四、Abp vNext 基础篇丨领域构建
系列文章列表,点击展示/隐藏
正文
介绍
我们将通过例⼦介绍和解释⼀些显式规则。在实现领域驱动设计时,应该遵循这些规则并将其应⽤到解决⽅案中。
领域划分
首先我们先对比下Blog.Core和本次重构设计上的偏差,可以看到多了一个博客管理和类别管理。
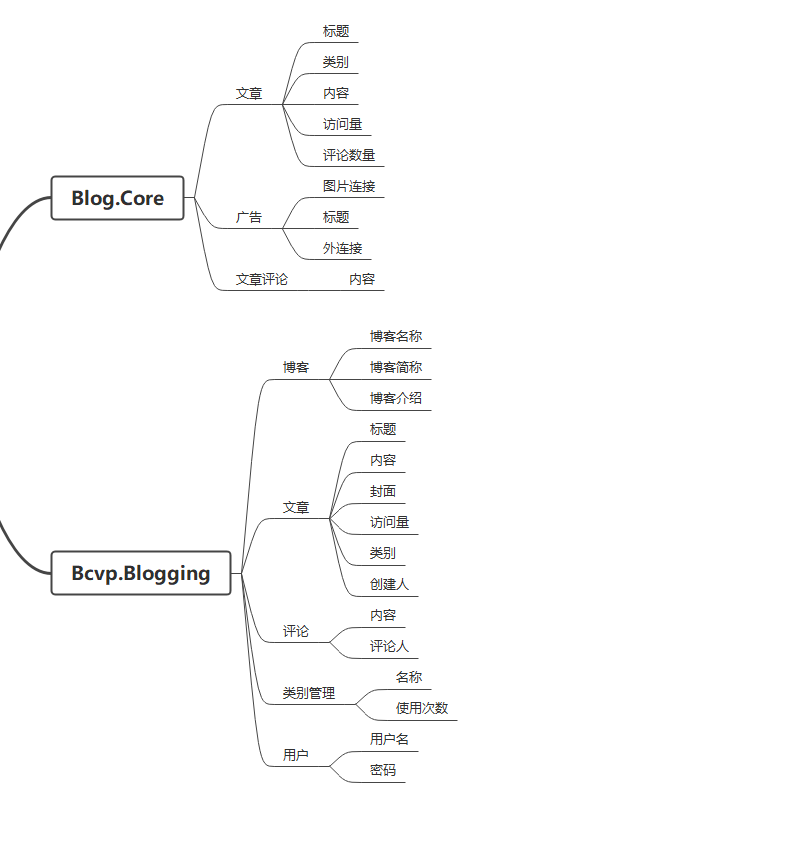
根据上面得到的业务脑图我们可以看到包含Blog(博客),Post(文章),Comment(评论),Tag(标签),User(用户),根据脑图画出领域图来指明关系。
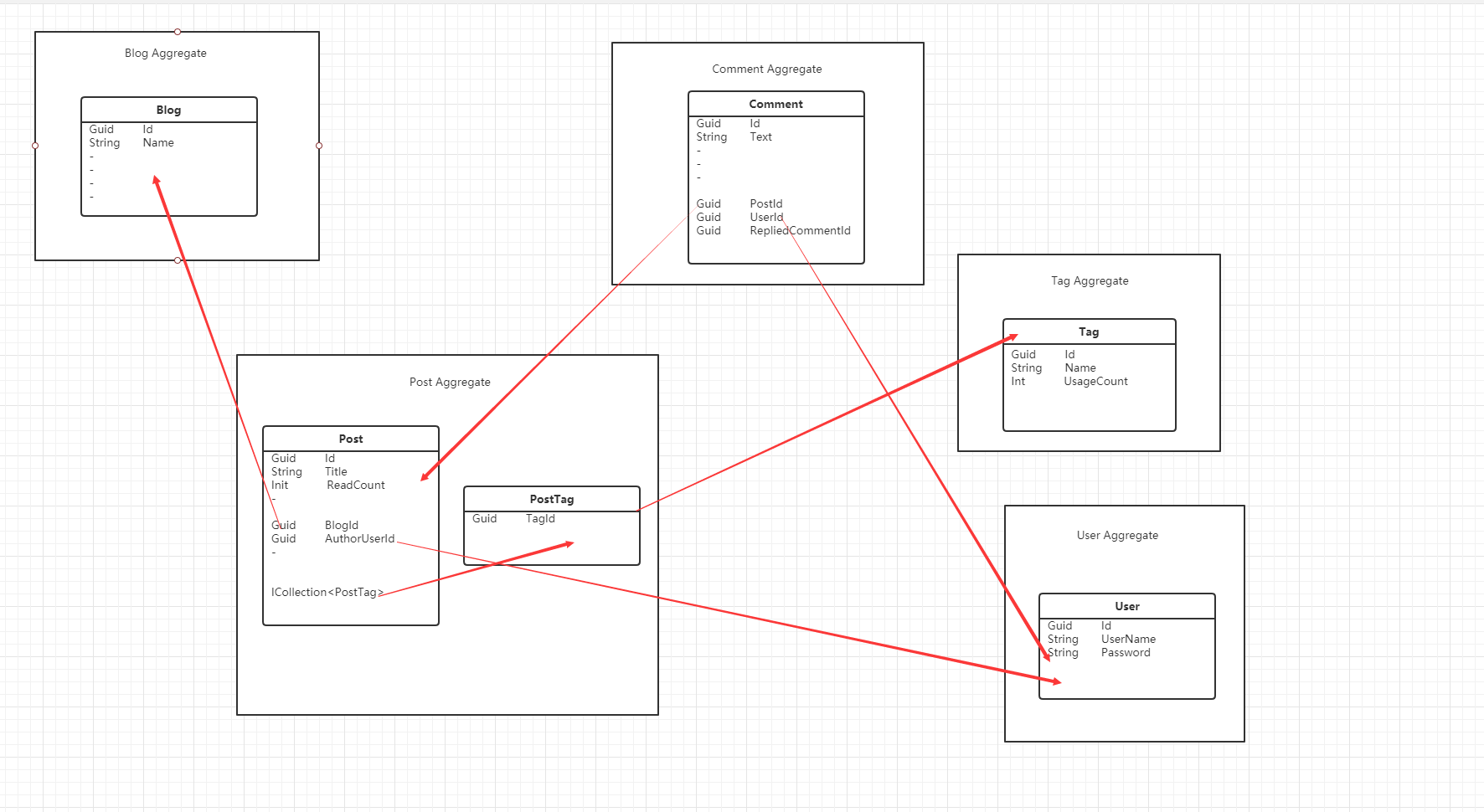
领域图连接地址:https://www.processon.com/view/link/611365c00e3e7407d39727ee
聚合根最佳实践
只通过ID引⽤其他聚合
⼀个聚合应该只通过其他聚合的ID引⽤聚合,这意味着你不能添加导航属性到其他聚合。
-
这条规则使得实现可序列化原则得以实现。
-
可以防⽌不同聚合相互操作,以及将聚合的业务逻辑泄露给另⼀个聚合。
来看下面的2个聚合根 Blog 和 Post.
- Blog 没有包含 Post集合,因为他们是不同聚合
- Post 使用 BlogId 关联 Blog
当你有一个 Post 需要关联 Blog的时候 你可以从数据库通过 BlogId 进行获取
public class Blog:FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
[NotNull]
public virtual string Name { get; set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string ShortName { get; set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Description { get; set; }
}
public class Post : FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public virtual Guid BlogId { get; protected set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string Url { get; protected set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string CoverImage { get; set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string Title { get; protected set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Content { get; set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Description { get; set; }
public virtual int ReadCount { get; protected set; }
public virtual Collection<PostTag> Tags { get; protected set; }
}
聚合根/实体中的主键
⼀个聚合根通常有⼀个ID属性作为其标识符(主键,Primark Key: PK)。推荐使⽤ Guid 作为聚合,聚合中的实体(不是聚合根)可以使⽤复合主键(后面讲),主键ABP已经帮我们做好了参阅文档:https://docs.abp.io/en/abp/latest/Entities。
public class Blog:FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
[NotNull]
public virtual string Name { get; set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string ShortName { get; set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Description { get; set; }
}
聚合根/实体构造函数
构造函数是实体的⽣命周期开始的地⽅。⼀个设计良好的构造函数,担负以下职责:
- 获取所需的实体属性参数,来创建⼀个有效的实体。应该强制只传递必要的参数,并可以将⾮必要 的属性作为可选参数。
- 检查参数的有效性。
- 初始化⼦集合。
public Blog(Guid id, [NotNull] string name, [NotNull] string shortName)
{
//属性赋值
Id = id;
//有效性检测
Name = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(name, nameof(name));
//有效性检测
ShortName = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(shortName, nameof(shortName));
}
- Blog 类通过构造函数参数、获得属性所需的值,以此创建一个正确有效的实体
- 在构造函数中验证输⼊参数的有效性,⽐如: Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(...) 当传递的值为空 时,抛出异常 ArgumentException
- 构造函数将参数 id 传递给 base 类,不在构造函数中⽣成 Guid,可以将其委托给另⼀个 Guid⽣成 服务,作为参数传递进来
- ⽆参构造函数对于ORM是必要的。我们将其设置为私有,以防⽌在代码中意外地使⽤它
实体属性访问器和⽅法
上⾯的示例代码,看起来可能很奇怪。⽐如:在构造函数中,我们强制传递⼀个不为 null 的 Name 。 但是,我们可以将 Name 属性设置为 null ,⽽对其没有进⾏任何有效性控制。
如果我们⽤ public 设置器声明所有的属性,就像上⾯的 Blog 类中的属性例⼦,我们就不能在实体的⽣命周期中强制保持其有效性和完整性。所以:
- 当需要在设置属性时,执⾏任何逻辑,请将属性设置为私有 private 。
- 定义公共⽅法来操作这些属性。
public class Blog:FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
[NotNull]
public virtual string Name { get; protected set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string ShortName { get; protected set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Description { get; set; }
protected Blog()
{
/*反序列化或ORM 需要*/
}
public Blog(Guid id, [NotNull] string name, [NotNull] string shortName)
{
//属性赋值
Id = id;
//有效性检测
Name = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(name, nameof(name));
//有效性检测
ShortName = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(shortName, nameof(shortName));
}
public virtual Blog SetName([NotNull] string name)
{
Name = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(name, nameof(name));
return this;
}
public virtual Blog SetShortName(string shortName)
{
ShortName = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(shortName, nameof(shortName));
return this;
}
}
业务逻辑和实体中的异常处理
当你在实体中进⾏验证和实现业务逻辑,经常需要管理异常:
- 创建特定领域异常。
- 必要时在实体⽅法中抛出这些异常
ABP框架 Exception Handing 系统处理了这些问题。
完成聚合的实体创建
根据 最佳实践的讲解完成,把其他实体创建出来,代码粘在这里了。
public class Blog:FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
[NotNull]
public virtual string Name { get; protected set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string ShortName { get; protected set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Description { get; set; }
protected Blog()
{
}
public Blog(Guid id, [NotNull] string name, [NotNull] string shortName)
{
//属性赋值
Id = id;
//有效性检测
Name = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(name, nameof(name));
//有效性检测
ShortName = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(shortName, nameof(shortName));
}
public virtual Blog SetName([NotNull] string name)
{
Name = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(name, nameof(name));
return this;
}
public virtual Blog SetShortName(string shortName)
{
ShortName = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(shortName, nameof(shortName));
return this;
}
}
public class Comment : FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public virtual Guid PostId { get; protected set; }
public virtual Guid? RepliedCommentId { get; protected set; }
public virtual string Text { get; protected set; }
protected Comment()
{
}
public Comment(Guid id, Guid postId, Guid? repliedCommentId, [NotNull] string text)
{
Id = id;
PostId = postId;
RepliedCommentId = repliedCommentId;
Text = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(text, nameof(text));
}
public void SetText(string text)
{
Text = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(text, nameof(text));
}
}
public class Post : FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public virtual Guid BlogId { get; protected set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string Url { get; protected set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string CoverImage { get; set; }
[NotNull]
public virtual string Title { get; protected set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Content { get; set; }
[CanBeNull]
public virtual string Description { get; set; }
public virtual int ReadCount { get; protected set; }
public virtual Collection<PostTag> Tags { get; protected set; }
protected Post()
{
}
public Post(Guid id, Guid blogId, [NotNull] string title, [NotNull] string coverImage, [NotNull] string url)
{
Id = id;
BlogId = blogId;
Title = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(title, nameof(title));
Url = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(url, nameof(url));
CoverImage = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(coverImage, nameof(coverImage));
Tags = new Collection<PostTag>();
Comments = new Collection<Comment>();
}
public virtual Post IncreaseReadCount()
{
ReadCount++;
return this;
}
public virtual Post SetTitle([NotNull] string title)
{
Title = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(title, nameof(title));
return this;
}
public virtual Post SetUrl([NotNull] string url)
{
Url = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(url, nameof(url));
return this;
}
public virtual void AddTag(Guid tagId)
{
Tags.Add(new PostTag(Id, tagId));
}
public virtual void RemoveTag(Guid tagId)
{
Tags.RemoveAll(t => t.TagId == tagId);
}
}
public record PostTag
{
public virtual Guid TagId { get; init; } //主键
protected PostTag()
{
}
public PostTag( Guid tagId)
{
TagId = tagId;
}
}
public class Tag : FullAuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public virtual Guid BlogId { get; protected set; }
public virtual string Name { get; protected set; }
public virtual string Description { get; protected set; }
public virtual int UsageCount { get; protected internal set; }
protected Tag()
{
}
public Tag(Guid id, Guid blogId, [NotNull] string name, int usageCount = 0, string description = null)
{
Id = id;
Name = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(name, nameof(name));
BlogId = blogId;
Description = description;
UsageCount = usageCount;
}
public virtual void SetName(string name)
{
Name = Check.NotNullOrWhiteSpace(name, nameof(name));
}
public virtual void IncreaseUsageCount(int number = 1)
{
UsageCount += number;
}
public virtual void DecreaseUsageCount(int number = 1)
{
if (UsageCount <= 0)
{
return;
}
if (UsageCount - number <= 0)
{
UsageCount = 0;
return;
}
UsageCount -= number;
}
public virtual void SetDescription(string description)
{
Description = description;
}
}
结语
本节知识点:
- 1.根据脑图划分聚合
- 2.根据领域图在遵守DDD的聚合根规范的情况下创建聚合
联系作者:加群:867095512 @MrChuJiu







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· AI技术革命,工作效率10个最佳AI工具