机器学习十讲--第二讲-回归












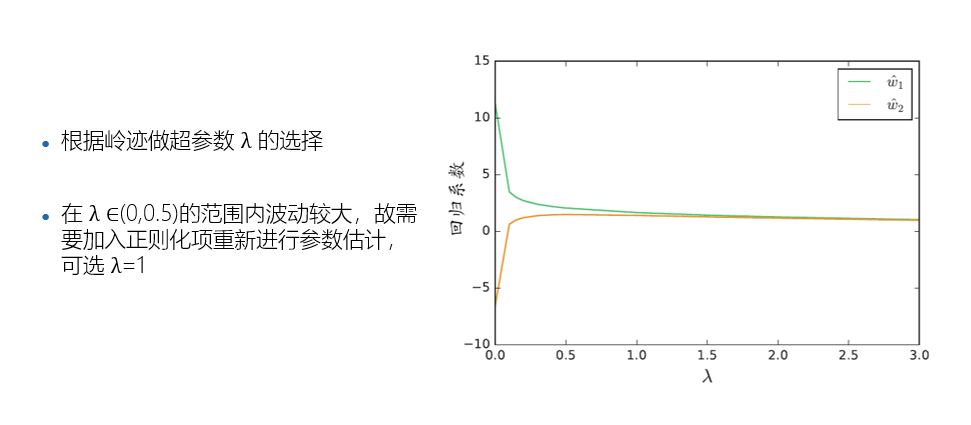


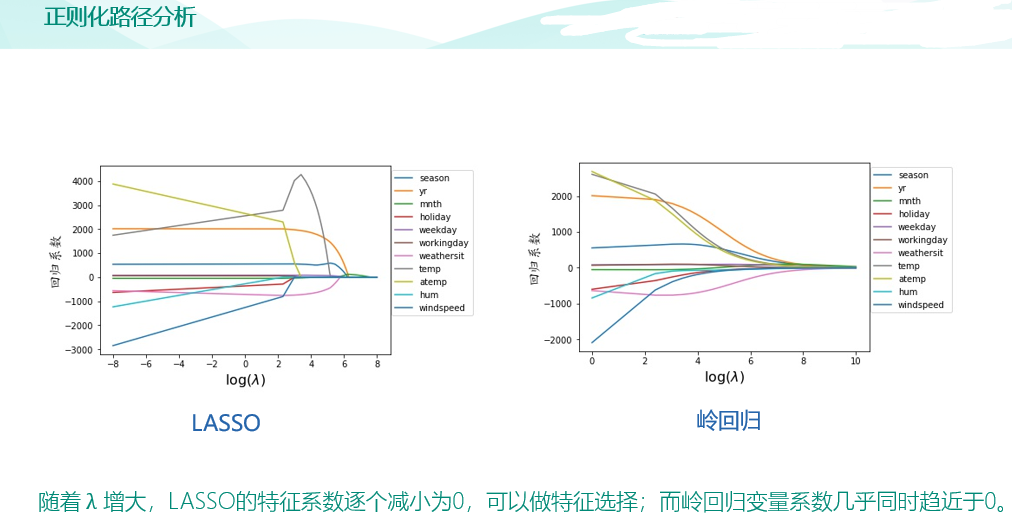
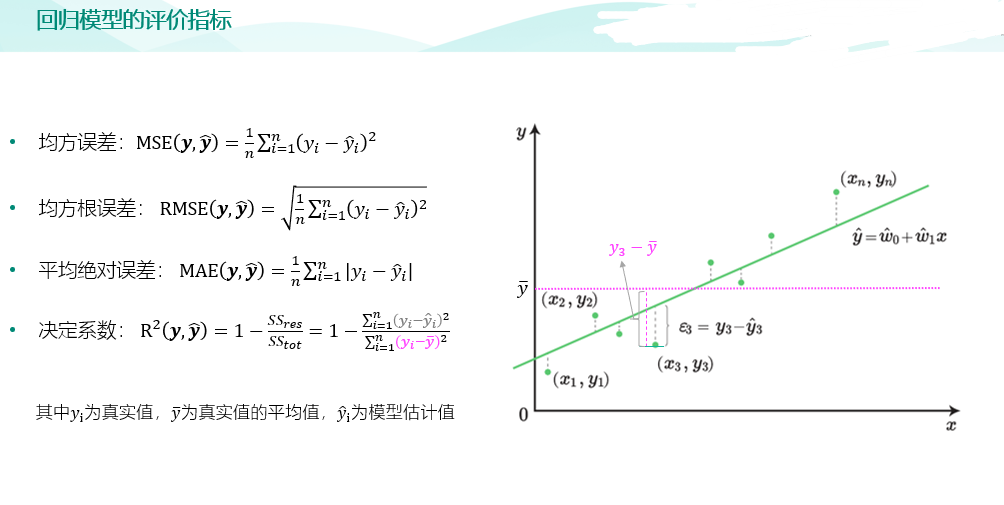

import pandas as pd data = pd.read_csv("input/abalone_dataset.csv") print(data.shape) #绘图中文字体 import matplotlib as mpl mpl.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei'] # #指定默认字体 SimHei为黑体 mpl.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus']=False # #用来正常显示负号 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt data["sex"].value_counts().sort_index().plot(kind="bar",title='sex') plt.show() #鲍鱼数据预处理 sex_onehot = pd.get_dummies(data["sex"], prefix="sex") # sex_onehot.info() #参数axis=0表示上下合并,1表示左右合并,ignore_index=True表示忽略原来的索引 data_new = pd.concat([data,sex_onehot],axis=1,ignore_index=False) data_new["ones"] = 1 #环数 rings 加上 1.5 得到年龄 data_new['age']=data_new['rings']+1.5 # print(data_new) #构造两组特征集 y = data_new["age"] features_with_ones = ["length","diameter","height","whole_weight","shucked_weight","viscera_weight","shell_weight","sex_F","sex_M","ones"] features_without_ones=["length","diameter","height","whole_weight","shucked_weight","viscera_weight","shell_weight","sex_F","sex_M"] x = data_new[features_with_ones] print(x) from sklearn import model_selection x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.2, random_state=111) from sklearn import linear_model lr = linear_model.LinearRegression() lr.fit(x_train[features_without_ones],y_train) from sklearn import linear_model ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=1.0) ridge.fit(x_train[features_without_ones],y_train) from sklearn import linear_model lasso = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=0.01) lasso.fit(x_train[features_without_ones],y_train) #均方误差和决定系数 R^2 from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error y_test_pred_lr = lr.predict(x_test.iloc[:,:-1]) print(round(mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_test_pred_lr),4)) y_test_pred_ridge = ridge.predict(x_test[features_without_ones]) print(round(mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_test_pred_ridge),4)) y_test_pred_lasso = lasso.predict(x_test[features_without_ones]) print(round(mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_test_pred_lasso),4)) from sklearn.metrics import r2_score print(round(r2_score(y_test,y_test_pred_lr),4)) print(round(r2_score(y_test,y_test_pred_ridge),4)) print(round(r2_score(y_test,y_test_pred_lasso),4)) #残差图是一种用来诊断回归模型效果的图。在残差图中,如果点随机分布在 0 附近,则说明回归效果较好。 # 如果在残差图中发现了某种结构,则说明回归效果不佳,需要重新建模。 plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6)) y_train_pred_ridge = ridge.predict(x_train[features_without_ones]) plt.scatter(y_train_pred_ridge, y_train_pred_ridge - y_train, c="g", alpha=0.6) plt.scatter(y_test_pred_ridge, y_test_pred_ridge - y_test, c="r",alpha=0.6) plt.hlines(y=0, xmin=0, xmax=30,color="b",alpha=0.6) plt.ylabel("Residuals") plt.xlabel("Predict") plt.show() #岭迹 import numpy as np alphas = np.logspace(-10,10,20) coef = pd.DataFrame() for alpha in alphas: ridge_clf = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=alpha) ridge_clf.fit(x_train[features_without_ones],y_train) df = pd.DataFrame([ridge_clf.coef_],columns=x_train[features_without_ones].columns) df['alpha'] = alpha coef = coef.append(df,ignore_index=True) coef.head().round(decimals=2) #绘图 plt.rcParams['figure.dpi'] = 300 #分辨率 plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6)) coef['alpha'] = coef['alpha'] for feature in x_train.columns[:-1]: plt.plot('alpha',feature,data=coef) ax = plt.gca() ax.set_xscale('log') plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.xlabel(r'$\alpha$',fontsize=15) plt.ylabel('系数',fontsize=15) plt.show() #LASSO 的正则化路径 coef = pd.DataFrame() for alpha in np.linspace(0.0001,0.2,20): lasso_clf = linear_model.Lasso(alpha=alpha) lasso_clf.fit(x_train[features_without_ones],y_train) df = pd.DataFrame([lasso_clf.coef_],columns=x_train[features_without_ones].columns) df['alpha'] = alpha coef = coef.append(df,ignore_index=True) coef.head() #绘图 plt.figure(figsize=(9, 6)) for feature in x_train.columns[:-1]: plt.plot('alpha',feature,data=coef) plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.xlabel(r'$\alpha$',fontsize=15) plt.ylabel('系数',fontsize=15) plt.show()

