BFS基本操作及其技巧
阅读本博客前建议先学习BFS
Flood Fill 泛洪算法
顾名思义,此算法就如同洪水泛滥一样遍历每个情况,从源点开始向四周扩展,主要处理连通块问题
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 120;
typedef long long LL;
struct node
{
int x, y;
};
int n, m ,cnt = 0; // cnt记录水坑数量
char ch[N][N];
int dx[8] = {-1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1}, dy[8] = {1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0}; // 方向盘,方便记录下一个坐标
void bfs(int x, int y)
{
queue<node> q;
node srt;
srt.x = x;
srt.y = y;
q.push(srt); // 推进起始位置
while(q.size())
{
node a = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) // 八连通
{
node t;
t.x = a.x + dx[i];
t.y = a.y + dy[i];
if(t.x >= 0 && t.x < n && t.y >= 0 && t.y < m && ch[t.x][t.y] == 'W') // 如果合法
{
ch[t.x][t.y] = '.'; // 走过了的点和干地性质,也可用vis / st数组记录走过的点,以防重复查找
q.push(t); // 推入bfs,继续找
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) cin >> ch[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
if(ch[i][j] == 'W') // 如果是水坑
{
bfs(i, j);
cnt++; // 水坑的数量++
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
return 0;
}
山峰和山谷
一本通在线评测
题目描述
给定一个
定义山峰和山谷如下:
均由地图上的一个连通块组成;
所有方格高度都相同;
周围的方格(即不属于山峰或山谷但与山峰或山谷相邻的格子)高度均大于山谷的高度,或小于山峰的高度。
求地图内山峰和山谷的数量。特别地,如果整个地图方格的高度均相同,则整个地图既是一个山谷,也是一个山峰。
输入
第一行一个整数
接下来
输出
输出一行两个整数,分别表示山峰和山谷的数量。
样例
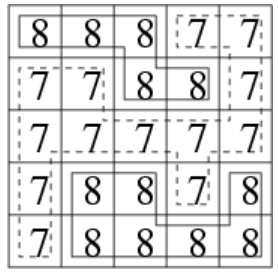
5
8 8 8 7 7
7 7 8 8 7
7 7 7 7 7
7 8 8 7 8
7 8 8 8 8
2 1
提示
样例1解释:
样例输入2:
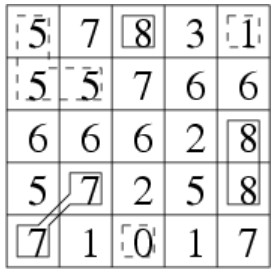
5
5 7 8 3 1
5 5 7 6 6
6 6 6 2 8
5 7 2 5 8
7 1 0 1 7
样例输出2:
3 3
样例2解释:
在FloodFill的基础上加上对山峰和山谷的判断
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
typedef long long LL;
int m[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
bool v, h;
int dx[9] = {0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1}, dy[9] = {1, 1, 0, -1, -1, -1, 0, 1}; // 方向盘
int hill, valley; // 记录山峰,山谷的数量
int n;
struct node
{
int x, y;
};
void bfs(int i, int j)
{
queue<node> q;
q.push({i, j});
vis[i][j] = true;
while(q.size())
{
node t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i ++)
{
int x = t.x + dx[i], y = t.y + dy[i];
if(x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > n) continue;
if(m[x][y] != m[t.x][t.y])
{
if(m[x][y] < m[t.x][t.y]) v = false; // 不符合山谷的定义
else h = false; // 同上
}
else if(!vis[x][y]) // 如果是一个联通块的
{
q.push({x, y}); // 更新bfs
vis[x][y] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)
cin >> m[i][j];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if(!vis[i][j])
{
h = v = true; // h == 1 => 是山峰 v == 1 => 是山谷
bfs(i, j);
if(h) hill ++;
else if(v) valley++;
}
cout << hill << " " << valley << endl;
return 0;
}
最短路模型
迷宫问题
一本通在线评测
定义一个二维数组:
int maze[5][5] = {
0,1,0,0,0,
0,1,0,1,0,
0,0,0,0,0,
0,1,1,1,0,
0,0,0,1,0,
};
它表示一个迷宫,其中的1表示墙壁,0表示可以走的路,只能横着走或竖着走,不能斜着走,要求编程序找出从左上角到右下角的最短路线。
输入
一个5 × 5的二维数组,表示一个迷宫。数据保证有唯一解。
输出
左上角到右下角的最短路径,格式如样例所示。
输入样例:
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0
输出样例:
(0, 0)
(1, 0)
(2, 0)
(2, 1)
(2, 2)
(2, 3)
(2, 4)
(3, 4)
(4, 4)
这题很大部分难度在于对于上一步的记录,本博客使用递归处理,
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N = 5; // 方便调试
typedef long long LL;
int maze[N][N]; // 地图
int dx[5] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[5] = {1, 0, -1, 0}; // 方向盘
struct node
{
int x, y;
}step[N][N]; // 记录上一步
void print(int x, int y)
{
if(x == 1 && y == 1) // 递归边界条件:找到起点
{
printf("(%d, %d)\n", 0, 0); // 输出起点下标0, 0
return;
}
print(step[x][y].x, step[x][y].y); // 递归寻找上一步
printf("(%d, %d)\n", x - 1, y - 1); // 由于下标从1开始,题目中要求输出从0开始,所以要-1
}
void bfs(int x, int y)
{
queue<node> q; // bfs板
node srt;
srt.x = x;
srt.y = y;
q.push(srt);
while(q.size())
{
node a = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int xx = a.x + dx[i], yy = a.y + dy[i];
if(xx > 0 && xx <= N && yy > 0 && yy <= N && maze[xx][yy] == 0)
{
maze[xx][yy] = 1;
q.push({xx, yy});
step[xx][yy] = a; // 记录如何到(xx, yy)的
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i ++)
for(int j = 1; j <= N; j ++)
cin >> maze[i][j];
bfs(1, 1);
print(5, 5); // 从终点开始往前找
return 0;
}
抓住那头牛
农夫知道一头牛的位置,想要抓住它。农夫和牛都位于数轴上,农夫起始位于点
1、从
2、从
假设牛没有意识到农夫的行动,站在原地不动。农夫最少要花多少时间才能抓住牛?
输入
两个整数,
输出
一个整数,农夫抓到牛所要花费的最小分钟数。
样例
5 17
4
来源
一本通在线评测
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n, k;
int vis[N], step[N];
void bfs()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(n);
vis[n] = true; // mark
step[n] = 0; // 起点到自己走0步
while(q.size())
{
int t = q.front();
q.pop();
if(t == k) // 即找到了
{
cout << step[k] << endl; // 直接输出
return; // 结束bfs
}
int d[3] = {t + 1, t - 1, t * 2}; // 方向盘
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++)
{
int x = d[i];
if(x >= 0 && x < N && !vis[x]) // 合法且未走过
{
q.push(x); // 继续bfs
vis[x] = true; // mark
step[x] = step[t] + 1; // 增加步数
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> k;
bfs();
return 0;
}
多源BFS
即将多个起始源点放入BFS队列中
题目意思
对于每一个点,输出
解法
多源bfs即源点有多个
我们在做普通bfs的时候,通常只需要在一开始给队列里推进一个源点,但是这道题需要推进多个源点,这就是二者的不同
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define x first
#define y second
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
const int N = 1010;
typedef long long LL;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
bool a[N][N];
int dist[N][N];
int n, m;
int dx[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
void bfs()
{
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist); // 初始化,-1表示未走过
queue<PII> q;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++) // 循环找到源点"们"
if(a[i][j])
{
q.push({i, j});
dist[i][j] = 0; // 推进源点,距离设为0
}
while(q.size())
{
PII t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
int x = t.x + dx[i], y = t.y + dy[i];
if(x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m) continue; // 不合法就跳过
if(dist[x][y] == -1) // 未走过则推入队列
{
dist[x][y] = dist[t.x][t.y] + 1; // 路径长度++
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++)
{
char ch;
cin >> ch;
a[i][j] = ch - '0'; // 由于cin会把一行当做一个int读入,所以需要char先存一下,血的教训>_<
}
bfs();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < m; j ++)
cout << dist[i][j] << " "; // 输出
puts("");
}
return 0;
}
最小步数模型
将魔板看成一维,寻找ABC操作的规律,之后用哈希表存储答案,排重
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
string st = "12345678", tg;
unordered_map<string, string> h;
string change(int op, string a)
{
if(op == 1)
{
reverse(a.begin(), a.end());
}
else if(op == 2)
{
for(int i = 3; i > 0; i --)
{
swap(a[i], a[i - 1]);
swap(a[7 - i], a[8 - i]);
}
}
else
{
swap(a[1], a[2]);
swap(a[1], a[5]);
swap(a[1], a[6]);
}
return a;
}
void bfs()
{
queue<string> q;
q.push(st);
h[st] = "";
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
string d[3] = {change(1, t), change(2, t), change(3, t)};
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i ++)
{
string x = d[i];
if(!h.count(x))
{
h[x] += h[t] + char(i + 'A');
if(x == tg) return;
q.push(x);
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 8;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int t;
cin >> t;
tg += char(t + '0');
}
if(tg == st)
{
cout << h[tg].size() << endl << h[tg] << endl;
return 0;
}
bfs();
cout << h[tg].size() << endl << h[tg] << endl;
return 0;
}
双端队列BFS
题目
给定一个图,图的边权为
铺好的电线就是0,没铺好的是1
算法分析
双端队列bfs相比朴素bfs只能处理权重相同的图的最短路径,它可以处理权重为
细节: 采用一个
-
要拓展的点的边权为1,则推入队尾
-
要拓展的点的边权为0,则推入队头
原因:贪心处理边权为
的边,可以发现 deque可以看成狭义上的堆,是阉割版的。
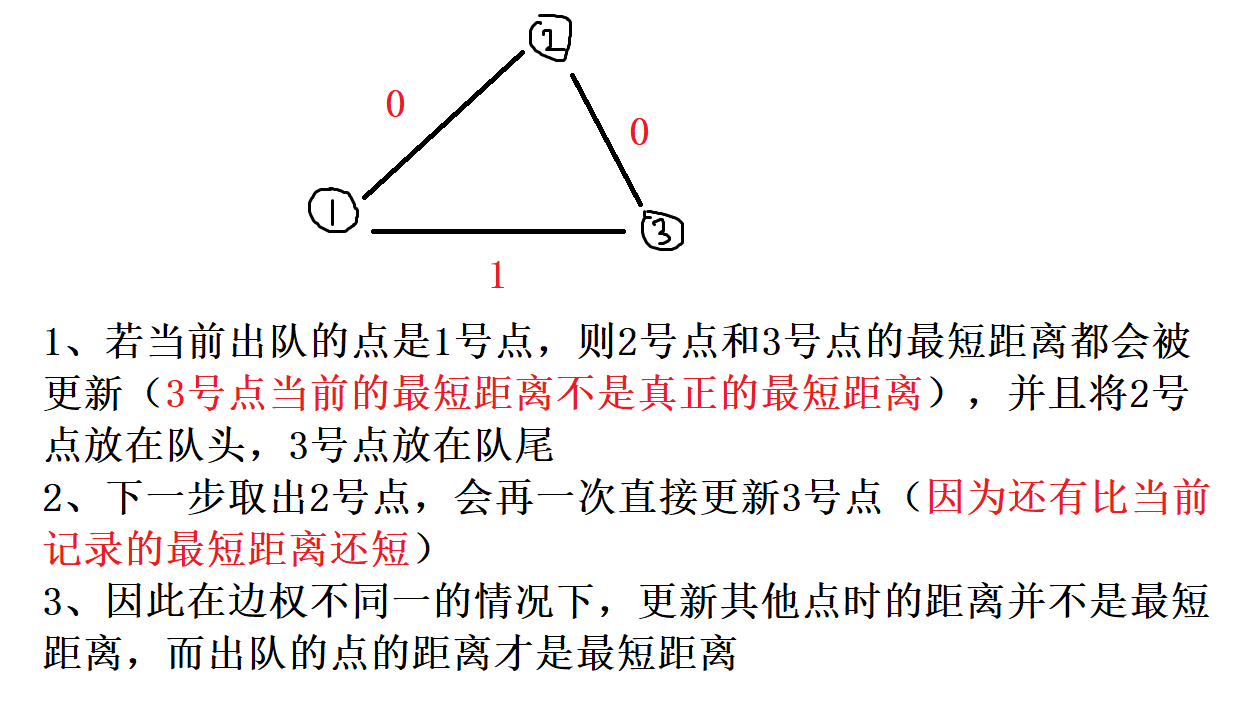
此题特色
此题特色在于对于方向盘(dx, dy, ix, iy)的处理
如下图:
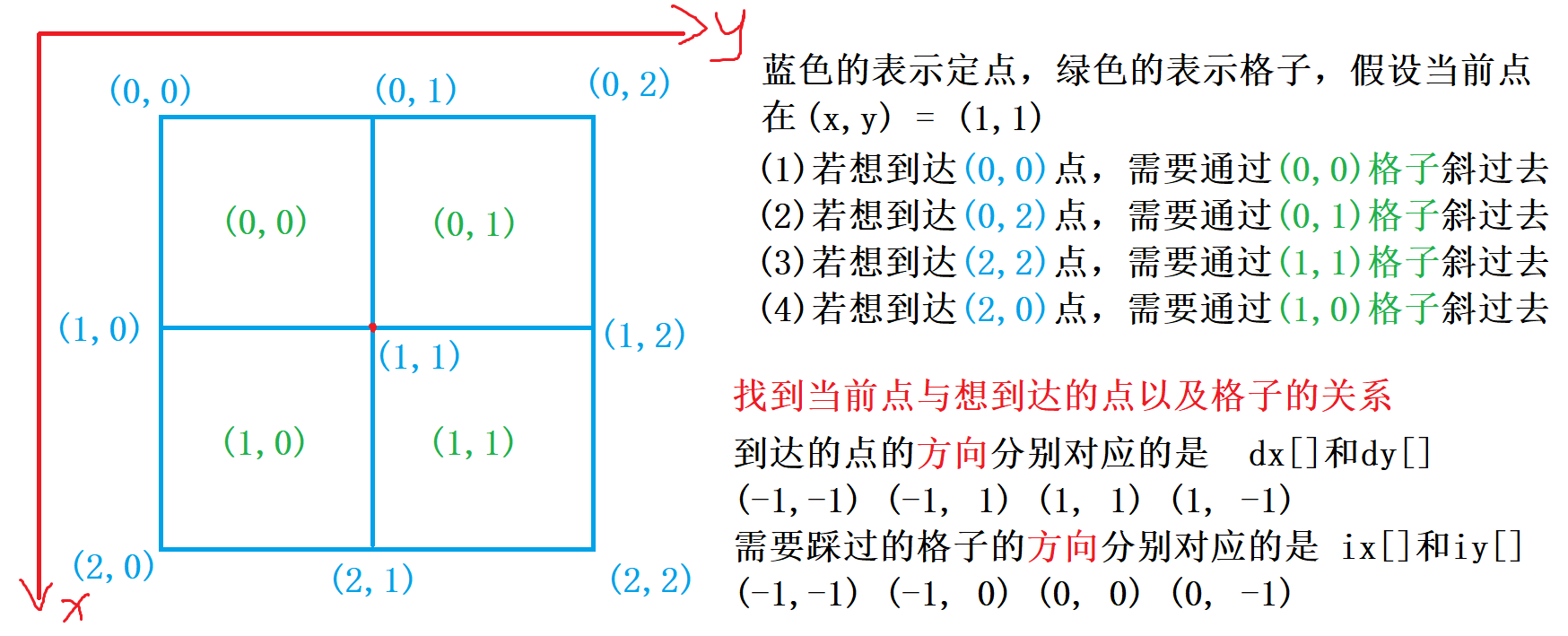
方向盘:
-
用
-
用
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <deque>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define N 510
using namespace std;
struct PII
{
int x, y;
};
char g[N][N];
char str[] = "\\/\\/"; // '\'是转义符,所以要多加一个
int d[N][N];
int ix[4] = {-1, -1, 0, 0}, iy[4] = {-1, 0, 0, -1}; // 方向盘
int dx[4] = {-1, -1, 1, 1}, dy[4] = {-1, 1, 1, -1};
bool st[N][N];
int bfs(int n, int m)
{
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof d); // distance初始化
deque<PII> q;
q.push_front({0, 0}); // 推进起点
d[0][0] = 0; // 起点到自身的距离为0
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop_front();
int x = t.x, y = t.y;
if(st[x][y]) continue; // 走过了就跳过
st[x][y] = true; // 标记
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
int px = x + dx[i], py = y + dy[i]; // 点坐标
if(px < 0 || px > n || py < 0 || py > m) continue; // 去掉不合法的情况
int ca = x + ix[i], cb = y + iy[i]; // 边坐标
int t = d[x][y] + (g[ca][cb] != str[i]); // 原距离加上代价
if(d[px][py] > t) // 相当于Dijkstra用t更新距离
{
d[px][py] = t; // 最短路径更新
if(g[ca][cb] == str[i]) q.push_front({px, py}); // 权值为0,推入队头
else q.push_back({px, py}); // 权值为1,推入队尾
}
}
}
return d[n][m];
}
int main()
{
int T = 1; // 由于SWOJ的题只有一套数据
while(T --)
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++)
scanf("%s", g[i]);
int t = bfs(n, m);
if (t == 0x3f3f3f3f) puts("NO SOLUTION"); // 也可以直接找出规律,但是我不会@_@
else printf("%d\n", t);
}
return 0;
}
双向BFS
此题数据限制严格,因此采取双向bfs,从起始状态和中止状态分别开始bfs,时间复杂度
Code
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define N 10
using namespace std;
string a[N], b[N];
int n;
// 扩展队列函数
int extend(queue<string>& q, unordered_map<string, int>& da, unordered_map<string, int>& db, string a[N], string b[N])
// 分别是:要扩展的队列,起点,终点,可变换字符串的规则,变换后字符串的规则
{
auto t = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) // 枚举规则
for(int j = 0; j < t.size(); j ++) // 枚举扩展起点
if(t.substr(j, a[i].size()) == a[i]) // 如果有符合规则的部分
{
string r = t.substr(0, j) + b[i] + t.substr(j + a[i].size()); // 把原字符串中符合规则a[]的部分替换成b[]
if(db.count(r)) return da[t] + 1 + db[r]; // 被另一个bfs走过了,则两边bfs会师,输出最小步数
if(da.count(r)) continue; // 被自己走过了,排除重复状态
da[r] = da[t] + 1; // 记录步数
q.push(r);
}
return 11;
}
int bfs(string A, string B)
{
if(A == B) return 0; // 相等则无需变换
queue<string> qa, qb;
unordered_map<string, int> da, db;
qa.push(A);
qb.push(B);
da[A] = db[B] = 0;
int step = 0;
while(qa.size() && qb.size())
{
int t;
if(qa.size() <= qb.size()) // 优先处理数据较少的队列
t = extend(qa, da, db, a, b); // 处理队列1
else
t = extend(qb, db, da, b, a); // 处理队列2
if(t <= 10) return t; // 即10步以内找到了答案
}
return 11; // NOT FOUND
}
int main()
{
string st, ed;
cin >> st >> ed;
while(cin >> a[n] >> b[n]) n++;
int t = bfs(st, ed);
if(t > 10) puts("NO ANSWER!");
else cout << t << endl;
return 0;
}

 Flood Fill 最短路模型 多源BFS 最小步数模型(不止地图) 双端队列bfs 双向bfs
Flood Fill 最短路模型 多源BFS 最小步数模型(不止地图) 双端队列bfs 双向bfs


【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· 为什么 退出登录 或 修改密码 无法使 token 失效