上) / in(在里面) / from(从...起) / to(到) / before(之前) / after(之后)(7个)
冠词:放在名词前面
- 冠词:
a / an / the / 零冠词(/)
数词
- 基数次:1 2 3 ...
- 序数词:第一、第二、第三
连词
-
and、but、so
-
一句话中只能有一个谓语动词。
杰克早上逛街,and杰克下午看电影
句子结构(基本句型)



(1)主谓(S+V)
(2)主谓宾(S+V+O)
(3)主系表(S+V+P)
(4)主谓双宾(S+V+Oi+Od)
(5)主谓宾宾补(S+V+O+Oc)
- 主语:动作发出者
- 谓语:动词
- 宾语:动作承担者
- 表语:说明主语的特征、属性、状态、身份等
- 补语:说明主语或宾语的身份、性质、状态等
各结构的构成(小蓝书)
- 主语:名词、非谓语动词、代词、从句。
- 谓语:一个拥有完整时态和语态的动词,一句话中有且只有一个。
- 宾语:从句、名词、非谓语动词、代词。
- 系动词:be动词、感官动词、变化、保持。
- 表语:从句、名词、非谓语动词、代词、形容词、介词短语、副词。
- 定语:从句、形容词、介词短语、非谓语动词、名词。
- 状语:介词短语、副词、状语从句、非谓语动词、名词。
- 补语:名词、形容词、副词、分词、介词短语。

一、主+谓
(1)我来了I come.
(2)我明白I get.
(3)他到了He arrives.
(4) The students(主) work(谓) very hard(副词).
二、主+谓+宾
(1)我的朋友们与我交谈 My companies(主语) talk with(谓语) me(宾语).
(2)他参加这项活动 He takes part in this activity.
(3)我放弃了出国的机会 I give up the chance of going abroad.
(4)他承担了后果 He suffered the consequences.
三、主+连系动词+表语(主系表)
- 表语:说明主语的特征、属性、状态、身份等
- 她变美
She(主)becomes(系)beautiful(表). - 流星转瞬即逝
The meteor(主)is(系)transient(表).- 没有动词时,查看
be动词(is)
- 没有动词时,查看
- 我们是一家人
Wearefamily. - 所有的游客看起来都挺开心的。
All the tourists(主)seem(系)happy(表). - 你是一名学生
Youarea student. - 那辆车是我的
That carismine.
3.1 常见的系动词(重点)
- be (am/is/are/was/were/have(has第三人称单数)/been/being) 8个
- 感官动词 look smell(闻气味) taste(尝味道) sound(听) feel(感觉) 5个
- 保持:keep(保持) stay(保持;停留) remain(保持)
- 变化:become(变为;成为) get(获得)
四、主谓双宾
-
He(主)awards(谓)me(宾)a book(宾). 他奖励了我一本书。 -
David(主)showed(谓)me(间接宾语)the way(直接宾语). 大卫为我指了路。 -
Mary(主)lent(谓)Michael(间接宾语)her dictionary(直接宾语). 玛丽把她的词典借给了迈克尔。 -
He(主)tells(谓)me(宾)that he wants a cake(宾). 他告诉我他想要一个蛋糕
主谓双宾可能会出现在名词性从句考点中,常见的谓语动词就是tell,除此以外还有:award(授予)、buy(买)、give(给)、leave(离开)、lend(借)、offer(提供;给予)、pay(支付)、show(显示)、teach(教) (10个重点) (当看到这些动词时大概率是主谓双宾)
学校 买了/支付/借(buy/pay/lend) 一些奖杯 给(give) 校长,校长 授予/提供(award/offer) 教(teach) 书的老师 展示(显示show) 他们的机会,最后便 离开(leave) 了。
常见句型:XXX tell/give/offer sb sth. xxx(主) 告诉(谓) 某人(宾) 某事(宾).(重点)
2022真题
- People sometimes cross their arms and this gesture may _____ us that they want to protect themselves.
- A.say B.tell C.speak D.talk
真题解析
People sometimes cross their armsand this gesturemay _____ us(宾)that they want to protect themselves(宾).(XXX tell sb sth.)- this gesture
may _____ us(宾)that they want to protect themselves(宾语从句).(XXX tell sb sth.) - 翻译:人们有时会交叉双臂,这个姿势可能会_____我们,他们想保护自己。
- 答案:B
- sometimes 有时
- cross 交叉
- their 他们的
- arms 【
n.臂(arm 的复数);[军]武器;纹章】【v.武装;配备(arm 的三单形式)】 - gesture 【
n.手势,姿势;姿态,表示】 【V.打手势,用动作示意】 - may 【
aux.可能,也许(表示某情况是可能的);可以(征求同意或表示允许);可能(表示某情况属实,另一情况也属实);祝,愿(用于表达愿望);可以,能够(表明目的);可以,也许(用于提出礼貌的建议)】【n.山楂花;五月(May)】 - want 【
v.想要,希望;需要;(用于提出建议)应该;缺少;搜捕,追捕;想见(某人),想与(某人)谈话;(用于疑问句中表示提议或邀请)想要,需要;(在性方面)想要(某人);照料,爱护(小孩);想要进去,想要出去;应受】 【n.缺乏,缺少;贫穷,贫困;渴望的东西,需要的东西】 - protect
v.保护,防护;(制订法律)保护;投保,为……买保险 - themselves
pron.他们自己;他们亲自
五、主+谓+宾+宾语补足语
- 本句型在语法题中仍然不多见。(只有一种,形容词做宾补)
- 补语:说明主语或宾语的身份、性质、状态等
Workers(主语)painted(谓语)the wall(宾)blue(宾补). 工人们把墙漆成了蓝色。The present(主语)makes(谓语)me(宾)happy(宾补). 这个礼物让我感到很开心
make sb done(过去分词)
扩充内容
一、主系表和主谓宾的区别
主系表和主谓宾的区别在于谓语部分,能做谓语的是拥有完整时态和语态的动词。
主系表的动词为系动词,主谓宾的动词为实意动词。
二、主谓和主谓宾的区别
主谓和主谓宾的区别在于动词部分,
主谓句型的动词为不及物动词,
而主谓宾句型的动词往往为及物动词。
2.1 及物动词和不及物动词的区别:
-
及物动词:后面必须跟宾语,句子意思才完整的实义动词。及物动词后面可以直接连接宾语。
I deem (意思不完整) -
不及物动词:本身意义完整,后面不必跟宾语的实义动词
I listen (意思完整)
也就是说,主谓宾结构中的谓语往往是及物动词;
主谓结构中的谓语往往是不及物动词。
I deem that you are right. 不及物动词后面需要加介词连接宾语。
I listen to you. 不及物动词没有被动
2.1.1 及物动词 和 不及物动词
- 用中文举例:
- 及物动词:中文中:动词+宾语(拿、偷、唱)
有被动形式:这本书被他拿/偷了。 - 不及物动词:中文中:动词+介词(一定要有介词)+宾语(成功、工作)
没有被动形式
他成功.../他在这方面成功了。
- 及物动词:中文中:动词+宾语(拿、偷、唱)
- 一个英文单词既可能是及物也可能是不及物,需要看他当时使用的情况看是否是及物动词。
例子
- 例①:I work at the factory. 我工作在这个工厂。
我们通过中文翻译,可以明确看到介词(at)存在,因此判断出本句话中的work为不及物动词,及当有介词时为不及物动词、主谓结构。
- 常用介词:
on / at / in / from / to / before / after
work为不及物动词,所以这个句子也可以写为:I work. 我工作。(没有宾语也正确写法,主谓结构)
I(主) work(谓语动词) at(介词) the factory.
因此I work at the factory.为主谓结构。
- 例②:I accept the invitation. 我接受这个邀请
我们通过中文翻译,可以通过翻译看出本句话中谓语动词和宾语之间没有出现介词。
因此判断出本句话中的accept为及物动词,后面必须有宾语。所以这个句子不能写为:I accept. 我接受。(错误写法:接受后面要有物体,accept为及物动词)
因此I accept the invitation.为主谓宾结构。
- 总结
- 1、I work at the factory.(语法正确)
2、I work.(语法正确)
3、I accept the invitation.(语法正确)
4、I accept.(语法错误)
2.1.2 总结背诵
- 主谓宾结构中的谓语往往是及物动词;
主谓结构中的谓语往往是不及物动词。 - 有介词时为不及物动词、主谓结构。
三、延续性动词和非延续性动词的区别:
- 英文中,动词根据其发生的方式、时长,可以分为延续性动词和非延续性动词。
- 延续性动词:动作可以持续很长一段时间。如:
play、sleep、walk等。 - 非延续性动词:又称为瞬间动词,动作不能持续很长一段时间,开始即结束。如:
buy、open、borrow、come、leave等。
四、练习
4.1 练习一:辨别句型
- 我打你。 I hat you. 主谓宾
- 我工作。 I word. 主谓
- 我变漂亮了。 I becom beautiful. 主系表
我给他两本书。 I gave him the two books. 主谓双宾givev.给,交给;赠送,赠与,gavev.给予(give 的过去式)himpron.他(宾格),hepron.他;(泛指的)人
4.2 练习二:辨别句型
- A little girl likes it.
- I swim in the swimming pool.
- I give you an apple.
- I read the news.
- We make the room comfortable
- This book brings me a lot of fun.
- He is an actor.
- He becomes a hero.
- The baby cries.
解析
A little girllikesit. 主谓宾Iswimin the swimming pool. 主谓,in介词Igiveyouan apple. 主谓双宾,give及物动词- 主语+谓语+宾语
I read the news. - 主语+谓语+宾语+宾语补足语
We make the room(宾语) comfortable( 宾语补足语). - 主语+谓语+间接宾语+直接宾语
This book brings me(间接宾语) a lot of fun(直接宾语). - 主语+连系动词+表语
He is(连系动词) an actor(表语). - 主语+连系动词+表语
He becomes(连系动词) a hero(表语). - 主语+谓语
The baby cries.
五、否定句的表达方式
- 添加否定词的常见情况:
(1)原句已有be动词、助动词、情态动词时直接加not。
can(could)、may(might)、must、need、ought to、dare(dared)、shall(should)、will(would)
① 如果是be动词,把not写后面。
You are charming. 你很迷人。
You are not charming. 你不迷人。
②如果是助动词,把not写助动词后。
You have been here many years. 你来这里很多年了。
You have not been here many years. 你很多年都没来这了。
③如果是情态动词,把not写在情态动词后。
You should go out. 你应该出去。
You should not go out. 你不应该出去。
- 如果是实意动词,把don't写前面。实意动词的否定在前面加
don't/doesn't/didn't。
实意动词:有实际意义的动词。
You have three books. 你有三本书。
You don't have three books. 你没有三本书。
六、基本句型在考试中的应用(作文)
老板很满意,并且我们订购了50部手机。
- 拆分结构
老板(主)很满意(谓语,没有动词就用be动词:老板 be 满意)
并且
我们(主)订购了(谓)50部手机(宾)。
the booswasvary satisfied
and
weordered50 mobile phones.
The boss was very satisfied and we ordered 50 mobile phones.
6.1 练习:翻译句子
- 我头痛。
- 孩子们正在睡觉。
- 我姐姐喜欢那部戏剧。
- 没有人能回答这个问题。
- 工人们把墙漆成了蓝色。
- 大卫为我指了路。
- 玛丽把她的词典借给了大卫。
- 那辆车是我的。
- 所有的游客看起来都挺开心的。
6.2 解析
-
我头(S)痛(V)。
My headaches. -
孩子们(S)正在睡觉(V)。
The childrenare sleeping. -
我姐姐喜欢那部戏剧。
My elder sister(S)enjoy(V)the play(O). -
没有人(S)能回答(V)这个问题(O)。
Nobodycould answerthe question. -
工人们(S)把墙漆成了蓝色。
Workers(S)painted(V)the wall(O)blue(Oc). -
大卫(S)为我指了路。
Daivd(S)showed(V)me(间接宾语)the way(直接宾语). -
玛丽把她的词典借给了(谓语动词)大卫(宾)。
Mary(S)lent(V)Daivd(间接宾语)her dictionary(直接宾语). -
那辆车(主)是(系)我的(表)。
That car(S)is(V)mine(P). -
所有的游客(主)看起来(系动词)都挺开心的(表)。
All the tourists(S)seem(V)happy(P).
6.3 收集的问题
-
①及物动词和不及物动词的区别还是有点难以分辨
看介词和被动形式 -
②怎么区分主谓双宾和主谓宾宾补
宾补可以加be动词 -
③有些动词既是及物也是不及物,这种不知道该咋分
-
④做题的时候还是有点不太能区分双宾和宾补
查看常见的主谓双宾的动词 -
⑤感官动词有什么需要注意的地方
感官动词没有被动
七、课后练习
-
以下不符合基本句型的是?
A)Cats and dogs are friends of man.
B)We protect the environment.
C)Protecting the environment brings beautiful
D)They arrived. -
以下不符合基本句型的是?
A)Jim told his friends that I was a clever man.
B)They are.
C)My dream is to be a fireman.
D)They succeeded. -
My teacher gives me
a thick book.句中划线词是什么成分?
A)主语
B)定语
C)宾语
D)表语 -
Tom goes to the swimming pool
every Saturday.句中划线词是什么成分?
A)状语
B)定语
C)宾语
D)表语 -
以下不属于系动词的是?
A)has been
B)feel
C)remain
D)take -
以下不能作主语的是?
A)名词
B)代词
C)名词性从句
D)分词 -
以下不能作表语的是?
A)形容词
B)不定式
C)定语
D)代词 -
以下不能作定语的是?
A)从句
B)分词
C)介词短语
D)动词 -
以下不能作状语的是?
A)非谓语动词
B)名词性从句
C)副词
D)时间名词 -
以下符合否定句表达的是?
A)Students should not be absent from class.
B)Students not should be absent from class.
C)Not students should be absent from class.
D)Students should be not absent from class.
7.1 解析
-
以下不符合基本句型的是?(C)
A)Cats and dogsarefriends of man. 主系表
B)Weprotect保护the environment环境. 主谓宾
C)Protecting the environment(动名词短语,名词主语)brings(谓语)beautiful(形容词)
D)Theyarrived抵达. 主谓
主谓结构的动词必须是不及物动词。 -
以下不符合基本句型的是?(B)
A)Jimtoldhis friendsthat I was a clever man. 主谓双宾
B)They are. 主系
C)My dreamisto be a fireman. 主系表
D)They succeeded. 主谓 -
My teacher(主)gives(谓)me(宾)a thick book(宾).句中划线词是什么成分?(C)
A)主语
B)定语
C)宾语
D)表语 -
Tom goes to the swimming pool
every Saturday.句中划线词是什么成分?(A) 主谓宾
A)状语
B)定语
C)宾语
D)表语
解析:不及物动词+介词to+宾语
every Saturday时间状语
基本成分:主谓宾(表)
修饰成分:定状补
-
以下不属于系动词的是?(D)
A)has been (be动词的时态变化)
B)feel
C)remain
D)take -
以下不能作主语的是? (D)
A)名词
B)代词
C)名词性从句
D)分词(非谓语动词) -
以下不能作表语的是? (C)
A)形容词
B)不定式
C)定语
D)代词 -
以下不能作定语的是?(D)?位置:23:00
A)从句
B)分词
C)介词短语
D)动词 -
以下不能作状语的是? (B)
A)非谓语动词
B)名词性从句
C)副词
D)时间名词 -
以下符合否定句表达的是? (A)
A)Students should not be absent from class.
B)Students not should be absent from class.
C)Not students should be absent from class.
D)Students should be not absent from class.
should 情态动词,如果是情态动词,把not写在情态动词后。
第二章 时态语态
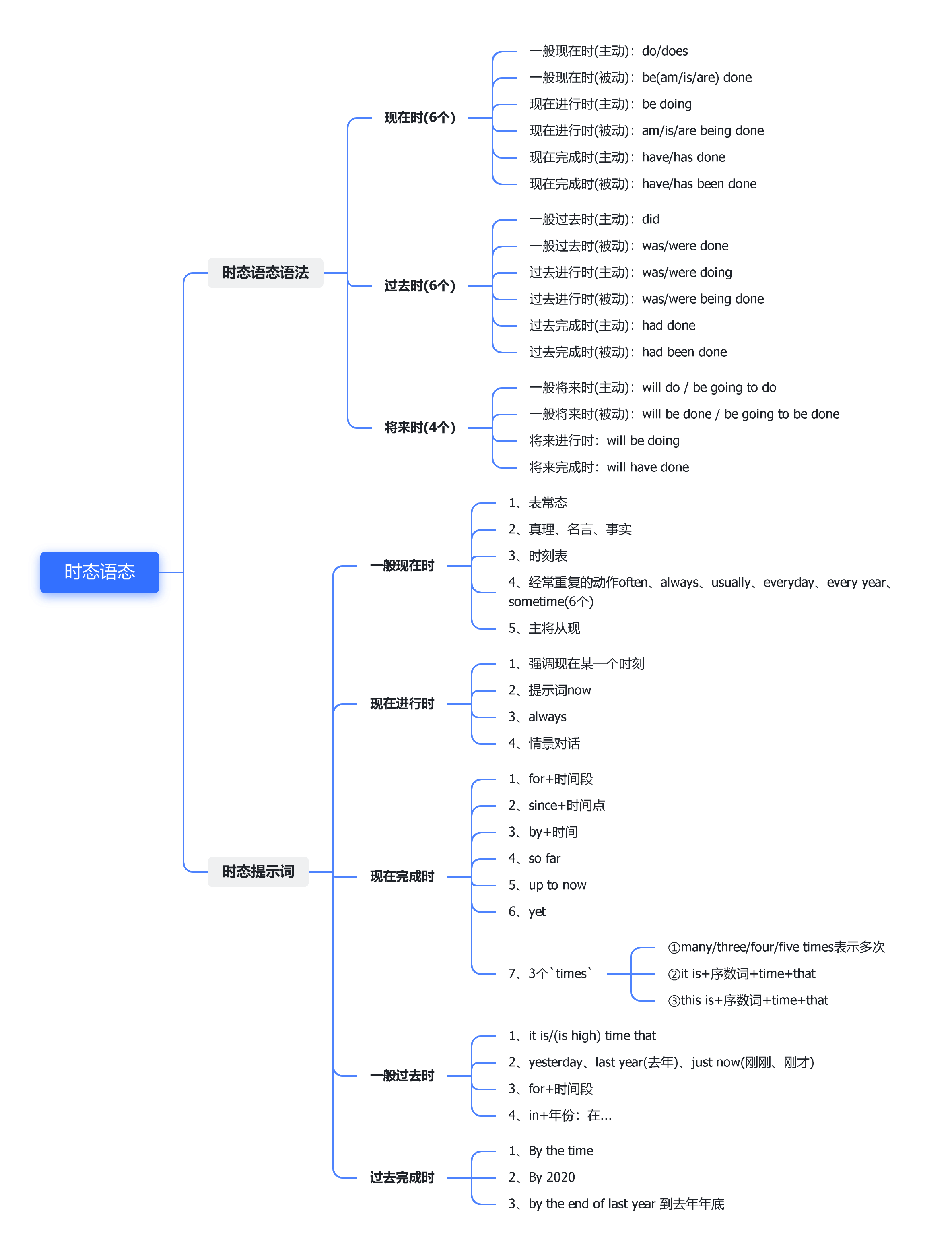
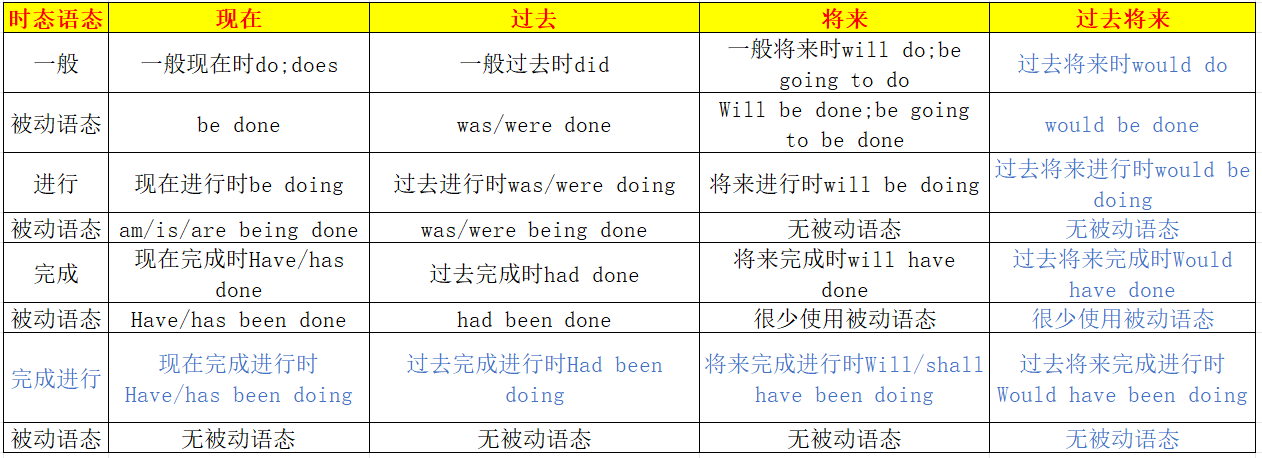
| 时态语态 | 现在 | 过去 | 将来 | 过去将来 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 一般 | (1.1.15个)一般现在时do;does |
(2.1.13个)一般过去时did |
一般将来时will do;be going to do | 过去将来时would do |
| 被动语态 | be(am/is/are) |
was/were done | will |
would |
| 进行 | (1.2.14个)现在进行时be |
过去进行时was/were |
将来进行时will |
过去将来进行时would be doing |
| 被动语态 | am/is/are |
was/were |
无被动语态 | 无被动语态 |
| 完成 | (1.3.19个)现在完成时Have/has |
(2.3.13个)过去完成时had |
将来完成时will |
过去将来完成时Would have done |
| 被动语态 | Have/has |
had |
很少使用被动语态 | 很少使用被动语态 |
| 完成进行 | 现在完成进行时Have/has been doing | 过去完成进行时Had been doing | 将来完成进行时Will/shall have been doing | 过去将来完成进行时 Would have been doing |
| 被动语态 | 无被动语态 | 无被动语态 | 无被动语态 | 无被动语态 |
注
be
being:be 的现在分词形式,be动词+ingbeen:be的过去分词
do
does:do 的第三人称单数done:动词的过去分词表被动动词+eddoing:do的ing形式,动词+ing
- 时态、语态、单复数
时态概念
- 发生在动词上(一般是谓语)
take took- 谓语是一个拥有完整时态语态的动词
- 我拿了一本书。
I took a book. - 我昨天拿了一本书。
I tooked a book.我拿ed了一本书。
语态概念
- 语态分为主动和被动
- 主动:动作由主语主动发出
I attack you.我 - 被动:动作被主语承担
I am attacked by you.我被你打了。
(主/被动 锁定主语和谓语的关系)
一、现在时
1.1 一般现在时
-
一般现在时
do(I、we)/dose(主动,使用动词原型) /be done(被动,be动词+过去分词)- 记忆:
动词原型/be动词+动词的过去分词(动词ed)
过去分词:动词后面加ed don't:do的否定形式
- 记忆:
-
I
watch(动词原型)a game. 我观看一场比赛。 -
A game
is watched(be动词+过去分词)by me. 一场比赛被我观看。
1.1.1 实际运用(5个重点)
- 句中没有出现特殊的时态(时间)提示词,请用一般现在时(常态)
The rose is red.玫瑰是红色。(并没有说明玫瑰什么时候是红色的,所以用一般现在时) - 真理、名言、事实(翻译后)也是一种常态,所以用一般现在时。
- 陈述时刻表使用一般现在时。(9:00,8:00,8:30,eight o'clock)
xxx(地铁)在xxx(7)点出发。 - 句子出现每一天、每一年或经常重复的动作提示用一般现在时
often、always、usually、everyday、every year、sometime(6个) - 在时间状语从句、条件状语从句、让步状语从句(较少)中往往用一般现在时表示将来。
- 主将从现:主句中使用一般将来时,从句使用一般现在时。
我会感激你(主句),当你帮助我的时候(从句)。
Iwill appreciateyou,when youhelpme.
1.1.2 举例
- I
go(动词用一般现在时)hikingevery Monday(时间提示词,经常重复的动作). 我每个星期一都去远足 - The train
leaves(leave的第三人称单数)at seven o'clock(时刻表). 火车7点开。 - The
boiling pointof water is 100℃. 水的沸点是摄氏100度。(真理)- boiling point 沸点、煮沸
- boil 煮
- If you
give(一般现在时)me a favor,youwill repay(将来时)you. 如果你帮我的忙,你会报答你的。(主将从现)
youwill repay(将来时)you,If yougive(一般现在时)me a favor.
1.1.3 变成例题
-
As we all know,i () hiking every Monday.
A.gone B.will go C.go -
The train () at seven o'clock.
A.leaves B.will leave C.left
答案:1.C 2.A
1.2 现在进行时
- 现在进行时:
be doing(主动) /be being done(被动)- 记忆:
be动词+动词ing/be动词+being+动词ed
- 记忆:
- I
am watchinga game. 我正在观看一场比赛 - The game
is being watchedby me. 比赛正在被我观看
1.2.1 实际运用(4个)
- 强调现在某一个时刻,如现在我正在看...,常出现的考点,如:当我朋友到达的时候,我正在看书。
- When you arrive,I
am reading. 当你到达的那一刻,我正在读书。 - arrive 到达(瞬间动词)
- When you
arrived(昨天到达),Iwas reading(昨天的那一刻正在看书). 从句是过去时,主句用过去进行时。 - When you
arrive(现在到达),Iam reading. 从句是现在时,主句用现在进行时。
- When you arrive,I
- 出现提示词
now- I'm reading a book now. 我现在正在看书。
- 当进行时与
always连用的时候表示“总是,老是”be always doing(重点) - 情景对话,描述打电话时的回复句
----This is Jack speaking.May I speak to Rose?
----sorry,Roseis clearingrooms.
1.2.2 变成例题
-
When you arrived,I ()
A、am reading B、was reading C、read -
I () a book now.
A、am reading B、was reading C、read
答案:1.B 2.A
2022年真题
- Doing Taichi exercise ()one of traditional Chinese sports.
A、is B、are C、was D、were
- 解析
- 1.Doing Taichi exercise 打太极
2.传统 traditional
3.翻译:打太极是中国的传统运动。(常态事实,使用一般现在时,was/were过去时排除CD)
4.前面是动名词短语做主语,答案A
1.3 现在完成时
- 现在完成时
have/has done(主动),have/has been done(被动)。have是原型,例如:I、we(我们,复数)has第三人称单数,例如:她、书...- done 做(do 的过去分词形式)
- I
have watcheda game. 我看完了一场比赛。 - A game
has been watchedby me. 一场比赛被我看完了。
1.3.1 提示词(9个重点)
- 当出现
for+时间段例如:for five days五天 since+时间点例如:since you arrive在……以后,自……以来by the+时间:by the time届时,By now现在完成时time可以改成为现在的时间by now,也可以改为将来的时间,过去的时间。 例如:by the end of this month
so far到目前为止(现在完成时)up to now到目前为止(现在完成时)yet已经- 3个
times(简便记忆)many/three/four/five times表示多次times表示次数
it is+序数词+time+that等词提示用现在完成时,例如:It is the first time that这是第一次this is+序数词+time+that
- 而具体使用现在完成还是过去完成,还是将来完成要看句子具体情况。
1.3.2 实际运用
- 强调事情已经完成,对目前造成影响或前后构成因果关系,
前者对后者造成影响。 - 完成时动词往往是延续性动词
我坐地铁去学校,我吃了俩包子。(没有因果关系)
我早上跑了2000米,我感到非常疲倦。
我 洗了(have taken a shower 先发生的事情使用完成时) 一小时的热水澡。我 感到(feel 前面的完成时对后面的事情造成的影响) 很疲倦。
1.3.3 举例
- Our economy
has maderapid progresssince 2008(since+时间点).since+时间点表示现在完成时,就此使用现在完成时has made。- 因为前面是现在完成时
has made,所以后面since we arrived,arrived使用一般过去时。 arrived抵达;抵港(arrive的过去式)
- Our company
had been founded(过去完成时)by the end of last year(by the+时间).end of last year去年年底(过去的时间),所以前面使用过去完成时。
It is the first time thatwe have come to this university.it is+序数词+time+that用现在完成时it was+序数词+time+that一般过去完成时的被动
So farIhave been abroadfive times.so far、five times现在完成时的提示词
- I've failed so
many times. - I
have watered(现在完成时the tree,and then IHave/has done)feel(tired.一般现在时do;does)- 过去浇水的事情给我后面造成的影响,因此前面是完成时,后面用一般时。
- 浇水是一般完成时,感到劳累是一般现在时。
翻译
- 2008年以来,我国经济发展迅速。
- 我们公司是去年年底成立的。
- 这是我们第一次来这所大学。
- 到目前为止我已经出国五次了。
- 我失败了很多次。
- 我给树浇了水,然后我觉得累了。
1.3.4 变成例题
-
Our economy () rapid progress since 2008.
A.made B.has made C.had made -
Our company() by now.
A.has been founded
B.has founded
C.found
答案:1.B 2.A(主语:Our company,谓语动词:found,公司主动创立还是被动创立。by now现在完成时的提示词Have/has done,现在完成时的被动Have/has been done)
1.3.5 总结
- 其中
so far、by now、up to now都是表示到目前为止,所以直接使用现在完成时。 since+时间点无论时间点是过去还是将来,主句用现在完成many times通常使用现在完成时by the time同时是时间状语从句特殊引导词。- By the time you arrive,I will have picked you up. (将来+完成)
1.3.6 练习
-
Mr Black often () fishing on Sundays.
A、went
B、goes
C、will go
D、is going -
The plane () at 10:00 p.m.…
A.leaves
B.have left
C.will be leaving
D.left -
Up to now the money () to help those suffering from the floods.
A.have collected
B.has been collected
C.have been collected
D.will have collected -
The life () greatly since 2000.
A.change
B.changing
C.changed
D.has changed -
When you buy this book,I ().
A、ride
B、riding
C、am riding
D、rid -
By the time I go to the library,you () to school.
A.come
B.came
C.will have come
D.will come -
It's the first time that the computer () since I bought it.
A、has been checked
B、will be checked
C、had been checked
D、is checking -
Betty will ring me up when she () in Beijing.
A.arrive
B.arrives
C.arrived
D.will arrive
答案及解析
- Mr Black
often(提示词,经常)() fishing onSundays(单词后面加了.s,表示每周末)
A、went
B、goes
C、will go
D、is going
- 经常重复的动作提示用一般现在时
often、always、usually、everyday、every year - goes:vi.前进;行走(动词原型go 的第三人称单数形式),
Mr Black是第三人称。
- The plane () at
10:00 p.m.(时刻表)…
A.leaves
B.have left
C.will be leaving
D.left
- leaves:v.离开;让...留下(动词原型leave 的第三人称单数),
plane是第三人称。
Up to nowthe money (B) to help those suffering from the floods.
A.have collected
B.has been collected
C.have been collected
D.will have collected
- up to now 到目前为止(现在完成时)
- money:第三人称单数
- 被动看主谓:
money主语;collect收集,ed表被动
- The
life(D) greatlysince 2000.
A.change
B.changing
C.changed
D.has changed
since+时间点现在完成时 have/has done(主动)life是第三人称has:have 的第三人称单数现在时,greatly:adv.大大地;非常;很。
- When you buy this book,I (C).
A、ride
B、riding
C、am riding
D、rid
- 前面
buy买 是瞬间动词,后面一定要用现在进行时be doing(主动)。 riding骑车
- By the time I go to the library,you (C) to school.
A.come
B.came
C.will have come
D.will come
by the+时间现在完成时,by the time届时同时在这里引导了一个从句- 主将从现:后面的主句中使用将来时,前面的从句使用现在完成时。
- will 将要
- It's the first time that the computer (A) since I bought it.
A、has been checked
B、will be checked
C、had been checked
D、is checking
It's the first time that提示词语,it is+序数词+time+that等词提示用 现在完成时bought买(buy 的过去式和过去分词)check检查(checked被动)computer计算机(主语),第三人称单数
- Betty will ring me up,when she (B) in Beijing.
A.arrive
B.arrives
C.arrived
D.will arrive
when she () in Beijing当她到达北京的时候 做时间状语Betty will ring me up贝蒂会给我打电话的(主句用了将来时will)- 后面从句用 一般现在时
arrives第三人称单数
1.4 现在完成进行时(可跳过)
-
现在完成进行时:
have/has been doing(一直在做某事,动作从过去持续到现在) -
I
have been lookingfor my book. 我一直都在寻找我的书。
1.4.1 实际运用
- 现在完成进行时是没有被动语态的,如果有现在完成进行时的主动结构的句子变为被动结构,可以用现在完成时。
- 完成进行时要翻译成“一直”或“已经”
练习(现在时)
-
Walmart,which is one of the largest American supermarket chains, () some of its stores open 24 hours on Mondays through Staturdays.
A.keeps
B.keep
C.have kept
D.had kept -
He used to have breakfast at nine o'clock when he lived alone.But nowdays he () it at ten.
A.used to have
B.is used to have
C.is having
D.has
二、过去时
2.1 一般过去时
- 一般过去时
did(主动) /was/were done(被动):过去的一般情况(发生在过去又没有特殊的词)- 记忆:
be动词+ed
- 记忆:
- I changed my mind. 我改变了我的想法。
- An entrance was blocked off yesterday. 昨天一个入口被封堵住了。
- 从句和主句时态一般要保持一致,从句如果用一般过去时,主句也要使用一般过去时。
2.1.1 实际运用(3个)
it is/(is high) time that句型中,that从句后的谓语动词用一般过去时或should do,其中should不要省略。在做题时,如果有一般过去时和should do2个选项,优先选择一般过去时。
it is/(is high) time that+一般过去时/should do- It is high that
we should study hard(should do). 很重要的是我们应该努力学习。 - It is high that
we should studied(一般过去时) hard.
- 如果句中出现了
yesterday、last year(去年)、just now(刚刚、刚才)等表过去的也用一般过去时。- We (C) a book
just now. - A、buy B、will buy C、bought
- 复数buys,第三人称单数buys,现在分词buying,过去式bought,过去分词bought
- We (C) a book
- 句子中出现了
for+时间段,且动词为非延续性动词(瞬间动词)时。(此类情况极其少见) in+年份在...(补充)
2.1.2 区分一般现在时和一般过去时(重点)
句中没有出现特殊的时态(时间)提示词,请用一般现在时或一般过去时。表常态或经常发生的事情时用一般过去时,如果强调过去用一般过去时。如下:I like playing football.我喜欢踢足球。(一般现在时)I liked playing football.我以前喜欢踢足球。(一般过去时)The rose is red.玫瑰是红色的。(一般现在时)The rose was red.玫瑰以前是红色的。(一般过去时)
- 一般过去时在叙事时,会像讲故事一样表达出来。
The hero saved the child.这个英雄救了那个孩子。
例题
- These pictures () on campus last week.
A、was taken B、were taken C、has taken D、have taken
- 解析
- These pictures () on campus
last week(上周,过去时).
A、was taken B、were taken C、has taken D、have taken
在选择谓语时要考虑时态、语态、三单
因为有last week所以排除AD选项。再看主谓一致,主语是These pictures复数are taken,are要用过去时所以用were taken。图片被拍摄,所以用被动语态。
翻译:这些照片是上周在校园里拍的。
答案:B
-
It is high time that we () hard.
A.should study B.study C.studied
答案:C -
We () a book just now.
A.buy B.will buy C.bought
答案:C
2.2 过去进行时
- 过去进行时:
was doing(主动) /was/were being done(被动)- 记忆:
was+动词ing(主动)/was/were+being done(被动) done:do的过去分词形式
- 记忆:
- 强调过去某一刻发生的事情,如警察盘问:昨天五点你在做什么?;也可以表示动作一直在进行(没有间断)
- When you arrived,I
was doinghomework.
举例
- When you arrived,I was reading.(过去进行时)
- When you arrive,I am reading.(一般现在时)
- I
was watching TVat home when it rainedlast weekend. 上周末下雨时,我正在家里看电视。 - The road
was beingbuilt lastlast year. 这条路是去年修建的。
动词为瞬间动词
2022真题
Tom () online,when his computer broke down.
A、was shopping
B、is shopping
C、shops
D、had shopped
解析
down坏掉(瞬间动词,过去坏掉的),主句应该用进行时broke弄坏;打碎;违反(break 的过去式形式)- 答案:A
was doing(过去进行时) - 翻译:因为他的电脑坏了,所以Tom在网上购物。
2.3 过去完成时
- 过去完成时:
had done/had been done- 记忆:
had+动词过去时/had+been+动词过去时
- 记忆:
- I
had watchedthe game for a long time yesterday. 我昨天看了一场比赛。 - 表示过去发生的事情,对后来的事情造成了影响,可以理解为过去的过去。
2.3.1 实际运用(3个提示词)
By the time在……时候:表示某个事件发生时的时间点,通常用来描述在某个特定时间之前或之后发生的事情。By 2020过去完成时by the end of last year到去年年底(过去完成时)
举例
- I
have cleared(现在完成时)my room.(先发生) Ifeel(一般现在时)very tired.(后感到疲倦) 我打扫了我的房间,我觉得很累。
feel后面是一般现在时,have cleared前面用现在完成时。- 因为我打扫了自己的房间,所以我感觉非常的疲倦。
- I
had cleared(过去完成时)my room.Ifelt(一般过去时)very tired. 我打扫了我的房间,我觉得很累。(过去的过去 -> 过去完成时)felt后面是一般过去时,had cleared前面用过去完成时。felt:感受到,体会到;觉得,相信;使人感觉……(feel 的过去式和过去分词)
- I
had waitedin line for an hour,then IrealizedI didn't have my wallet. 我排了一个小时的队,然后我意识到我没带钱包。
- 排队发生在没带钱包之前。
realized一般过去时,had waited过去完成时。(将2个动词画线,然后思考时态) - 先后关系 = 因果关系
- By the end of 2010,I
had hadthree books. 到2010年底,我已经有了三本书。
had done过去完成时have的过去分词是hadhad had是have的过去完成时
例题
- I (C) in line for an hour,then I
realizedI didn't have my wallet
A、will wait B.wait C.had waited
2.4 过去完成进行时(可跳过)
- 过去完成进行时:
had been doing(过去完成进行时表示动作从过去持续到现在就结束了。- 记忆:
had+been+动词ing
- 记忆:
- By the time Jane arrived we
had been waitingfor 3 hours. 到Jane到达的时候,我们一直等了三个小时。 - 完成进行时可以翻译成“一直”或“已经”
练习
-
Everybody () before she got to the station.
A.has left
B.had left
C.left
D.would left -
By the time he arrived,every one () medical care.
A.has received
B.will receive
C.had received
D.would receive -
I () in a car factory for two years before I came here.
A.have worked
B.worked
C.had worked
D.would work
解析
- Everybody (B) before she got to the station.
A.has left
B.had left
C.left
D.would left
翻译:在她到达车站之前(已经是过去了),大家都走了(过去的过去had done)。
- By the time he arrived,every one (C) medical care.
A.has received
B.will receive
C.had received
D.would receive
翻译:当他到达时,每个人都接受了治疗。
arrived是过去时,每个人都接受了治疗过去完成时
- I (C) in a car factory
for two years(完成时的提示词)before I came here(过去的过去).
A.have worked
B.worked
C.had worked(过去完成时)
D.would work
翻译:在我来这里之前,我已经在一家汽车厂工作了两年。
三、将来时
3.1 一般将来时
- 一般将来时(表示发生在将来的事情):
will/shall do(主动)/will/shall be done(被动)be going to do(主动)/be going to be done(被动)
will do≈be going to do- I
will dowell in the exam. 我将在考试中取得好成绩 - The gift
will be wrapped. 这个礼物将被包起来 - I
am going tothe park.be going to do(主动)我将要去公园。
3.1.1 实际运用(3个)
- 动作或事情还没有发生用一般将来时,表示将来的事情。
- 时间提示词:
next dat、next year、tomorrow、2035、in the future - 主将从现
例题
- I () the university in the future.
A.attend B.attended C.will have attended D.will attend
- 解析:提示词
in the future一般将来时will do(主动),选择D
- By the time I go to the library,you (C) to school.
A.come B.came C.will have come D.will come
- 解析:
by the time现在完成时的提示词,主将从现,主语用will be done - 第三人称单数: comes;现在分词: coming;过去式: came;过去分词: come
3.2 将来完成时
- 将来完成时:
will/shall have done/will have been done - EX:The work will have been finished tomorrow. 这个工作将在明天被完成。(很少使用被动)
- I will have finished my homework next week. 下周我将完成我的作业(将来才能完成的事情)
3.3 将来进行时
- 将来进行时:
will/shall be doing/无被动(表示将来某一时刻正在发生的事情) At 12 o'clock tomorrow, alarm will be ringing up.明天12点,闹钟会响。
3.4 将来完成进行时(了解)
- 将来完成进行时:
will/shall have been doing动作在将来某一时刻才能完成 - EX:By the time John retires,James will have been practicing for 10 years. 到约翰退休的时候,詹姆斯已经练了10年了。
特别注意
- 主将从现一般出现在状语从句中,和定语从句、名词性从名
- 主将从现只和状语从句有关:让步状语从句(虽然...)、时间状语从句(当...的时候)、条件状语从句(如果...)
- 主将从现,主情从现,主祈从现
at the time是时间状语,by the time才是完成时提示词。
拓展内容
(一)现在完成进行时和过去完成进行时的区别
- 现在完成进行时:表示动作从过去持续到现在,并且还可能进行下去。
- 过去完成进行时:表示动作从过去持续到现在就结束了。(刚刚结束)
(二)当我们看到完成时提示词( 的时候,for+时间段、by the time、so far)完成进行时也是考虑范围之一。也就是说,若选项中没有完成时的时候,我们可以选择完成进行时。
(三)既然我们提到完成时提示词可能也会考虑完成进行时。那么应该如何区分完成时和完成进行时?
- 完成时强调结果。
Ihave written(homework. 我写了作业。have done现在完成时)
written:write 的过去分词形式 - 完成进行时强调过程。
Ihave been writing(homework.` 我一直在写作业。have been doing现在完成进行时)
writing:write的现在分词
如下对话:
-- Why do you look so tired? 为什么你看起来如此疲倦?
-- I have been writing( it for two weeks. 我一直写了两周作业。have been doing)
例题
I () there with my friends every morning,since the opening of new sports park near my community.
A. have jogged
B. jog(慢跑)
C. are jogging
D. have been jogging
解析:
- 看到完成时的提示词
since+时间点考虑完成时和完成进行时,选项A强调结果,选项D强调过程。 - 翻译:自从社区附近新的体育公园开放以来,我每天早上都和朋友们去那里慢跑。
for+时间段的特殊用法
for+时间段可以使用完成时,同样可以使用一般过去时。一般来说当动词为延续性动词,句子使用完成时;当动词为非延续性动词(瞬间动词)则使用一般过去时。- 重点:
for+时间段考虑动词性质(延续性动词/非延续动词)- 延续性动词使用完成时
- 非延续动词使用一般过去时
例题
【例1】--I remember you were a talented pianist at college.Can you play the piano for me?
--Sory,I () the piano for years.
A.don't play
B.wasn't playing
C.haven't played
D.hadn't played
- 解析
- 1、for years(
for+时间段),play the piano弹钢琴(延续性动词使用完成时)
2、翻译:我好多年没有弹钢琴了。(是现在好多年没有弹钢琴了,使用现在完成时。不是以前好多年没有弹钢琴)
3、haven't现在完成时,hadn't played已经(用于过去完成时态)
4、答案:C
【例2】
--I remember you were a talented pianist at college.Can you play the piano for me?
--Sory,I () the piano for years.before i took part in other club.
A.don't play
B.wasn't playing
C.haven't played
D.hadn't played
- 解析
- 1、翻译:对不起,我弹钢琴好多年了。在我参加其他俱乐部之前。
2、“在...之前” 使用过去完成时
3、答案:D
【例3】He was unhappy when he sold his guitar.After all,he () it for a very long time.
A.has had
B.had had
C.has
D.had
- 解析
- 1、
for a very long time(for+时间段)使用完成时/一般过去时。
2、has(have的第三人称单数);had(have 的过去式和过去分词)
3、had拥有(延续性动词,使用完成时had done)
4、翻译:他卖掉吉他时很不高兴。毕竟,他已经拥有它很长时间了。
5、思路:拥有钢琴是在他卖掉吉他和不高兴之前。属于过去的过去(had done),答案B。
【例4(可跳过)】He () football regularly for many years when he was young.
A.was playing
B.played
C.has played
D.had played
- 解析
- 1、
for many years when he was young.(for+时间段)
2、regularly定期地(副词修饰动词play),“定期的踢足球”非延续性动词。
3、翻译:他年轻时经常定期地踢足球。(过去的一种常态:过去经常踢足球,而不是一直持续的动作。)
4、答案:B
【例5】His father () the party for more than 50 years.
A.joined
B.has joined
C.was in
D.has been in
- 解析
- 1、
for more than 50 years(for+时间段使用完成时,排除AC选项)
2、join加入(瞬间动词)
3、has joined已经加入了(瞬间动词),has been in一直在(延续性动词)
4、翻译:他父亲入党50多年了。
答案:D
四、过去将来时(可跳过)
- 他
曾经(使用过去时)说他将会(使用将来时)成为一名教师。
时态/语态总结
结合语态
- As we all know,he never ().
A.smoking
B.smoked
C.smokes
D.to smoke
- 解析
- 1、没有时间提示词,表常态。
2、翻译:我们都知道,他从不抽烟。
3、he第三人称单数
4、答案:C
- See the clouds!It () rain!
A.will
B.is going to
C.must
D.would
- 解析
- 1、翻译:看那些云!将要下雨了!
2、will主观的将要,is going to(be going to do一般将来时) 客观的将要
答案:B
- Look!He () a red shirt today.
A.wears
B.wear
C.is wearing
D.wore
- 解析
- 1、前面是
look、should这些词语时,都是进行时。
2、答案:C
- -What did the teacher say just now?
-Sorry.I didn't catch it.I () something else.
A.think about
B.will think about
C.was thinking about
D.thought about
- 解析
- 1、
thought认为,觉得;思考,考虑;想做,打算做(think 的过去式和过去分词形式)
2、翻译:我没听清楚,我当时在想别的事。
3、答案:C(结合语境)
- ---Have you moved into the new house?
---Not yet.The rooms ().
A.are painting
B.are being painted
C.are painted
D.have painted
- 解析
- 1、根据语境选择,房子正在被粉刷
2、答案:B
位置:9:30
没有提示词时,容易弄混的两个时态
- 一般过去时
- 现在完成时(动词往往是延续性动词)
I opened the window. 我打开窗户。(现在的状态不清楚)
I have opened the window. 现在窗户是开的
He wrote a book. 他写了一本书
He has wrote a book.他写了一本书
时态/语态练习
- —— How is he getting along with the difficulty?
—— He () it by the end of last week.
A、overcome
B、had overcome
C、overcomes
D、has overcome
- 解析
- 1、
overcome:克服,解决;征服,战胜,使受不了,do一般现在时;
2、had overcome:过去完成时had done
3、overcomes:一般现在时does
4、has overcome:现在完成时have/has done
5、第三人称单数overcomes,现在分词overcoming,过去式overcame,过去分词overcome。
6、句意:他如何应付的困难?到上周末他已经克服了。
7、根据"by the end of last week可知,此句时态是过去完成时,故选B。
- A new school () in our neighborhood
next year.
A、built
B、was built
C、will build
D、will be built
- 解析
- built:
build的过去式和过去分词形式
1、built建造,动词过去式或过去分词;
2、was built被建造,一般过去时被动语态;
3、will build将建造,一般将来时结构;
4、will be built将被建造,一般将来时被动语态。
5、A new school与谓语动词build之间为被动关系,应用被动语态
6、根据next year"可知,时态为一般将来时,
7、所以此处用一般将来时的被动语态,结构为:will be done。故选D.
8、句意:明年我们附近将建一所新学校。考查动词语态
- A speech on robots () in the school hall next Friday afternoon.
A、gives
B、is given
C、will give
D、will be given
- 解析
- 1、
gives一般现在时
2、is given一般进行时
3、will give一般将来时
- Sally () on the phone,so i just passed her without saying anything.
A、has talked
B、will talk
C、was talking
D、talked
- 解析
- 1、翻译:萨莉正在打电话,所以我一言不发地从她身边走过。
2、从翻译中我们可以看出发生了2件事情,一是走过去,二是打电话。事情2是在事情1之前发生,所以“打电话”是过去进行的事情。
3、强调过去某一时刻正在做某事,用过去进行时,答案:C
- The videos about cooking tell us how food ()
A、makes
B、made
C、is made
D、was make
- 解析
- 1、
cooking现在时
2、翻译:这个关于烹饪的视频告诉我们食物是如何制作的。
2、该句是对现在情况的描述,则应用一般现在时
2、从句主语food和谓语make是被动关系,则此处应用一般现在时的被动语态,其结构是主语+is/am/are done。故选C。
- The boys () loudly when the teacher came into the classroom.
A、talk
B、talked
C、are talking
D、were talking
- 解析
- 1、翻译:当老师走进教室时,男孩子们正在大声说话。本题考察过去进行时。
2、when引导的时间状语从句,从句中的谓语动词是came,一般过去时,排除主将从现(从句都用过去时了,哪还有主将从现呢)。
3、从句和主句时态一般情况下要保持一致,从句使用了过去时,主句也要使用过去时(注意,这里说的是过去时,过去时包含过去进行时、过去完成时、一般过去时等)
4、当老师走进教室时,came是瞬间动词,强调的是某一时刻,两者结合起来,主句用过去进行时,答案选择D。
- Up to now,Beijing () the first city in the world to host both a summer and winter Olympic event.
A、has become
B、cecomes
C、has been
D、was
- 解析
- 1、句意:到目前为止,北京是世界上第一个既举办过夏季又举办过冬季奥运会的城市。
2、根据“Up to now”可知,此处用现在完成时,排除BD两项。时间状语“Up to now”,表,示时间段,与延续性动词连用
3、become"成为”,是瞬间性动词; be“是”,是延续性动词;故选C。
- While one gest furious, he () some inappoppriate decisions.
A、is going to make
B、made
C、makes
D、is made
总结
- 时态(现在/过去/将来)、语态、三单
- 在填写动词时,先看这个动词的主语的语态。
- 看清主宾,选择单复数
- 延续性动词和非延续性动词
- 过去式和过去完成时区别在哪里?
- 完成时:过去对现在造成的影响
- 主被动看主语和谓语
- 句中同时出现
everyday和so far时选择语态,看强调常态(一般现在时)还是过去对现在的影响(现在完成时)?
第三章 主谓一致
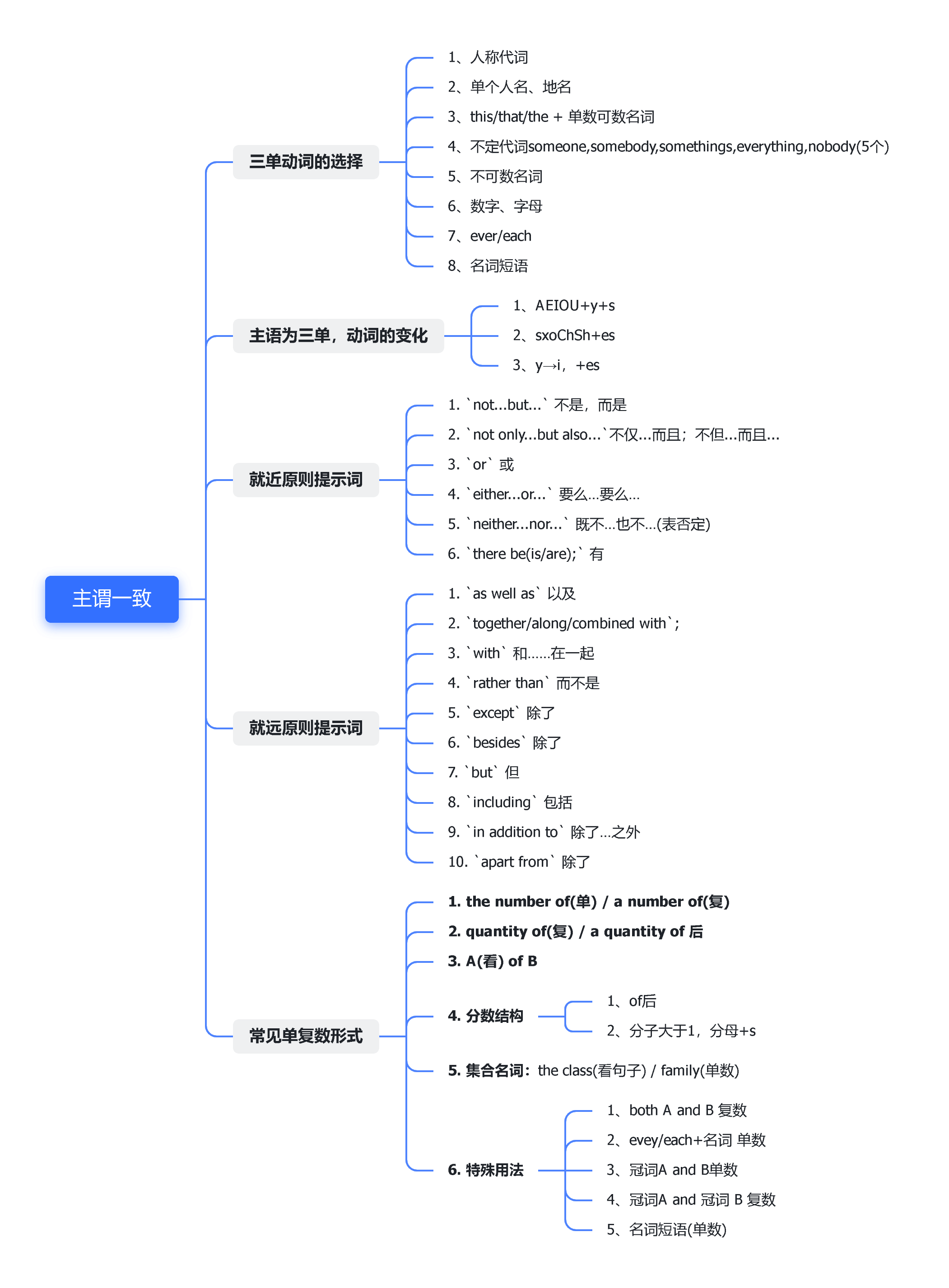
第三人称单数
- 第三人称单数的定义:可以理解为,除了“你
you(们)”、“我(们)”以外的人称都是第三人称,如:it(它)、he(他)、then(他们)。 - 个数为"1”则称为单数。
- 满足以上两个条件的主语为第三人称单数。如:
he(他),a volunteer,Jack(姓名),a desk(物品)均为三单。此时动词要写为三单形式()。
三单动词的选择(重点)
- 主语是
i→ be动词用am,动词看时态选择 - 主语是
we/you→ be动词用are,动词看时态选择 - 主语是
he/she/it→ be动词用is/动词+s - 总结:主语是第三人称单数(
he/she/it)时动词要加s,也就是我们常说的动词的第三人称单数形式,若动词为be动词,则写为is。 - 主语是复数,动词用原型;主语是单数,动词用三单。
其他的三单情况(重点)
- 人称代词
he/she/it是第三人称单数 - 单个人名、地名或称呼作主语,是第三人称单数
- 单数可数名词或"this/that/the+单数可数名词"作主语时,是第三人称单数。
- 不定代词
someone,somebody,somethings,everything,nobody(5个)等,及指示代词this,that作主语时,是第三人称单数。 - 不可数名词作主语时为第三人称单数。
- 当数字或字母作主语时,看作第三人称单数。
- 当
every、each等词修饰单数或复数,看作第三人称单数,如:every students。 - 动名词短语是三单
三单的用法
(1)当主语为第三人称单数时,动词要用第三人称单数形式。
(2)谓语动词的第三人称单数形式只发生在一般现在时中。
(3)所谓动词“s”型的构成,可按名词变复数的规则来记。
常见的单复数形式(重点)
- 统一理解为:
- 谓语动词用单数形式 → 谓语动词用三单
- 谓语动词用复数形式 → 谓语动词不用三单
- 主语是三单,动词用三单形式;主语不是三单,动词不用三单形式
一、名词后常见的谓语动词的单复数形式
(一) number of类
-
用法
(1)the number of...,意为“…的数量”,其后的谓语动词用单数形式。The number of特指一类群体。
(2)a number of...,意为“大量的、许多”,其后的谓语动词用复数形式。 -
例句
①The number of citydwellersis growing. 城市居民的数量日渐增长。
②A number of friendssupportmy view. 许多朋友都支持我的观点。
动词的第三人称单数形式
动词分类(助动词、实意动词、系动词、情态动词)
- 助动词:在句子中充当成分,但没有实际意义。
- 助动词:I
was(was表示被动语态,充当了含义) presented with a prize;Ihavefinished the work. 我被授予奖品,我已经完成了这项工作。 - 实意动词:有具体含义的词(基本能够做出动作的词)
- 实意动词:I
buy(买)a cake. - 系动词:be动词、感官动词、变化、保持。
- 情态动词:情态动词+动词原形,构成谓语动词
- 情态动词:I
must buya cake. - 常见的情态动词:
can(could)、may(might)、must、need、ought to、dare(dared)、shall(should)、will(would)(重点)
- 情态动词:I
中文举例:
- 你今天
吃(动词)饭了吗? - 你
看(动词)得清吗?
英文举例:
- he
imitatesmy action. 他模仿我的动作。 - she
selectsher book from the bag. 她从包里选择了她的书。 - I
persuadeyou getting from here. 我劝你离开这儿。 - you
talk withme. 你和我交谈。 - he
isa volunteer. 他是一个志愿者。 - you
area kingdom. 你是一个国王。 - we
arefamily. 我们是一家人。 - I
amthe best player in the world. 我是世界上最优秀的运动员
主语是三单时,动词的变化(重点)
-
在动词尾直接加
s,或圆音字母AEIOU+y结尾的单词,后面直接+s。如:
play—plays,want—wants,work—works,know—knows,help—helps,get—gets -
以字母
s、x、o、ch、sh结尾的动词 +es;如:
guess—guesses,fix—fixes,teach—teaches,brush—orushes,go—goes,do—does,watch—watches,catch—catches -
以辅音字母(除了圆音字母
AEIOU以外的全部是辅音字母)+y结尾的动词,先变y为i,再+es。如:
study-studies,carry-carries,fly-flies,worry-worries
就近原则+就远原则
- 什么是就近原则?
- 答:当一个句子中出现了多个主语时,根据就近原则提示词,判断谓
语根据哪一个主语来选择动词的形式。
I or you.I or you () a handsome boy.我或你是一个英俊的男孩。- 当一个句子中出现了多个
主语时,根据就近原则提示词,判断谓语根据哪一个主语来选择动词的形式。那么我们则根据离谓语动词最近的这个主语选择i/you谓语动词用哪一个。is/am/are
就近原则的提示词(重点)
not...but...不是,而是not only...but also...不仅...而且;不但...而且...or或either...or...要么…要么…neither...nor...既不…也不…(表否定)there be(is/are);有
就近原则的例句:
- Neither you nor he is tired. 你和他都不累。
- He or I am in the wrong. 不是他就是我错了。
- Not you but I am to win. 不是你而是我要赢了。
- Not only the students but also their faculty is enjoying in this movie. 不仅是学生,连教师也很喜欢这部电影。
例句解析:
Neither you norheis(离动词主语最近的是tired. 你和他都不累。he)- He
orIamin the wrong. 不是他就是我错了。 NotyoubutIamto win. 不是你而是我要赢了。Not onlythe studentsbut alsotheir(主语) facultyis(动词) enjoying in this movie. 不仅是学生,连教师也很喜欢这部电影。
就远原则
- 当一个句子中出现了多个主语时,根据就近远则提示词,判断谓语根据哪一个主语来选择动词的形式。
I(主语)as well as(提示词)you(主句)am(动词)a fan of the Little Blue Book.
那么我们则根据离谓语动词较远的这个主语选择谓语动词用哪一个。
就远原则常见提示词(重点):
as well as以及together/along/combined with;with和……在一起rather than而不是except除了besides除了but但including包括in addition to除了…之外apart from除了
例句
Everybody(离动词远的主语)except(提示词)youis(就远原则,be用三单is)down(动词)on me. 除了你,大家都看不起我。John(离动词远的主语),rather thanhis roommates(主语),is(三单用to blame. 约翰,而不是他的室友,应该受到责备。is)Jim,together withhis classmates,has(三单)seenthe film. 吉姆和他的同学一起看了这部电影。The son,as well ashis parents,wants to go there. 不但儿子想去那儿,而且他的父母也想去。A womanwithtwo childrenhas(三单)come.
一位妇女带着两个孩子已经来了。has come完成时
2022真题
- Bob () his parents often takes a-long walk in the evening.
A.and
B.both
C.as well as
D.but also
- 解析
- 1、当看到
as well as时就要想到就远原则
2、主语Bob单数;主语his parents复数
3、动词takes使用了三单,说明主语选择了一个三单的主语。所以选择就远原则
4、答案:C
习题
- Either Bill or you () on duty yesterday morning.
A.is
B.are
C.was
D.were
- 解析
- 1、主语
Bill三单,you后面接are。
2、or就近原则,yesterday过去式
2、答案:D
- Not only I but also Willian and Joe () tired of having so many examinations.
A.am
B.is
C.are
D.be
- 解析
- 1、
Not only I but also就近原则
2、主语I单数,Willian and Joe复数,选择C
- Neither Tom nor Henry and Jack () how to solve this problem.
A.know
B.knew
C.knows
D.knowing
- 解析
- 1、
neither nor就近原则
2、Tom三单,Henry and Jack复数,动词不用复数形式,所以排除选项C,选项D不是谓语动词
3、没有任何时间提示词,表常态,选择A
- The teacher and writer,as well as many guests () invited to the party held yesterday.
A.is
B.were
C.are
D.was
- 解析
- 1、
as well as就远原则
2、主语The techer and writer单数,排除BC,many guests
3、yesterday过去时,答案:D
- The teacher,with 6 girls and 8 boys of her class,() visiting a museum when the earthquake struck.
A.was
B.were
C.had been
D.would be
- 解析
- 1、
the teacher单数
2、with就远原则
3、提示:此处的struck为strike的过去式
4、提示:when...,the teacher正在做什么进行时考点,由于struck是过去式并且是瞬间动词,所以主句是过去进行时,答案:A
be 动词的三单现在时用is,过去式用was,请答题:
1.Amy, as well as her brothers,________ (give) a warm welcome last week. (所给词的适当形式填空)
2.The number of people present at this meeting now________ 300.(be)(所给词的适当形式填空)
3.Not only the students but also the teacher________(be) invited. (所给词的适当形式填空)
4.Either you or she________(be) to go to take care of the sick old man. (所给词的适当形式填空)
5.Neither his parents nor he_________(know) anything about it now. (所给词的适当形式填空)
- 解析
- 1、
as well as就远原则,Amy三单(单数),last week过去式was done,答案:was gave
2、the number of单数,答案:is
3、Not only...but also...就近原则,teacher单数(is),invited被邀请(be done),答案:was
4、either...or...要么...要么...(就近原则),she三单,答案:is
5、neither...or...就近原则,he三单,答案:knows
常见的单复数形式(重点)
一、英文中名词常见的单复数形式
(一)number of类
- 用法:
(1)the number of单数,意为“...的数量”,如:the number of cars
(2)a number of复数,意为“大量的、许多” - 例句:
- The number of friends
is(主语是单数,动词is使用三单)nine. 朋友的数量为9个。 - A number of friends
support(主语是复数,动词不用三单)my view. 许多朋友都支持我的观点。support:复数supports,第三人称单数supports
- The number of friends
(二)quantity of类
- 用法:
(1)quantities of复数,意为“许多、大量的”
(2)a quantity of单复数由of后面的名词决定,若of后面名词为不可数整体看作单数,若of后名词为复数则整体为复数,意为“一些” - 例句:
(1)Quantities of peoplewear(主语是复数,动词不用三单)masks. 许多人戴着口罩。
(2)A quantity offlowers(“花”可数复数,整体就是复数)have(动词用复数形式)withered. 很多花都枯萎了。
(3)A quantity ofmoney(不可数名词,整体就是单数)is(动词用三单)lent to you. 许多钱都借给你了。
(三)A of B结构
- 用法:
(1)A of B本结构单复数取决于of前者- 翻译:
A of B翻译为B的A,color of cars车的颜色
- 翻译:
- 例句:
(1)Thecolor of cars(color不可数,单数)is(主语单数用is)red. 汽车的颜色是红色的。
(2)Thepackages of the gift(packages复数)are(主语是复数)very beautiful. 礼物的包装非常漂亮(包装为复数)
(四)分数结构(重点:分数看后者)
- 用法:
two fifths of...五分之二,分数结构单复数取决于of后者one-third of...(同a third of) 三分之一,分数结构单复数取决于of后者- 分子大于1,分母要+s,上同。如:
two-thirds of - 前面基数词,后面序数词
- 分子大于1,分母要+s,上同。如:
70 percent of...百分比结构单复数取决于of后者
- 例句:
(1)Two fifths of thebooks(复数)areblack. 五分之二的书都是黑色的。
(2)One fifth of the books are new. 五分之一的书都是新的。
(3)One-third of the books are old. 三分之一的书都是引旧的。
(4)70 percent of thefactoryis ours. 百分之七十的工厂是我们的。
(五)集合名词
1.用法:
(1)the class 表示整个班级(物,名词)时为单数,表示全体同学(人)时为复数
(2)family 表示整个家庭时为单数,表示家庭成员时为复数
2.例句:
(1)The class support this decision. 全班同学都支持这个决定。(由于只有人才能支持,所以我们可以判断出the class为全体同学。)
(2)The class ranks(三单) first in grade. 班级排名年级第一。(根据意思判断,不可能是全体同学排名年级第一,应该是班级,所以动词用了三单形式。)
(六)特殊用法
-
用法:
(1)both A and B复数,2个人,意为“A和B都.”
(2)evey/each+名词单数,意为“每、每一个”
(3)冠词A and B单数,意为“A兼B”,A和B为一个人的两个身份
(4)冠词A and 冠词 B复数,意为“A和B”,A和B为两个人。
(5)名词短语单数,如:taking part in activities整体看作名词。 -
例句:
(1)Both pencils and erasersare(主语是复数)our stationery.铅笔和橡皮擦都是我们的文具。
(2)Every studenttakes(主语是单数,三单)part in the activity. 每一名学生都参加了这个活动。
(3)The teacher and writeris(主语是单数,三单)my friend
这名教师兼作家是我的朋友。
(4)The teacher and the writerare(主语是复数,2个my friends.这名教师和这名作家都是我的朋友the,特指2个人)
(5)Reading books is a good habit. 读书是一种好习惯。
二、英文中定语从句先行词常见的单复数形式
- 用法
(1)the only one of+复数名词+定语从句(唯一的一个),定语从句动词用三单形式,
(2)one of+复数名词+定语从句定语从句动词由修饰词决定。 - 例句:
(1)He is the only one of students who is selected. 他是唯一一个被选中的学生
(2)He is one of students who are selected. 他被选中的学生之一。
练习
- () she () I have read the e-mail.We know nothing about it.
A.Both;and
B.Either;or
C.Neither;nor
D.Not only;but also
- 解析
- 1、动词
have原型,就近原则,答案:C
both...and...两者都,带入句中:两人都读了
Either...or...要么...要么...
Neither;nor既不...也不...,带入句中:他既没有读,我也没有读
Not only...but also不仅...而且
- Amy,as well as her brothers,() a warm welcome when returning to the village last week.
A.is given
B.are given
C.was given
D.were given
- 解析
- 1、
as well as以及(就远原则)
2、Amy三单,last week过去式,答案:C
- Three fifths of the students () going to Nanjing for the Study Trip(研学旅行) next month.
A.are
B.is
C.be
D.were
- 解析
- 1、分数看后面,
students可数复数,排除BC,
2、be going to do表将来,答案:A
- The number of the doctors from Chongqing () 1636.
- 解析
- 1、
The number of the doctors单数
2、来自重庆的医生人数是1636人。表事实,用is
- Look!The boy () by the pool and drinking apple juice now.
A.sit
B.sits
C.is sitting
D.are sitting
- 解析
- 1、
now、Look进行时
2、The boy三单
- A number of used textbooks () to the village schools last month.
A.give away
B.gave away
C.are given away
D.were given away
- 解析
- 1、
A number of大量许多(复数),动词用are
2、last month过去式was/were done
3、主语textbooks,given赠送,被动,答案:D
- The population of India () than that of Malaysia.
A. arr bigger
B. is less
C. are amaller
D. is larger
- 解析
- 1、句意:印度人口比马来西亚多。
2、考查主谓一致和形容词比较级。population意为“人口”,是不可数名词表单数,be动词用is,排除A、C
3、less更少;larger更多的;英语中常用“large/big”或“small”形容人口“多”或“少”。故选D。
4、注意!如果主语是the population往往是不可数名词,但如果是几分之几population那么是复数形式。
三单总结
- are一般现在时,主语是复数
- is一般现在时,主语是单数
- was一般过去时,主语是单数
位置:3.4习题讲解
易错可数/不可数名词
- 可数名词:
- 不可数名词(用
is):money、population(人口,large/big/small形容人口“多”或“少”)、
- 主语是
the population往往是不可数名词,但如果是几分之几population那么是复数形式。
第四章 非谓语动词
谓语动词:一句话中有且只有一个,并且拥有完整的时态语态。
非谓语动词:不作谓语的动词,非谓语动词作主宾表定状
一句话中如果有2个动词,一个作为谓语动词,另一个要改成非谓语动词。
非谓语动词举例
- 弹钢琴是一件很难的事情。(
play the piano) - Play the piano
isa difficult thing.
我们前面说过了,动词不能做主语,
play the piano主语,将动词改成动名词,其中动名词短语属于三单。
Playing the piano is a difficult thing.
英文举例:
- My favorite thing
is(谓语动词)reading(非谓语动词). - I
stand(谓语动词) outsidewaiting(非谓语动词) for Mr.Chen.I Climbing mountain(非谓语动词)is(谓语动词) very interesting.- I
contacted(谓语动词) my teacherto ask for(非谓语动词) advice.我联系我的老师寻求建议。(不定式to do,表示目的/将来)
- 尝试一下
- 我看到Jim在打篮球用非谓语怎么说?
I(主语)see(谓语动词) Jim play football.
一、非谓语动词的分类:
- 不定式
to do,表示目的/将来 - 分词
doing/donedoing现在分词,进行、主动,主动进行的动作- I stand outside
waiting(等待,表动作) for Mr.Chen. - My favorite thing is
reading(阅读,动名词). Climbing mountain(登山,动名词) is very interesting.
- I stand outside
done过去分词,完成、被动- I stand outside waited. 我站在外面被等待.
- Tom
lives(谓语动词) in lunatic hospital,Tom studied(非谓语动词,被研究).
- 动名词
doing,仅改变词性,不改变意思。- My favorite thing is
reading(阅读,动名词).read动词
- My favorite thing is
词性区别
wait
to wait不定式:为了等待(去等待)、将等待waiting现在分词:正在等待、主动等待waited过去分词:被等待、已经等了waiting动名词:等待
purchase 购买
to purchase不定式:为了购买(去购买),将购买purchasing现在分词:(主动)正在购买purchased过去分词:(被动)已购买purchasing动名词:购买- the price of this television purchased increases. 已经购买的电视机涨价了。
二、非谓语动词的变型:
2.1 不定式:
to do(主动) /to be done(被动)to have done(为了完成...) /to have been done(为了被完成...)to be doing/to be being done
I contacted my teacher to ask for advice. 我联系我的老师寻求建议。
I contacted my teacher to be guided. 我联系了我的老师寻求被指导。
2.2 动名词:
- 关注idols be able to close our distance. 偶像可以拉近我们的距离。
- Paying attention to idols
isable to close our distance. 关注偶像可以拉近我们之间的距离。
- Paying attention to idols
- Being noticed has affected my normal life. 受到关注影响了我的正常生活。
be noticed被关注,to be done(被动)
2.3 现在分词:
- I
had wateredthe tree,then Ifelttired. 我给树浇了水,然后我觉得累了。- I
havingwatered the tree,then I felt tired.
- I
- The tree
had been wateredby me,then I felt tired.- The tree
having been wateredby me,then I felt tired.
- The tree
do → doing
have/had done → having done
have/had been done → having been done
2.4 过去分词
I was hinted,I worked this problem out. 有人暗示我,我解决了这个问题。
位置:终极语法4-2,1:00:00
第四章 非谓语动词
- 谓语动词:一句话中有且只有一个,并且拥有
完整的时态语态。 - 非谓语动词:不作谓语的动词,非谓语动词作主宾表定状
例子
The book () is blue.填写定语- 什么能作定语?形容词非谓语定语从句介词短语
一、非谓语动词的分类
- 不定式
to do表示目的/将来 - 分词
doing/done- ①现在分词:
doing表示进行、主动 - ②过去分词:
done表示完成、被动
- ①现在分词:
- 动名词
doing仅改变词性,不改变意思
例子
- 动词
work:不定式to work(为了工作/将要工作) help:帮助(表动词,帮助...)to help(不定式):为了帮助/将会帮助helping:正在帮助/主动帮助helped:被帮助已经被帮助helping:帮助(名词)- 原型:
have helped,动名词形式为haing helped
非谓语动词分类(总结)
- 不定式
to do:为了.../将要...to be done:为了被.../将要被...to have done:为了完成...to have been done:为了被完成
- 动名词
doing:不改变词意仅改变词性变为名词being done:不改变词意仅改变词性变为名词
- 分词
- 现在分词
doing:主动进行having done:完成时的主动having been done:完成时的被动being done:正在被...
- 过去分词:
done(被动、完成)
- 现在分词
三大分类的变型及含义示例
- 以
eat为例
①动名词:eat → eating吃(意思不变,仅从动词变成名词)
②现在分词:eat → eating正在吃
③过去分词:eat → eaten被吃完
④不定式:eat → to eat将要去吃 - 以
have eaten为例
①动名词:have eaten → having eaten已经吃了(名词)
②现在分词:have eaten → having eaten正在吃(动词)
③不定式:have eaten → to have eaten为了听 / 将要吃 - 以
make为例
①动名词:make → making制做(意思不变,仅从动词变成名词)
②现在分词:make → making正在制做
③过去分词:make → made被制做
④不定式:make → to make将要制做
二、非谓语动词能充当什么成分(重点)
非谓语动词能充当什么成分
①动名词
②分词(现在分词、过去分词)
③不定式
①主语、宾语、表语可以是:动名词、不定式
②定语可以是:分词、不定式
③状语可以是:分词、不定式
三、常考考点及应用一
- 省略主语,非谓语动词在句首(又称非谓语动词做状语,本类考点往往是两句话,中间会有一个逗号隔开;本类考点有时可能有从句引导词在句首。非谓语中能够做状语的只有
分词、不定式) - I
get up(起床) early this morning,Ispend(花了) five minutes. 我早上起床很早,我花了五分钟。get up起床和spend花了,是2个动词,一句话中不能出现2个动词原型,所以是错误的。Getting up(起床) early this morning,i spend(花了) five minutes.省略主语,非谓语动词Getting up(起床)在句首,非谓语中能够做状语的只有分词(doing:主动进行)、不定式。I get up(起床) early this morning,spending(花了) five minutes.I get up(起床) early this morning主谓宾完整,spending(花了) five minutes.作状语,能够做状语的只有分词、不定式。(总结:当主谓宾完整时,就要看其他句子是否是作状语,状语只有分词、不定式。)
getting up early this morning,i spend(花了) five minutes.
示例一
- 示例(填写go的形态):
____(go) to the famous school,I study hard. I study hard.有主谓宾,主句完整。____(go) to the famous school因为逗号隔开,所以这句状语。(注意:一般逗号隔开,且在句首的就是状语。其中状语只有分词、不定式)- 找到状语中被省略的主语
i,I ____(go) to the famous school,I study hard. - 判断分词的关系
- 考虑时态变化
- 根据题意翻译句子:我为了去著名的学校,所以我努力学习。
- 因此填写
to go,I to go(go) to the famous school,I study hard.
- 找到状语中被省略的主语
示例二
she ____(go) to the famous school,I study hard.她想要去著名的学校,所以我努力学习。- 填写:
to go
示例三
- 示例:
if ____(ask) to do the job,I will agree with you. - 补充主语:
if i ____(ask) to do the job,I will agree with you.,翻译:如果我被要求(询问)去工作,我将会同意和你一起。 - 填写过去分词:
asked(被动)或having been asked(完成时的被动)
总结(非谓语动词)
①找到被省略的主语
②考虑是否有不定式的关系
③判断分词的关系
④考虑时态变化
四、常考考点及应用二
- 动名词的考点(又称非谓语动词做名词,往往是一句话,句中已有谓语动词,句子缺少主语、宾语、表语;虽然不定式也可以充当这些成分,但总体考得比较少,本类考点使用最多的是
动名词。)
- (1)
Taking exercise can improve our immunity.锻炼身体(一件事情)能够提高免疫力。- 动名词
doing/being done和不定式to do做主语。 - 动名词
doing/being done和不定式to do需要考虑被动。
- 动名词
- (2)
Making friends broadens our circle of friends.交友拓宽了我们的朋友圈。
动名词和不定式的区别
- 动名词和不定式的区别:动名词表示的是一件事情;不定式
to do是将要发生的事情。 my drear is to be a doctor.我的梦想是成为一名医生。(将来会发生的事情,用to do)
五、常考考点及应用三
- 直接将非谓语与其前面的名词进行比较(又称非谓语动词作定语,本类考点特点是通常为一句话,在主句中内容基本成分完整,不缺少主谓宾,非谓语动词中能够充当定语的只有:分词、不定式)。
The student loving his country is my friend.这名热爱祖国的学生是我的朋友。The student is my friend.这名学生是我的朋友。(主谓宾都有,主谓完整)loving his country热爱祖国做定语,学生和热爱祖国之间为主动热爱
The student praised by the teacher is my friend.这名被老师表扬的学生是我的朋友。- 学生和表扬之间为被表扬
The student to be praised is my friend.这名将要被表扬的学生是我的朋友。- 学生和将被表扬之间是将来、被动的关系,所以用了不定式的被动语态
总结:一名话中,主句(包含主谓宾)完整时,定语一般在名词或代词的后面,状语一般使用逗号隔开。在定语中,动词又分为分词(现在分词和过去分词)和不定式to do。
总结:非谓语动词(背诵)
- 找到被省略的主语
- 句子完成:补充状语(逗号隔开)、定语(在名词/代词后面)
- 句子不完成:补充主宾表
- 考虑是否有不定式的关系
- 判断分词的关系
- 考虑时态变化
六、短语only to do
only to do(主动)/only to be done(被动)表示意想不到(意料之外)的结果。doing表示顺其自然的结果。- 介词后面+动名词
短语
only to find却发现only to be told却被告知
to do和doing的区别
- 此类题目的考点在于,
doig是动名词,强调事情或已经发生事情的过程;to do是不定式强调动作或将来。 - 固定搭配:
enjoy doing喜欢做;乐于做;享受的事情 动词+doing:stop doing停止一件事情,stop talking停止讲话动词+to do:stop to do停下来去做某事,stop to read停下来去看书remember doing记得做过某事remember to do记得去过某事
位置:unit11
第五章 名词性从句
从句的定义:从句本质上也是一个句子,作为一个句子,就必须得符合英语句子的基本结构。另外,从句都有一个引导词,所以,引导词+一个完整的句子=从句。这也是从句与主句的区别所在。
例子
例一
原句:她非常喜欢我(这件事,表主语)众所周知(形容词)。
补充:她非常喜欢我(这件事,表主语)是(系动词)众所周知的(形容词)。
句子结构:xxx(主) is(系) know(表).
主语:名词、代词、从句、动名词、名词短语、不定式
主语“她非常喜欢我”不是名词、代词、动名词、名词短语、不定式
,主语是一个句子(含有主谓宾),因此从句(句子)做主语。
主语从句属于名词性从句,因此that xxx is know
例二:主语从句
- 原句:
____ she likes me is known to us. - 句子结构
- 主语:
____ she likes me,主谓宾都有,主语是一个句子。一个句子如果是主语那么它就是主语从句,因此前面要填写一个引导词。 - is(系动词)
- 表语:
known to us
- 主语:
例三:宾语从句
- 原句:
his friend said ____ she likes me. - 句子结构
- 主语:
his friend - 谓语:
said - 宾语:
____ she likes me,主谓宾都有,宾语是一个句子,所以是宾语从句。
- 主语:
知识点
从句:主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句,通过分析句子,从句作做么成分叫xx从句。
名词性从句是由一个从句来充当名词的作用。因为某些时候一个单词作主语、宾语、表语,不能完整地表达我们所需要的意思,所以我们需要一个句子来表达。
名词性从句举例
- 我(主语) 认为(动词) 森林是地球的肺(宾语是一个句子,所以是宾语从句)。
- 我(主语) 听到(动词) 他昨天被老师批评(宾语是一个句子,所以是宾语从句)。
- 我们(主语) 坚持(动词) 每天运动可以保持健康(宾语是一个句子,所以是宾语从句)。
- 我们坚持每天运动(主语是一个句子,所以是主语从句) 可以(动词) 保持健康。
名词性从句分类
①主语从句
②宾语从句
③表语从句
④同位语从句(在句子中不充当基本成分)
一、从属连词(记忆)
从属连词:在句子中不充当成分。
| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 用法 |
|---|---|---|
| that | 无任何含义 | 用于句子完整、不缺少含义、不缺少成分的时候使用 |
| whether | 是否 | 可以用于句首,常与or not连用,不用于否定句中 |
| if | 是否 | 不用于句首,不和or/or not连用 |
例子
- 我(主语) 认为(动词) 森林是地球的肺(宾语是一个句子,所以是宾语从句)。
- 引导词
that:I think that 森林是地球的肺
- 引导词
- 我想知道我是否能够出去玩。
- 我(主语) 想知道(谓语) 我是否能够出去玩(宾语)。
- I went to know
i can go out or not(宾语完整,但缺少含义). - 缺少含义:want to know whether(是否) I can go out or not.(句中有
or not,所以whether)
- 我想知道你到达的时候。
- 我(主语) 想知道(谓语) 你到达的时候(宾语完整,宾语从句)。
- I went to know
you arrive(你到达的时候). - 缺少含义:I went to know
when you arrive.
二、连接副词
连接副词:使用在从句成分完整,但缺少含义的时候。连接副词不充当成分的引导词,只充当含义。
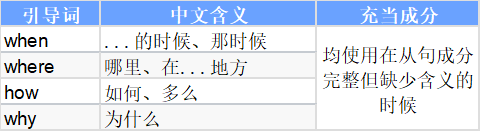
不充当成分的引导词,只充当含义
①连词(从属连词)
②连接副词
Whether the plan is feasible remains to be proved.这个计划是否可行仍需被证实。- 谓语:
remains 保持;留下 - 从句在谓语的前面,所以是主语从句。
- 谓语:
Whoever comes here is not important.无论谁来到这都不重要。- 主语从句
三、连接代词
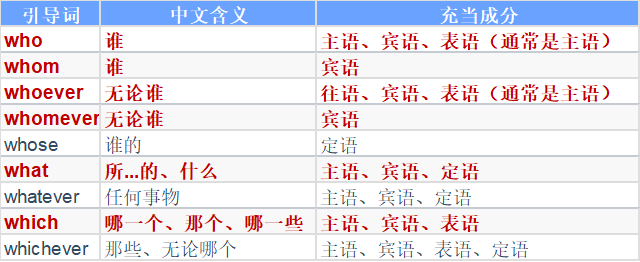
| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 充当成分 |
|---|---|---|
| who | 谁 | 主语、宾语、表语(通常是主语) |
| whom | 谁 | 宾语 |
| whoever | 无论谁 | 往语、宾语、表语(通常是主语) |
| whomever | 无论谁 | 宾语 |
| whose | 谁的 | 定语 |
| what | 所...的、什么 | 主语、宾语、定语 |
| whatever | 任何事物 | 主语、宾语、定语 |
| which | 哪一个、那个、哪一些 | 主语、宾语、表语 |
| whichever | 那些、无论哪个 | 主语、宾语、表语、定语 |
例子
what he said surprised me.他所说的惊讶到了我。- 主语:
what he said,主语是由主语从句构成,he said他说缺少宾语,因此在连接代词里面选择, - 谓语:
surprised - 宾语:
me
- 主语:
what和which同时在选项中出现时,选择what的正确率是90%。
四、名词性从句做题流程
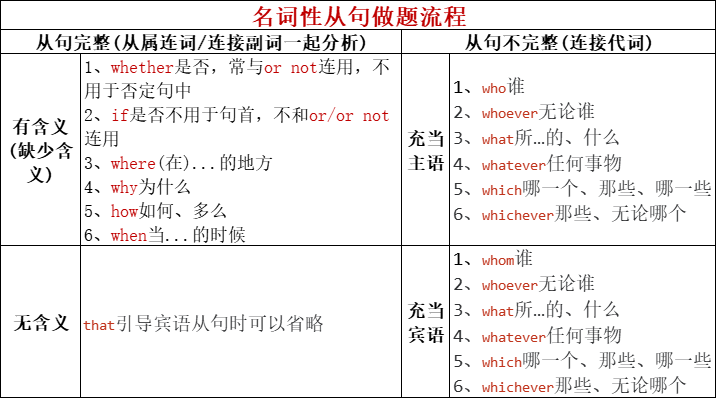
- 找到谓语动词,判断从句类型
- 从句完整(
从属连词/连接副词一起分析)- 有含义(从句完整,缺少含义)
whether是否可以用于句首,常与or not连用,不用于否定句中if是否不用于句首,不和or/or not连用where(在)...的地方why为什么how如何、多么when当...的时候
- 无含义:
that引导宾语从句时可以省略
- 有含义(从句完整,缺少含义)
- 从句不完整(连接代词)
- 充当主语(6个):
who谁,whoever无论谁,what所...的、什么,whatever任何事物,which哪一个、那些、哪一些,whichever那些、无论哪个 - 充当宾语/表语(6个):
whom谁,whoever无论谁,what所...的、什么,whatever任何事物,which哪一个、那些、哪一些,whichever那些、无论哪个
- 充当主语(6个):
- 从句完整(
名词性从句(例子)
一、主语从句
____ the plan is feasible remains to be proved.这个计划可行仍需被证实。- 主语:
the plan(主) is(系) feasible(表)计划可行 - 谓语:
remains - 缺少含义:
whether the plan is feasible计划是否可行,这个计划是否可行仍需被证实。
- 主语:
- 主语从句:
____ comes here is not important.来到这都不重要。- 主语:
comes here,主语从句,从句不完整,缺少主语 - 谓语:
is not - 表语:
important - 动词:
comes、is2个动词 - 缺少主语:
whoever comes here is not important.无论谁来到这都不重要。
- 主语:
二、宾语从句
- 宾语从句:
We demanded ____ we should be good in every thing.- 2个动词:
demanded(从句一前一后出现两个动词,前面是主句的谓语动词)、should be good in2个动词 - 谓语:
demanded - 宾语从句:
____ we should be good in every thing.
- 2个动词:
- 宾语从句:
He says (that) he will go to Shanghai tomorrow.他说他明天要去上海。- 谓语:
says - 宾语从句:
____ he will go to Shanghai tomorrow. 知识点:宾语从句的引导词如果是that,那么可以省略。
- 谓语:
- 主谓双宾的例子:
____ he told me is right.- 2个动词:
told、is,空格后面出现2个动词,离的较远的是主句的谓语动词 - 谓语动词:
is - 主语从句:
____ he told me,told表示主谓双宾 - 主谓双宾:
what he told me xxx
- 2个动词:
- 总结:空格后面出现2个动词,离的较远的是主句的谓语动词;空格(从句)一前一后出现两个动词,前面是主句的谓语动词。
三、表语从句
- 表语从句:
Their first idea was that Jack had hidden it.他们的第一个想法就是Jack把它藏起来了。- 主语:
Their first idea - 系动词:
was - 表语:
that Jack had hidden it表语从句, 知识点:即使引导词是that,在表语从句中也不能省略
- 主语:
The problem is who will get it.问题是谁将得到它。- 主语:
The problem - 系动词:
is - 表语:
who will get it表语从句
- 主语:
四、同位语从句
- 同位语从句:当有一个完整的句子时,后面出现一个从句,这个从句在对前面的名词进行解释。同谓语从句只是修饰抽象名词。
I have an idea that we ought to walk to school.我有一个想法,我们应该走路去学校。I have an idea 我有一个主意,主谓宾完整,句子完整- 这个主意是
we ought to walk to school
There is a fact that we ought to walk to school.有一个事实,我们应该走路去学校。fact(抽象名词) =that we ought to walk to school.(同位语从句)知识点:同位语从句不充当主干的基本成分。
- 抽象名词:同位语从句的被修饰词往往是抽象名词,抽象名词如:
fact,idea,hope,wish,neWs,promise,opinion,suggestion,truth等。 - 同位语从句95%填写
that
that在名词性从句中的省略(背诵)
(1)可以省略:that做宾语从句引导词,不充当意思,不充当成分,可以省略。
(2)不能省略:主语从句、表语从句、同位语从句,that不能省略。
名词性从句:名词性从句是一件事情
what he told me is my friend. 他所告诉我的一件事情是我的朋友。表述有问题,应该是that we arrive is 5 o'clock. 我们到达是5点钟。表述有问题,应该是
形式主语 形式宾语
形式主语:为了避免句子出现头重脚轻的情况,于是我们一般使用it做形式主语,将真正的逻辑主语放在后面。
Observing traffic regulations is quite vital.遵守交通规则非常重要。- 变为:
It is quite vital to observe traffic regulations.遵守交通规则非常重要。

识别形式主语
识别形式主语(例句)
It is extremely obvious that you have been lying about her identity.很明显你一直在隐瞒她的身份。it表示that you have been lying about her identity.- 逻辑主语(真正的主语):
that you have been lying about her identity. - 从后面开始翻译(中文翻译):
that you have been lying about her identity is extremely obvious
It was pretty hard for him to bring up the child on his own.对他来说,独自抚养这个孩子很难。- 逻辑主语(真正的主语):
to bring up the child on his own.
- 逻辑主语(真正的主语):
总结(记忆)
It be... that...如果逻辑主语是一个完整的句子,请用that。It be... to...如果逻辑主语是动词,请用to。- 如果句首是
it be(it is/it was)等形式就要考量他是否是形式主语,形式主语一定从后面(to/that)开始翻译
强调句型
It be... that/who/whom(中间是被强调部分) ,把it be... that/who/whom去掉它是一个完整的句子,那么这个句子就是强调句型;子如果去掉it不是一个完整的句,那么就是形式主语。It was not until... that(中间是被强调部分)
判断方式
It was he that read three books in the library yesterday.- 把
it be(it was)去掉,he that read three books in the library yesterday.是一个完整的句子,那么这个句子就是强调句型。
- 把
It was in the library that he read three books yesterday.- 从
that he read three books yesterday后面开始翻译,再翻译前面It was in the library
- 从
It was yesterday that he read three books in the library.
- 总结(做题流程)
- ①去掉
it be... that...是一个完整的句子,那么是强调句型。
②通过从that后面开始翻译,如果翻译通顺,那么是形式主语;如果翻译不通顺,那么是强调句型。
例题
It is my duty ____ care for patient.As we all know.
A. to
B. which
C. that
D. for
- 解析
-
- 去掉
it is,my duty care for patient 我的职责照顾病人句子不完整,确实is是,所以不是强调句型,那么就是形式主语。
- 去掉
- 验证形式主语:
care for patient is my duty 照顾病人是我的职责,翻译通顺,句子是形式主语。 - 查看形式主语是否完整,
care for patient 照顾病人缺少主语,句子不完整,因此填写to do,选择A.
解题思路
- 看到
it分析其为代词 - 形式主语
- 强调句型
- 省略法
- 翻译法
形式宾语/to do、that的区别
Tom makes it possible to land the moon.汤姆使登月成为可能。Tom makes it possible. Tom成为可能- 宾语:
to land the moon.后面的解释是一个动词,就填写to,构成to do
Tom makes it possible that the patient stands up.汤姆使这个患者站起来成为可能。- 如果后面的解释是一个从句,那么填写
that
- 如果后面的解释是一个从句,那么填写
句型
句型:主+谓+it形式宾语+宾补+that/to do…(本句型中,宾补也可以省略)
名词性从句用陈述句语序(名词性从句用主谓宾/主谓/主系表语序)
——Can you tell me ____?
——Sure!No problem.
A.what does he look like
B.what she looks like
C.how does she look like
D.how she looks like
主谓双宾:you tell me sth. 你告诉我某事,sth.只能是陈述句
引导词+主谓宾/主谓
疑问问:what does、how does
第六章 定语从句
定语的定义:修饰成分,修饰名词或代词
基本成分:主谓宾
修饰成分:定状补
判断定语从句:主句完整,并且又在修饰名词的就是定语。当从句在充当定语时,就是定语从句。
例句
The boy who was wearing a black coat bought a dictionary yesterday.这个身穿黑色衣服的男孩昨天买了一本字典。The boy bought a dictionary yesterday.这个男孩买了一本字典。- 定语:
who was wearing a black coat 这个穿着黑体衣服的修饰前面的名词the boy
The noodle that my mother cooks is delicious.我母亲做的面条非常好吃。The noodle is delicious.这个面条非常的美味- 定语:
that my mother cooks 我母亲做的修饰前面的名词the noodle
The school which I attended was very large.我上学的那个学校非常大。The school was very large.这个学校非常的大- 定语:
which I attended
I remember the day when our band was formed.我仍记得我们乐队成立的那一天。- 主谓宾完整:
I remember the day我仍然记得那一天 - 定语:
when our band was formed. 我们乐队成立那一天指乐队成立那日。修饰the day
- 主谓宾完整:
I don't know the reason why she got so angry this morning.我不知道她早上生气的原因。I don't know the reason我不知道原因- 定语:
why she got so angry this morning.他早上生气的原因。修饰the reason
- 翻译顺序:定语+的+先行词(名词),定语修饰名词
关系代词

| 关系代词 | 指代先行词 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| who | 人 | 通常做主语,有时候做表语、和宾语;做宾语时前面不能有介词 |
| whom | 人 | 可以做宾语 |
| which | 物、整个句子 | 可以做主语、宾语(可省略) ,which指代一句话时只能放在先行词后面 |
| that | 人、物 | 可以做主语、宾语(可省略)、不用于逗号后 |
| as | 人、物、整个句子 | 主语、宾语(指代人或物时与the same / as / such / so连用);as引导的定语从句修饰一句话时可以放在句首、句中或先行词后 |
| whose | 所属关系 | 先行词司前后两个词构成所属关系 |
who(在从句中充当主语)
The girl who digs the ores is my friend.挖矿石的这个女孩是我的朋友。- 主语:
the girl,who指代the girl,因此动词digs使用三单
- 主语:
The person who is buying rugs is my classmate.正在购买地毯的人是我的同学- 主语:
The person
- 主语:
The old woman,who lives on her own,has a cat for company.独自生活的老奶奶养了一只猫作为陪伴。The old woman has a cat for company.这个老奶奶有一只猫作为陪伴。- 主语:
the old woman
- 总结:先行词
who必须是人,从句缺主语。 - 知识点:
who、those在修饰人的时候,并同时在选项出现选项中,优先选择who
whom
I know the man whom you are talking to.我认识和你交谈的这个人。- 宾语:
man
- 宾语:
I hate the guy whom you're dating.我讨厌你正在约会的那个人。- 宾语:
guy
- 宾语:
- 总结:先行词
whom必须是人,从句缺宾语。引导词必须在句首,虽然他代指主语或宾语。
which
The fish,which I bought this morning,was very fresh.我今天早上买的这条鱼非常新鲜。The fish was very fresh.这条鱼非常新鲜- 主语:
The fish - 从句:
which I bought this morning,which从句的宾语,this morning从句的状语,which从句的主语,修饰前面的物fish
My stock,which I bought two years ago,is worth a lot of money.我两年前买的股票现在非常值钱。My stock is worth a lot of money.我的股票非常值钱。
He failed the exam,which made his father very angry.(一整句话)他考砸了,这个事使他的父亲非常生气。- 总结:先行词
which必须是指物、事情、整个句子。
that
The new house that I has just bought is behind a stadium.我刚买的新房子就在体育场的后面。The new house is behind a stadium.新房子就在体育场的后面。- 主语:
The new house - 从句:
that I has just bought,缺少宾语,因此引导词填写that/which/不填写 - 知识点:
that/which在从句中充当宾语时可以省略。当that/which省略时,句子就会变成名词+主谓 (The new house) + (I has just bought)
They planted some trees that didn't need much water.他们种植了一些不需要太多水的树。- 定语从句:
that didn't need much water. 不需要太多水分的植物,that代指trees,trees是一个物,所以使用that - 从句主语:
that从句主语不能省略 - 主干完整:
They planted some trees
- 定语从句:
I hate the guy you are talking with. (省略了that)我讨厌正在和你说的那个人。- 省略了
that构成名词+主谓,名词the guy,主谓you are talking with - 定语从句:
that you are talking with
- 省略了
as
He spoke in such easy English as every body could understand.他讲的是很简单的、每个人都能听懂的英语。- 主句完整
He spoke in such easy English 他说的是一种很简单的英语 - 定语从句:
every body could understand缺少成分(缺少宾语) - 从句主语
every body,从句谓语could understand,understand及物动词后面接宾语 - 先行词
easy english(他是一个物),可以填写which/that/us。先行词easy english被such修饰,所以只能填写as as作主语、宾语(指代人或物时与the same/as/such/so连用);as引导的定语从句修饰一句话时可以放在句首、句中或先行词后
- 主句完整
As is known to us,Beijing is the capital of China.众所周知,北京是中国的首都。Beijing is the capital of China,as is known to us.,as指Beijing is the capital of China.(这件事情)as可以放在句首/句中/句末尾,如果有which就先填写which- 句首:As is known to us,Beijing is the capital of China.
- 句中:Beijing,As is known to us,is the capital of China.
- 句末:Beijing is the capital of China,as is known to us.
- Beijing is the capital of China,which is known to us.
- 一个定语从句在修饰前面一整句话,定语从句在句首/句中用
as,定语从句在句末用which
- 这里的
as指代的是前面一整句话,放在了被修饰句子前面,是as的特殊用法之一。as,代指人、物、整个句子,用于主语、宾语(指代人或物时与the same/as/such/so连用);as引导的定语从句修饰一句话时可以放在句首、句中或先行词后。
whose
The tourist wanted to book a room __ window faces south.游客想预定一间窗户朝南的房间。a room和window构成所有格关系- 所有格关系:
...的,房间的窗户,因此填写whose
We went to see our teacher Miss Wang, __ husband will move to abroad.我们去看望了我们的老师王小姐,她的丈夫将移居国外。miss wang和husband构成所有格关系- 所有格关系:
...的,王小姐的丈夫,因此填写whose
- 当空格前面2个词构成所有格关系就用
whose(从前往后翻译),whose后面不能出现the
which和that的区别
- that不能修饰非限定性定语从句;不用于逗号后。
- which可以修饰前面一整句话;
- that可以指代人、物;
- which不能指代人。
关系副词
| 关系副词 | 指代先行词 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| where | 地点 | 不充当成分 |
| when | 时间 | 不充当成分 |
| why | 原因 | 不充当成分 |
where(抽象地点/位置)
The hotel where we stayed was very clean.我们住的这个旅馆非常干净。The hotel was very clean这个旅馆非常的干净,主语the hote 这个旅馆- 定语从句:
where we stayed,hotel前面是一个地点,填写there
I go to the point where I can drink stream.我走到我可以喝小溪的地方。I go to the point我走到这个地方。- 定语从句:
where I can drink stream
- 抽像地点:身体到不了的地方,如:我达到了某种瓶颈/境地;我遇到某种情况;
when
I'll never forget the time when we first obtain the scholar.我永远不会忘记我们第一次获得奖学金的那一刻。I'll never forget the time我永远不会忘记那一刻when we first obtain the scholar.从句完整,修饰时间用when修饰前面的时间time
why
The reason why I resist the job is that I hate my boss.我抵制这份工作的原因就是我恨我的老板。The reason is that I hate my boss.原因是我恨我的老板。
The reason why she was late was that she missed her plane.她迟到的原因是她错过了飞机。The reason was that she missed her plane.原因是她错过了飞机
the reason __ I want to tell you is thisthe reason is this这个原因是它,主语:the reason原因- 从句
i want to tell you,tell表示主谓双宾,缺少一个宾语,从句不完整,不能填写关系副词why,只能填写关系代词。 - 填写
that
特别注意
if、what、how不用于定语从句中:- 当先行词有最高级的时候只能使用
that;this is the best book __ i have ever read最高级best修饰book,只能使用that
- 当先行词被
the only,the very,just the,the right,any,every,no,all,much,many,little,few等词修饰的时候只能用that; - 当先行词被
all,much,something,everything,nothing,none,the one等不定代词修饰候只能用that; - 当先行词被序数词修饰的时候只能使用
that; - 当先行词既有人又有物的时候只能使用
that。 - 逗号后不要使用
that - 注意:②到⑥适用于从句不完整、选择关系代词时使用,适用于从句不完整。
this is the best book __ I have ever read.有最高级修饰使用thatthis is the best book __ I have ever read it.从句完整,不能填写关系代词that
- 可以省略引导词的情况:
that、which在从句中充当宾语可以省略 - 当先行词是
the way时,后面可以填that/in which/不填
第七章 状语从句
定义
状语从句:状语主要用来修饰主句(一整句话)或谓语(谓语动词)。状语还可以修饰形容词、副词。
辨认状语从句:从英文的角度出发
能作状语的有副词、时间名词、状语从句、介词短语
状语举例
判断一个句子缺少状语,但不能说是状语从句
I like the moive + ...:后面的内容(省略号)一定是修饰成分,...可以是定语、状语、补语,定语修饰名词moive,状语修饰谓语like或一个句子I like the moive。I like the moive extremely- 状语
extremely在修饰动词like。
- 状语
状语从句
状语从句:一个词不能表达完整的状语,使用一个句子充当状语。(当一个句子来充当状语的时候就称作状语从句)
We will have a meeting during holiday.我们将会在假期开会。- 按照英文表达方式排列后:我们将开会在假期。(时间状语)
- 介词+名词构成介词短语作状语:
during holiday作时间状语,介词during,名词holiday
I will go to school by bus.我将会乘公交上学。- 按照英文表达方式排列后:我将会上学通过乘公交的方式。(方式状语)
例句
When I was young(时间状语),I had three hobbies. 当我很小的时候,我有三个爱好。If I have own car(条件状语),I will take you. 如果我有自己的车,我将载着你。As she was not well(原因状语),I went there alone. 因为她感觉不适,所以我独自来了。- 以上3个是由句子构成的状语,所以称作状语从句。
状语从句引导词分类
1. 时间状语从句(时间状语引导词)
| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 特别注意 |
|---|---|---|
| when | 当...的时候 | 常与be about to do连用 / when it comes to |
| while | 在...期间 | 无 |
| as | 当...的时件、一边...一边... | as含义较多,定要区分其在句子中到底充当的是什么意思 |
| before | 在......之前 | 常伴随过去的过去(过去完成时)考点 |
| since | 自从...以来... | 常伴随现在完成时考点(since+时间点) |
| till/until | 直到 | 无 |
| hardly... when... | 刚...就 | 常伴随半倒装考点 |
| as soon as | 一...就... | 特殊引导词,不易看出是时间状语从句 |
| not... till/until | 直到......才 | not在句子中不易发现,把not翻译成了“不”是常见错误,not...until的正确翻译是“直到......才” |
| after | 在...安 | 无 |
| no sooner... than... |
一...就... | 常伴随半倒装考点 |
| the moment | 一...就...、立刻 | 特殊引导词,不易看出是时间状语从句 |
| by the time | 等到、到.......的时候 | 特殊引导词,不易看出是时间状语从句,并且是完成时提示词,遇到by the time时既要注意主将从现、还要注意完成时(主句常用将来完成时) |
not...until...
not... till/until:not在句子中不易发现,把not翻译成了“不”是常见错误,not...until的正确翻译是“直到......才”I didn't realize the importance until you told me this fact.直到你告诉我这个事实,我才意识到它的重要性。
2. 地点状语从句
| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 特别注意 |
|---|---|---|
| where | 在...地方 | 无 |
| wherever | 无论哪里 | 无 |
3. 原因状语从句
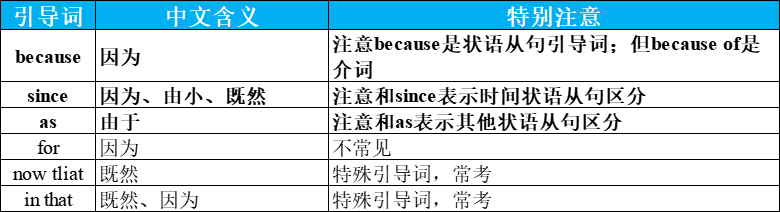
| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 特别注意 |
|---|---|---|
| because | 因为 | 注意because是状语从句引导词;但because of是介词 |
| since | 因为、由小、既然 | 注意和since表示时间状语从句区分 |
| as | 由于 | 注意和as表示其他状语从句区分 |
| for | 因为 | 不常见 |
| now tliat | 既然 | 特殊引导词,常考 |
| in that | 既然、因为 | 特殊引导词,常考 |
4.目的状语从句
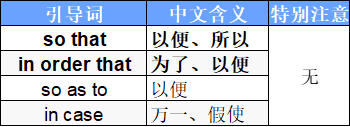
| 引导词 | 中文含义 |
|---|---|
| so that | 以便、所以 |
| in order that | 为了、以便 |
| so as to | 以便 |
| in case | 万一、假使 |
| lest | 以免、恐怕 |
5. 结果状语从句

- 例句1:
you seems __ graceful that many people fall in love with you.你看起来很优雅,很多人都爱上了你- 空格后面是形容词
graceful so后面接的形容词graceful
- 空格后面是形容词
- 例句2:
you are __ the graceful student that many people fall in love with you.你是许多人爱上你的优雅的学生- 句中有一个
that,填写so...that.../such...that... - 空格后面是名词
the graceful student,因此空格填写such
- 句中有一个
6.让步状语从句(欲扬先抑/欲抑先扬)

- 例句1:
Although you are smart but your grades are poor. 虽然你很聪明但是你的成绩很差。前后是相反的话(欲扬先抑/欲抑先扬)- 英文中的
but是连接2个句子的,所以but前后是2个主句(句子)。
- 英文中的
7.比较状语从句
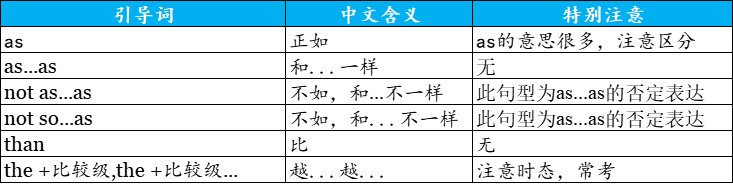
| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 特别注意 |
|---|---|---|
| as | 正如 | as的意思很多,注意区分 |
| as...as | 和...一样 | 无 |
| not as...as | 不如,和...不一样 | 此句型为as...as的否定表达 |
| not so...as | 不如,和...不一样 | 此句型为as...as的否定表达 |
| than | 比 | 无 |
| the+比较级,the+比较级... | 越...越... | 注意时态,常考 |
the higher you are,the better you play basketball. 你越高,篮球打得越好。the higher...,the better...- the+比较级+主谓,the+比较级+主谓/主谓宾
8.条件状语从句

| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 特别注意 |
|---|---|---|
| if | 假设,如果 | 条件状语从句中的if一般翻译成“如果”, 而名词性从句中的if一般翻译为“是否” |
| unless | 如果不,除非 | 无 |
| as/so long as | 只要 | 无 |
| on condition that | 在...条件下 | 特殊引导词,常考 |
9.方式状语从句

| 引导词 | 中文含义 | 特别注意 |
|---|---|---|
| as | 像…那样地 | 无 |
| just as | 正像 | 无 |
| as if | 好像 | 无 |
| as though | 好像 | 无 |
知识点
- 95%的状语从句引导词都不充当基本成分,所以我们在写状语从句题时,无需判断引导词是否充当成分的问题。
第八章 介词
定义
常见使用方法
- 英文中介词往往和名词或代词构成搭配,形成
介词短语,如:in the room,on the table等;- 常见的介词短语作定语、状语、表语。
- 介词短语一般是:
介词+名词(介词在前,名词在后)
- 介词也常与动词构成搭配,形成
动词短语,整体在句子中充当成分,如:take off,work out(锻炼身体)等- 常见的动词短语作谓语
- 动词短语一般是:
动词+介词(动词在前,介词在后)
- 介词后面填写名词(名词、动名词、名词短语、名词性从句)或代词
after __ ,he has a book
常见介词
常见介词
- ①in:在...里面/用/在...期间:
- ②on:在...上面/关于/向:
- ③at:在...地点/以...价格/(武器)瞄准;
- ④with:随着/有/和...一起/用/由于:
- ⑤by:通过...方式/经过/由于/在...旁边
- ⑥for:因为/为了/给
- ⑦from:源于/来自/由...制成
- ⑧about:大约/关于
- ⑨of:的/属于/关于
常见介词用法
(一)介词in
- Her words in my heart. 他的话在我心里
- the winter in America. 美国的冬天
- in person 亲自(固定搭配)
第九章 倒装
定义:谓语位于主语之前,或部分谓语位于主语之前。
半倒装:半倒装又称部分倒装,将助动词、be、情态动词提前到主语的前面
助动词:助动词区别于实意动词,往往助动词在翻译中没有含义,帮助构成某种时态或语态。
- I have read the book
have助动词表示时态(完成时)
- she had realized the fact
had助动词表示时态(过去完成时)- 倒装:had she realized the fact.
- he loves my new novel.
- 隐藏的助动词
半倒装的常见方法
(一)句子隐藏助动词的情况下
倒装方式:先写一个助动词放在主语前,谓语动词写原型。本情况中的助动词为do,但会根据主语是三单或时态是过去时而变为does和did。
举例
- 正序:Tom has three books. 汤姆有三本书。
- 隐藏助动词时,先在主语前面加上
do,do Tom has three books. - 根据时态改变三单改变
do的时态三单:动词是原型就写do;动词是过去式就写did;动词是三单has,所以用does。 does更改完成后,将动词has还原为原型have- 半倒装:
Never does Tom have three books.汤姆从未有过三本书。
- 隐藏助动词时,先在主语前面加上
- 正序:
Tom had three books.汤姆以前有三本书。- 半倒装:Never did Tom have three books.汤姆以前从未有过三本书。
- 正序:
he loves my new novel.- 主语前加
do,do he loves my new novel. - 根据三单变化
do,does he loves my new novel. - 动词
love变原型:does he love my new novel.(半倒装)
- 主语前加
(二)句子直接出现助动词的情况下
倒装方式:助动词提前放在主语前,谓语动词不变。
举例
- 正序:
Tom has finished his work.汤姆完成了他的工作。- 直接将助动词
has提前:has Tom finished his work.
- 直接将助动词
- 半倒装:
Never has Tom finished his work.汤姆从未完成他的工作。
(三)句子中有be动词时
倒装方式:直接将be动词放在主语前,其他部分不变。
举例
- 正序:
His homework is finished.他的作业被完成了。- 直接将
be动词is提前:is His homework finished.
- 直接将
- 半倒装:
Never is his homework finished.他的作业从未被完成。
(四)句子中出现情态动词
倒装方式:直接将情态动词放在主语前,其他部分不变。
举例
- 正序:Tom can open the windows. 汤姆可以打开窗户。
- 情态动词
can放在主语前:can Tom open the windows.
- 情态动词
- 半倒装:Never can Tom open the windows.汤姆永远不能打开窗户。
半倒装常见考点:半倒装提示词(重点)
①否定词在句首;
②so/such...that中的so/such放置句首;
③hardly when / no sooner than;
④让步状语从句半倒装:
⑤省略if的虚拟语气:
⑥only+状语在句首;
⑦so/nor/neither的回复句。
(一)否定副词在句首
常见否定词:little,seldom,hardly,few,nowhere,scarcely,neither,nor,no longer,not until,not once,in no way,in no case,at no time,no sooner...than...,hardly...when...
例句
Hardly had I got out of the house when it began to rain.我一离开房子,天就下雨了。Hardly在句首,句子就是半倒装- 原句:
Hardly i had got out of the house when it began to rain.(助动词had被提前了)
Never will he forget his first time to take a plane.他永远都不会忘记他第一次乘坐飞机。never在句首,句子就是半倒装Never he will forget his first time to take a plane.,情态动词will
(二)so/such...that中的so/such放置句首
常见情况:so/such...that句型中,so在句首接形容词/副词时要半倒装;such在句首接名词时要倒装。
例句
So proud was Linda that she never listened to any advice.琳达太骄傲了,以至于她从来不听任何建议。so在句首,so/such...that句型- 原句:Linda was
soproudthatshe never listened to any advice.`
(三) hardly...when / no sooner...than
常见情况:
- No sooner...than:主句用过去完成时,than后面的从句用一般过去时。
- Hardly...when:主句用过去完成时,when引导的从句用一般过去时。(②中的nardly可以被scarcely,barely等词代替)
注意:这一类也属于否定词在句首,但是他们在选择题中出现不仅考倒装,还会考到时态搭配。
No soonerhad I arrived my homethanI finished homework. 我一到家就完成了作业- 主句
had I arrived my home用过去完成时+倒装 - 从句
I finished homework用一般过去时
- 主句
Hardlyhad I got out of the housewhenit began to rain. 我一离开房子,天就下雨了。- 主句
had I got out of the house用过去完成时+倒装 - 从句
it began to rain.用一般过去时
- 主句
(四)让步状语从句半倒装
常见情况:
(1)as引导的让步状语从句必须半倒装:
(2)though引导的让步状语从句可以半倒装,也可以不倒装:
(3)although引导的让步状语从句不能倒装:
(4)no matter how/however引导的让步状语从句需半倒装。
例子
4.1 as/though引导的让步状语从句半倒装
(1)示例
- 正序:
As he is rich,he never spends a cent on clothes.虽然他很有钱,他从不花一分钱买衣服。- 主系表:
he is rich 表语+as+主语+系动词变为半倒装:Rich as he is,he never spends a cent on clothes.虽然他很有钱,他从不花一分钱买衣服。- 句型:形容词/分词/动词原形/副词/名词+as/though+主+谓
- 主系表:
- 正序:
as he is a smart student.- 半倒装:
a smart student as he is - 如果前面有冠词,去掉冠词:
smart student as he is
- 半倒装:
4.2 no matter how/however引导的让步状语从句半
- 例句:
No matter how hard you try,you can't go back.无论怎么努力,你都回不到过去了。no matter how+ hard(形容词/副词)+you(主语)+try(谓语)
- 公式:
no matter how+形容词/副词+陈述句
(五)省略if的虚拟语气
- 正序:
If Mark had invited me,I would have been glad to come.如果马克邀请了我,我会很高兴来的。 - 变为半倒装:
Had Mark invited me,I would have been glad to come.如果马克邀请了我,我会很高兴来的。 - 变化步骤:
①将虚拟语气句中的if省略;
②将助动词提前到主语前。
(六)only+状语在句首
副词、介词短语、状语从句、非谓语从句可以作状语。
6.1 only+副词位于句首
Only then did I realize that I was wrong.只是到了那时我才意识到是我错了。
6.2 only+介词短语位于句首
Only by working hard can you succeed.只有努力工作你才能成功。- 介词短语:
by working hard - 因为倒装,所以
can提前了
- 介词短语:
Only in the reading-room can you find him.你只有在阅览室才能找到他。- 介词短语:
in the reading-room
- 介词短语:
6.3 only+状语从句位于句首。如:
Only when one loses freedom does one know its value.一个人只有在失去自由后才知道自由的可贵。- 状语:
when one loses freedom(状语不要倒装) - 主句倒装:
does one know its value.
- 状语:
6.4 only+时间名词位于句首。如:
Only yesterday was I very happy.只有在昨天我才非常开心。
(七)so/nor/neither的回复句半倒装
7.1 当在肯定句中(指回复句的上一句为肯定句)满足以下3个条件即可半倒装。
①两个句子主语不同;
②两个句子助动词一致:
③在要在肯定句中。
回答句型:so+助动词+主语
7.2 当在否定句中(指回复句的上一句为否定句),满足以下3个条件即可半倒装。
①两个句子主语不同:
②两个句子助动词一致(同一类的都可以):was和is也是助动词一致;did和does也是一致.
③回复句的上一句为否定句
回答句型:neither/nor+助动词+主语
示例
——So proud was Linda that she never listened to any advice.(主语Linda,助动词was,否定never)
——Yes.So was Tom.(主语Tom,助动词was)
——琳达太骄傲了,她从来不听任何建议。
——是的。汤姆也是。
知识点:上一句是肯定句,那么下一名也用肯定句;上一句是否定句,那么下一名也用否定句。肯定句用or,否定句用nor/neither。
全倒装
全倒装的定语:整个谓语放在主语的前面,往往主语不能是人称代词,动词是不及物动词。
只有满足全倒装的定语和全倒装提示词才属于全倒装。
全倒装提示词
①there+be
②here/now/then在句首+不及物动词+名词
③out/in/up/down/away在句首+不及物动词+名词
④介词短语(表地点)在句首+不及物动词+名词
⑤Such+be+主语
重点:here/now/then/out/in/up/down/away/介词短语(表地点)在句首+不及物动词+名词
(二)here/now/then+不及物动词+名词
- 正序:
Your turn comes to perform the operation now.
现在该你做手术了。- 主语
Your turn,谓语comes - 把整个谓语
comes放在主语Your turn的前面是全倒装 - 全倒装:
Now comes your turn to perform the operation.现在该你做手术了。
- 主语
(三)out/in/up/down/away+不及物动词
- 正序:
The children rushed out.孩子们冲了出去。- 主语
The children,动词rushed/rushed out - 把整个谓语
rushed out放在主语the children的前面是全倒装 - 全倒装:Out rushed the children.
- 主语
The they rushed out.- 主语
the they是人称代词就不能全倒装
- 主语
(四)介词短语(表示地点)+不及物动词+名词
- 正序:
The sound of music came from the window.音乐声从窗口传来。- 介词短语
from the window,不及物动词came,名词sound of music - 全倒装:
From the window came the sound of music.音乐声从窗口传来。
- 介词短语
第十章 虚拟语气
虚拟语气的定义:表示假想、假设、现在不可能实现(不能回到过去改变)、难以实现甚至是与事实相反的情况。
例句
If you had followed the doctor's advice,you would not be in so much pain now.如果你听了医生的建议,你现在就不会那么痛苦了。But for your help,I wouldn't have got the certificate so smoothly.要不是你的帮助,我不会如此顺利地拿到证书。
虚拟语气分类
①if虚拟语气
②特殊用法
③情态动词表示猜测的虚拟语气
(一)if的虚拟语气使用原则:
当从句使用did/were,主句使用would do;
| 从句 | 主句 | |
|---|---|---|
| 现在 | did/were | would do |
| 过去 | had done | would have done |
| 将来 | were to do/should do | would do |
注:表中would可以为should/night/could
if虚拟语气与现在事实相反
1.1 对应时态:If did/were+...,would/should/could/might+do
- 例子1:
If I were you,I would call him.如果我是你,我会联系他。- 从句用
were,主句用would call(would to)
- 从句用
- 例子2:
If he received this magic code,he could help me.如果他有魔法,他一定会帮助我。- 从句用
did,主句用would help(would to)
- 从句用
- 知识点(记忆):无论第几人称,虚拟语气
if从句中的be动词一律写were.
1.2 对应时态:If had done+...,would have done
- 例子1:
If I had won the lottery,I would have bought a villa.如果我中了彩票,我将买一套别墅。- 从句用
had won(had done),主句用would have bought(would have done)
- 从句用
- 例子2:
If I had known your number yesterday,I would have phoned you.如果我昨天知道你的手机号,我将会给你打电话。- 从句用
had known(had done),主句用would have phoned(would have done)
- 从句用
1.3对应时态:If should do/were to do,would do
- 例子1:
If it should rain tomorrow,you could stay at home.万一明天下雨,你就可以待在家里。- 主语用
should rain(should do),主句用could stay(would do)
- 主语用
- 例子2:
If you were to come home next year,we would go to the park together.如果你明年能回家,我们就一起去公园。- 主语用
were to come(should do),主句用would go(would do)
- 主语用
- 知识点:此处的虚拟翻译为:万一
特殊用法
特殊用法(一)
- 主句的
谓语动词(表示要求、命令、建议等)+宾语从句的句型,动词请写(should)+do(主动)/(should)+beng+done(被动),其中should有时可以省略。 - 例子:
My friend orders that everyone in his room (should)take off their shoes.我的朋友要求在他房间的每一个人都要脱掉鞋子。orders要求- 定语从句:
that everyone in his room (should)take off their shoes.,定语从句中用should take(should do),其中should可以省略。
- 需要单词查看在句子中是否表示“要求、建议、命令”含义,否则即使出现提示词也不符合要求
①要求ask,demand,equire,request,insist
②建议advise,suggest,recommend
③命令order,command
特殊用法(二)
- 表示
要求、命令、建议等名词后面的同位语从句,动词部分请写(should)+do(主动)/(should)+beng+done(被动) - 例子:
He set out requirements that everyone (should)follow his arrangement.他发出了一些要求,每个人都应该遵守他安排。requirements要求,同位语从句that everyone (should)follow his arrangement,同位语从句中用should follow(should do)
特殊用法(三)
it is+形容词+that:it is important/necessary/natural/essential/advisable/....+that+主语(should)+do- 例子:
It is important that you (should) stay at home.你应该待在家里是非常重要的。It is important that- 从句
that you (should)stay(that+主语(should)+do)
特殊用法(四)
- wish后面接宾语从句时,请用虚拟语气,句型:
主语+wish+that+宾语从句使用虚拟 - 对应时态:
①与过去不一致:had done
②与现在不一致:did
③与将来不一致:would/could/should+do(should不可省略) - 例子:
I wish that you hadn't been to this activity.我真希望你没有参加过这个活动。- 言下之意:你已经参加了这个活动。(过去式)
- 与过去不一致:
hadn't been(had done)
特殊用法(五)
lt is (high) time that...+did/were/should do(should不要省略)- 举例1:It's time that you thought about your future. 是时候考虑一下你的未来了。
thought(did)过去式
- 举例2:lt's time that you should think about your future.是时候考虑一下你的未来了。
should think(should do)
did/should do同时出现选择did/were
特殊用法(六)
- 表示“没有”、“要不是”、“以免”、“否则”等介词提示为含蓄的虚拟语气
- 对应时态:
①对过去事实相反:主句的谓语常用would/should/could/might have done的形式。
②对现在或将来的虚拟:主语的谓语常用would do的形式。 - 举例:
But for his help,I couldn't have done it.要不是他的帮助,我肯定做不到。(对过去事实相反:主句的谓语常用would/should/could/might have done的形式。)- 翻译“他已经帮助过我了”,过去式
- with,without,but for,otherwise,or,under
- 句式:
for fear that/lest/in case+必接should do(不用考虑时态,后面直接加should do)
时态错综的虚拟语气
- 当从句表示的行为的时间和主句发生的时间明显不一致,那么本句中的动词要根据其句子的时态作出调整。
- 例子:
If you had followed my advice,you would be better right now.如果你之前听了我的建议,你现在一定会感觉很好。- 从句:
had followed 之前听建议以前发生的事情(从句过去) - 主句:
you would be better right now. 你现在一定会感觉很好现在发生的事情(主句现在)
- 从句:
- 这里的主句和从句时态产生了明显了变化,主句使用了
right now表面是对现在的虚拟,主句使用would do。
虚拟语气半倒装
- 半倒装的情况:
if虚拟语气需要使用半倒装。 - 虚拟语气半倒装(步骤):
- 省略if
- 将助动词提前到句首
- 示例1:
If I were you,I would smack him.- 省略if:
I were you - 将助动词
were提前到句首:Were I you - 最后变为:
Were I you,I would smack him.
- 省略if:
- 示例2:
If I had won the lottery,I would have bought a villa.- ①省略if:
I had won the lottery - ②将助动词
had提前到句首:had I won the lottery - 最后变为:
Had I won the lottery,I would have bought a villa.
- ①省略if:
- 总结(根据以上情况我们又可以做出总结):
①if省略的虚拟语气发生在if从句里。而不是主句;
②if省略的虚拟语气通常会直接把助动词放在句首。(否定词在句首的半倒装句首一定是否定词)
第十一章 特殊句型/考点
分类
- 基数词:one two three
- 序数词:first second third
- 序数词、最高级前必须有
the - 如果序数词被其他的词语修饰可以不用加
the,如my first friend
表示第一段:
- Paragraph 1
- Paragraph one(P尽量大写)
- the first paragraph
基数词-名词原型=形容词
two-day holiday:两天的假期
分数的表达:基数词+序数词,分子大于1分母+s
- One third 三分之一
- Two thirds
- Two-thirds
常见数词表达
- More than+基数词+thousand/hundred+名词复数(准确数字)
more than one thousand students超过一千的学生
- 基数词+thousand/hundred+名词复数
five thousand students五千名学生
- 基数词+thousand/hundred of
the+名词复数five thousand of the students
- Thousands/hundreds of+名词复数
thousands of students上万的学生
年龄表达
- 5 years old
- 5-year-old
第十二章 反义疑问句
定义:反义疑问句是又称附加疑问句,表示提问题的人对陈述的事实不敢肯定。
特点(反义疑问句符合以下3个原则)
①前一部分是一个陈述句,后一部分是一个疑问句。
②疑问句部分的人称、助动词、时态都应该与陈述句一致。
③遵循“前肯后否、前否后肯”的原则(有特例)。I
例句
You like swimming,don't you?你喜欢游泳,不是吗?He is not a student,is he?他不是一名学生,不是吗?You finished your homework last night,didn't you?
你昨晚完成了你的作业,不是吗?
常见考点(小蓝书P165)
考点一
- 陈述部分的主语为
somebody,nobody,anybody,everybodyl时,反义疑问句主语用they,有时用he。 - 如:
Everybody enjoyed the party,didn't they?每个人都喜欢这个聚会,不是吗?
考点二
- 陈述部分主语为
something,anything,everything,nothing等表物的不定代词时,反义疑问句的主语用it。 Something is wrong with the machine,isn't it?这台机器有毛病,不是吗?
考点七
- 当出现既可以做助动词或情态动词又可以做实意动词的词时,要根据句意判断,疑问句助动词部分如何写。
- 如:
She has a bottle of milk,doesn't she?她有一瓶牛奶,不是吗? - 这里的
has就是实义动词,助动词是does,可以写doesn't she。 - 同时
has/have这个词存在特殊性,当它表示“所有”“有"的时候,反义疑问句也可以直接用has
第十三章 代词
代词:代词常用来指代前文已经出现过的名词,能够避免上下文的重复,如中文里的“他”、“它”、“这个”、"他们”、"这些”、"那些”,英文中常见的代词有he,it,one,that等。
常见分类
(一)物主代词
I have three books,and this book is __ favorite book.- 主语
this book, 系动词is - 表语
my favorite book 我最喜欢的书,核心词是book,book有2个修饰my favorite.
- 主语
some books are on the table and they are __- 主语
then,系动词are,表语__(填写名词性的物主代词,我的)
- 主语
- 朋友的店比我的好
my friend's shop is better than __- 介词
than后面缺少名词mine
- 介词
my friend's shop is better than __ shopshop是名词缺少修饰,所以填写my
(二)不定代词
运用思维导图做题目(小蓝书P177)

- I admired the painting,and Ed said he would like me to have __ as a gift from him.
A.one
B.it
C.this
D.some
解析:the painting可数名词,单数,the表特指(同类同物),且指物,选择B
- In many ways,the education system in China is different from __ in the UK.
A.it
B.those
C.one
D.that
解析:the education system不可数名词,排除BC;且同类不同物。答案:D
五、it作形式主语或形式宾语:
- it takes sb.+时间 to do sth.(形式主语句型)
- itis..that从句/todo..(形式主语句型)
- 主+谓+it形式宾语+宾补+hat从句/todo. (形式宾语句型)
例子
it takes me(sb.) three years(时间) to improve(do) my spoken English(sth.)我花了三年时间提高我的英语口语it is important to study hard努力学习很重要I made it(形式宾语) possible to improve my spoken English.
第十四章 冠词
冠词的分类
- 不定冠词(翻译为“一个”)
a、an - 定冠词(翻译为“这个”)
the - 零冠词(无需翻译)
冠词的三个原则
- 可数名词的单数形式必须加冠词
- 可数名词的复数形式及不可数名词泛指时可以不加冠词,即
可数名词的单数不能单独出现 - 无论什么名词,表示特指时前面必须加定冠词the
冠词的用法
(一)不定冠词
- 常见的不定冠词有:
a、ana用于读音为辅音音素的单词前面an用于读音为元音音素(A、E、I、O、U)的单词前面
- 示例
- 通常用于修饰
泛指的可数名词单数形式,翻译为“一个”如: I want to buy a car.我想买一辆车。- 这里的汽车没有说明是具体哪一辆,所以a car是表示泛指的可数名词单数。
- 通常用于修饰
(二)定冠词
- 定冠词的用法:
①用于单数名词前,指具有某种特点的一类人或事物:
②用于某些具有特征或特殊时期的国家和民族的名词前(无特征时无需加the);
③用于表示独一无二的事物的名词前;
④用于姓氏的复数形式前,表示全家人或夫妇俩;
⑤用于形容词最高级及起特定作用的比较级前;the more...the more...
⑥用于序数词或其他表示顺序的词前;the first book
⑦用于某一特定时刻存在,但其他时刻不存在的情况。 - 示例
- 定冠词通常
the是特指的,翻译为“这个”,如: I want to buy the car.我想买这辆车。- 这里的汽车是特指的,指的是具体的某一辆车。
- 定冠词通常
(三)零冠词
- 零冠词的意思是在名词前既不填定冠词,也不填不定冠词,可以理解为名词前什么都不填
- 专有名词前不加冠词
We had a good time on Christmas Day.圣诞节那天我们过得很愉快。- 这里的“圣诞节”为专有名词,前面无需添加其他冠词。
- 零冠词的用法
①国名、地名、人名等专有名词前通常不用冠词(无特征时使用):
②季节、月份、星期等名词前不加冠词(这里指具体的月份专有名词,如:January)
③在表示一日三餐、球类运动和娱乐运动的名词前不加冠词;乐器前必须加the,play the+乐器。
④名词前已有this,that,my,his,every,some等词修饰时,不用冠词,如:my left hand...,my other... 我的左手...,我的右手...使用了the other语法,但有my的存在,所以把the去掉。
⑤放在非特指的不可数名词前。
第十五章 名词及名词所有格
第十六章 情态动词
shall是will的第一人称形式
①用于shall well / shall i表示将来
②含义:...好吗? ...要不要?表示主动提供帮助
③必须、一定(法律上、规则上、原则上)
can
①可以做某事/有能力做某事:I can do this
②可以做某事?(征求意见)/请求做某事:can i...?
③能够(请求、礼貌提出帮助:你能/可以帮我吗?)
④允许...(我可以晚上出去玩)
⑤表示可能性(可能会...(将来可能发生的事情);可以..)可能会下雨
would
①用于will的过去
②会(征求意见:你会帮助...)
③过去常常
④愿意、想:我愿意做...;我想做...
need
①需要(劝告、建议:你需要看书了)
②有必要
实意动词need to do
情态动词need do
must
①必须
②一定(肯定的推测,有证据的推测)
must do(对现在的猜测) 现在一定做了...
must have done(对过去的猜测) 过去一定做了...
may
①可能、也许
②征求同意、意见(下级对上级的征求意见) may I have your attention please 我可以打搅一下你吗
③表示猜测时是毫无证据的猜测may do、may have done
should
①应该(如:你18岁了应该有独立生活的能力)
②应该、可以(建议)
③本应该(should have done)
should have done:本来应该做,但没做
would have done:本来会做(要做),但没做
could have done:本能够做什么,而没有做
must have done:一定做过某事,(没有否定,只能用can't/couldn't have done代替)
might have done:可能做过某事
常见的否定含义
can't不可能shouldn't不应该mustn't不允许,不准,禁止won't不会
主情从现
主情从现:主句使用情态动词,从句使用现在时
- If you __ to buy the computer,you should know its price.
A.want
B.wanted
C.will want
D.would want
- 解析
-
- 主句用情态动词
should,从句用现在时want,排除CD
- 主句用情态动词
- 句子是主动,排除B,选择A
情态动词的问答(仅供参考)
Could的问句,回答使用can;can'tMay的问句,回答使用please,can;can'tMust的问句,回答使用must;needn't,may not,(don't have to可以使用,但不是情态动词)Need的问句,回答must,have to,should(不能用need);needn't,(don't have to可以使用,但不是情态动词)Can的问句,回答使用can;can'twill的问句,回答使用will;won't- 用什么问 就用什么答
第十七章 数词
数词的分类
- 基数词
one、two、three、four - 序数词
first、second、third。序数词前面要有the,也有加a的情况,但很少见。a second time第二次、又一次、再一次
例子
This is the first book he bought.这次他买的第一本书
表示第几章、第几段、第几幕
表示第几章、第几段、第几幕: 名词(首字母大写)+基数词/the+序数词+名词
例子
- 第一单元:
Unit one/The first unit - 对话一:
Conversation one/the first conversation - 第5页:
Page five/the fifth page
数词的单位
- 百:
hundred100 - 千:
thousand1000 - 百万:
million1,000,000 - 十亿:
billion1,000,000,000 - 万亿:
trillion1,000,000,000,000 - 记忆:每次递增3个0
常见的数词表达
- More than基数词+thousand+名词复数(准确数字)
- 基数词+thousand+名词复数:
three thousand students - 基数词+thousand of the+名词复数
- Thousands of+名词复数:
thousands of students几干名学生,成干上万名学生 hundreds of thousands100×1000=100,000
年龄的表达
5 years old+名词:the boy is 5 years old5-year-old+形容词
分数的表达
One thirdTwo thirds分子大于1,分母+sTwo-thirds
特殊考点
基数词-名词原型=形容词:Two-day vacation 2天的假期
音标/发音
- 单词后缀
tion,发音/ʃən/,如:fiction、pollution pro:program、
常见单词变化
| 原型 | 三单 | 复数 | 现在分词 | 过去式 | 过去分词 | 否定 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| have | has | / | having | had | had | |
| will | wills或will | wills | willing | willed或would | willed或would | won't |
| feel | feels | feels | feeling | left | left | |
| take(拿) | takes | / | taking | took | taken | |
| come(到达) | comes | / | coming | came | / | / |
| cost(花费/费用) | / | / | / | cost | cost |
固定短语
be good for有易于...enjoy doing喜欢做;乐于做;享受的事情


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号