结构体数组/结构体指针/结构体嵌套结构体/结构体做函数参数/包含consat的结构体C++
1.结构体数组:
作用:将自定义的结构体放入到数组中方便维护。
语法:
先定义结构体,才能定义结构体数组
例:



2.结构体指针:
作用:通过指针访问结构体中的成员
(可以利用操作符->通过结构体指针访问结构体属性)


注意指针的数据类型。。。

3.结构体嵌套结构体:

图中,老师的结构体内嵌套了学生的结构体。。

给相应的变量赋值。
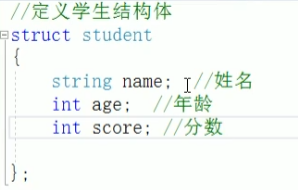
4.结构体做函数参数:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //定义学生结构体 7 struct student{ 8 string name; 9 int age; 10 int score; 11 }; 12 13 //打印学生信息 14 //1.值传递 15 void printStudent1(struct student s){ 16 cout << "name:" << s.name << endl; 17 cout << "age:" << s.age << endl; 18 cout << "score:" << s.score << endl; 19 } 20 21 //2.地址传递 22 void printStudent2(struct student * p){ 23 cout << "name:" << p->name << endl; 24 cout << "age:" << p->age << endl; 25 cout << "score:" << p->score << endl; 26 } 27 28 int main(){ 29 struct student s; 30 s.name = "你好"; 31 s.age = 20; 32 s.score = 60; 33 34 printStudent1(s); 35 printStudent2(&s); 36 37 38 system("pause"); 39 return 0; 40 }
注意值传递和地址传递中,形参和实参的问题。。。
采用地址传递的原因时,一个地址只占四个字节,可以减少内存的开销,提高运行效率。。
5.包含consat的结构体:
作用:防误操作
主要用于函数的地址传递时,传递的值在函数体内被修改

采用指针是为了节约空间。
如图,形参启用了const后,s->age = 150;变得不再可用。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号