深度学习02--数据读取
文件读取
读取流程
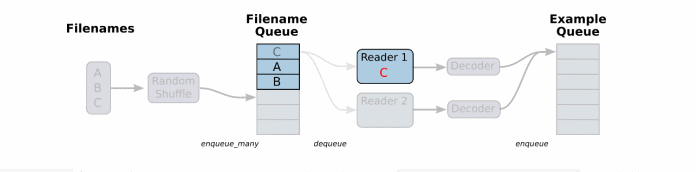
- 第一阶段构造文件名队列
- 第二阶段读取与解码
- 第三阶段批处理
注︰这些操作需要启动运行这些队列操作的线程,以便我们在进行文件读取的过程中能够顺利进行入队出队操作。
构造文件名队列
将需要读取的文件的文件名放入文件名队列
API
tf.train.string_input_producer(string_tensor, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True, seed=None, capacity=32, name=None)
- string_tensor:含有文件名+路径的1阶张量
- num_epochs:过几遍数据,默认无限过数据
- return文件队列
读取与解码
从队列当中读取文件内容,并进行解码操作。
文本逗号分隔值(CSV)
- 读取:tf.TextLineReader()
- 解码:tf.decode_csv()
图片
- 读取:tf.WholeFileReader()
- 解码:
- tf.image.decode_jpeg(contents) return:uint8张量,3-D形状[height, width, channels]
- tf.image.decode_png(contents) return:uint8张量,3-D形状[height, width, channels]
二进制
- 读取:tf.FixedLengthRecordReader(record_bytes)
- 解码:tf.decode_raw()
TFRecords
- 读取:tf.TFRecordReader()
注
- 读取方法均返回读取器实例
- 它们有共同的读取方法: read(file_queue),并且都会返回一个Tensors元组(key文件名字,value默认的内容(一个样本))
- 由于默认只会读取一个样本,所以如果想要进行批处理,需要使用tf.train.batch或tf.train.shuffle_batch进行批处理操作,便于之后指定每批次多个样本的训练。
批处理
解码之后,可以直接获取默认的一个样本内容了,但如果想要获取多个样本,需要加入到新的队列进行批处理。
API
tf.train.batch(tensors, batch_size, num_threads = 1, capacity = 32, name=None)
- 读取指定大小(个数)的张量
- tensors:可以是包含张量的列表,批处理的内容放到列表当中
- batch_size:从队列中读取的批处理大小
- num_threads:进入队列的线程数
- capacity:整数,队列中元素的最大数量
- return:tensors
tf.train.shuffle_batch
线程操作
- 以上用到的队列都是tf.train.QueueRunner对象。
- 每个QueueRunner都负责一个阶段,tf.train.start_queue_runners函数会要求图中的每个QueueRunner启动它的运行队列操作的线程。(这些操作需要在会话中开启)
开启线程
tf.train.Coordinator()
- 线程协调员,对线程进行管理和协调
- request_stop():请求停止
- should_stop():询问是否结束
- join(threads=None, stop_grace_period_secs=120):回收线程
- return:线程协调员实例
开启会话
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=None, coord=None)
- 收集图中所有的队列线程,默认同时启动线程
- sess:所在的会话
- coord:线程协调器o return:返回所有线程
案例
狗图片读取
图像基本概念
在图像数字化表示当中,分为黑白和彩色两种。在数字化表示图片的时候,有三个因素。分别是图片的长、图片的宽、图片的颜色通道数。那么黑白图片的颜色通道数为1,它只需要一个数字就可以表示一个像素位;而彩色照片就不一样了,它有三个颜色通道,分别为RGB,通过三个数字表示一个像素位。TensorFlow支持JPG、PNG图像格式,RGB、RGBA颜色空间。图像用与图像尺寸相同(heightwidthchnanel)张量表示。图像所有像素存在磁盘文件,需要被加载到内存。
图像大小压缩
大尺寸图像输入占用大量系统内存。训练CNN需要大量时间,加载大文件增加更多训练时间,也难存放多数系统GPU显存。大尺寸图像大量无关本征属性信息,影响模型泛化能力。最好在预处理阶段完成图像操作,缩小、裁剪、缩放、灰度调整等。图像加载后,翻转、扭曲,使输入网络训练信息多样化,缓解过拟合。Python图像处理框架PIL、OpenCV。TensorFlow提供部分图像处理方法。
- tf.image.resize_images 压缩图片到指定大小
代码
import tensorflow as tf import os def read_picture(): tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution() """ 读取狗图片案例 :return: """ # 1、构造文件名队列 # 构造文件名列表 filename_list = os.listdir("../dog") # 给文件名加上路径 file_list = [os.path.join("../dog/", i) for i in filename_list] # print("file_list:\n", file_list) # print("filename_list:\n", filename_list) file_queue = tf.compat.v1.train.string_input_producer(file_list) # 2、读取与解码 # 读取 reader = tf.compat.v1.WholeFileReader() key, value = reader.read(file_queue) print("key:\n", key) print("value:\n", value) # 解码 image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(value) print("image_decoded:\n", image_decoded) # 将图片缩放到同一个大小 image_resized = tf.compat.v1.image.resize_images(image_decoded, [200, 200]) print("image_resized_before:\n", image_resized) # 更新静态形状 image_resized.set_shape([200, 200, 3]) print("image_resized_after:\n", image_resized) # 3、批处理队列 image_batch = tf.compat.v1.train.batch([image_resized], batch_size=100, num_threads=2, capacity=100) print("image_batch:\n", image_batch) # 开启会话 with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 开启线程 # 构造线程协调器 coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.compat.v1.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord) # 运行 filename, sample, image, n_image = sess.run([key, value, image_resized, image_batch]) print("filename:\n", filename) print("sample:\n", sample) print("image:\n", image) print("n_image:\n", n_image) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads) return None if __name__ == "__main__": # 代码1:读取狗图片案例 read_picture()

二进制数据读取
代码
import tensorflow as tf import os class Cifar(): def __init__(self): # 设置图像大小 self.height = 32 self.width = 32 self.channel = 3 # 设置图像字节数 self.image = self.height * self.width * self.channel self.label = 1 self.sample = self.image + self.label def read_binary(self): """ 读取二进制文件 :return: """ # 1、构造文件名队列 filename_list = os.listdir("../cifar-10-batches-bin") # print("filename_list:\n", filename_list) file_list = [os.path.join("../cifar-10-batches-bin/", i) for i in filename_list if i[-3:]=="bin"] # print("file_list:\n", file_list) file_queue = tf.compat.v1.train.string_input_producer(file_list) # 2、读取与解码 # 读取 reader = tf.compat.v1.FixedLengthRecordReader(self.sample) # key文件名 value样本 key, value = reader.read(file_queue) # 解码 image_decoded = tf.compat.v1.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8) print("image_decoded:\n", image_decoded) # 切片操作 label = tf.slice(image_decoded, [0], [self.label]) image = tf.slice(image_decoded, [self.label], [self.image]) print("label:\n", label) print("image:\n", image) # 调整图像的形状 image_reshaped = tf.reshape(image, [self.channel, self.height, self.width]) print("image_reshaped:\n", image_reshaped) # 三维数组的转置 image_transposed = tf.transpose(image_reshaped, [1, 2, 0]) print("image_transposed:\n", image_transposed) # 3、构造批处理队列 image_batch, label_batch = tf.compat.v1.train.batch([image_transposed, label], batch_size=100, num_threads=2, capacity=100) # 开启会话 with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 开启线程 coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.compat.v1.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord) label_value, image_value = sess.run([label_batch, image_batch]) print("label_value:\n", label_value) print("image:\n", image_value) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads) return None if __name__ == "__main__": tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution() cifar = Cifar() cifar.read_binary()

TFRecords存储与读取
代码
import tensorflow as tf import os class Cifar(): def __init__(self): # 设置图像大小 self.height = 32 self.width = 32 self.channel = 3 # 设置图像字节数 self.image = self.height * self.width * self.channel self.label = 1 self.sample = self.image + self.label def read_binary(self): """ 读取二进制文件 :return: """ # 1、构造文件名队列 filename_list = os.listdir("../cifar-10-batches-bin") # print("filename_list:\n", filename_list) file_list = [os.path.join("../cifar-10-batches-bin/", i) for i in filename_list if i[-3:]=="bin"] # print("file_list:\n", file_list) file_queue = tf.compat.v1.train.string_input_producer(file_list) # 2、读取与解码 # 读取 reader = tf.compat.v1.FixedLengthRecordReader(self.sample) # key文件名 value样本 key, value = reader.read(file_queue) # 解码 image_decoded = tf.compat.v1.decode_raw(value, tf.uint8) print("image_decoded:\n", image_decoded) # 切片操作 label = tf.slice(image_decoded, [0], [self.label]) image = tf.slice(image_decoded, [self.label], [self.image]) print("label:\n", label) print("image:\n", image) # 调整图像的形状 image_reshaped = tf.reshape(image, [self.channel, self.height, self.width]) print("image_reshaped:\n", image_reshaped) # 三维数组的转置 image_transposed = tf.transpose(image_reshaped, [1, 2, 0]) print("image_transposed:\n", image_transposed) # 3、构造批处理队列 image_batch, label_batch = tf.compat.v1.train.batch([image_transposed, label], batch_size=100, num_threads=2, capacity=100) # 开启会话 with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 开启线程 coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.compat.v1.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord) label_value, image_value = sess.run([label_batch, image_batch]) print("label_value:\n", label_value) print("image:\n", image_value) coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads) return image_value, label_value def write_to_tfrecords(self, image_batch, label_batch): """ 将样本的特征值和目标值一起写入tfrecords文件 :param image: :param label: :return: """ with tf.compat.v1.python_io.TFRecordWriter("cifar10.tfrecords") as writer: # 循环构造example对象,并序列化写入文件 for i in range(100): image = image_batch[i].tostring() label = label_batch[i][0] # print("tfrecords_image:\n", image) # print("tfrecords_label:\n", label) example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={ "image": tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[image])), "label": tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[label])), })) # example.SerializeToString() # 将序列化后的example写入文件 writer.write(example.SerializeToString()) return None def read_tfrecords(self): """ 读取TFRecords文件 :return: """ # 1、构造文件名队列 file_queue = tf.compat.v1.train.string_input_producer(["cifar10.tfrecords"]) # 2、读取与解码 # 读取 reader = tf.compat.v1.TFRecordReader() key, value = reader.read(file_queue) # 解析example feature = tf.compat.v1.parse_single_example(value, features={ "image": tf.compat.v1.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), "label": tf.compat.v1.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64) }) image = feature["image"] label = feature["label"] print("read_tf_image:\n", image) print("read_tf_label:\n", label) # 解码 image_decoded = tf.compat.v1.decode_raw(image, tf.uint8) print("image_decoded:\n", image_decoded) # 图像形状调整 image_reshaped = tf.reshape(image_decoded, [self.height, self.width, self.channel]) print("image_reshaped:\n", image_reshaped) # 3、构造批处理队列 image_batch, label_batch = tf.compat.v1.train.batch([image_reshaped, label], batch_size=100, num_threads=2, capacity=100) print("image_batch:\n", image_batch) print("label_batch:\n", label_batch) # 开启会话 with tf.compat.v1.Session() as sess: # 开启线程 coord = tf.train.Coordinator() threads = tf.compat.v1.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord) image_value, label_value = sess.run([image_batch, label_batch]) print("image_value:\n", image_value) print("label_value:\n", label_value) # 回收资源 coord.request_stop() coord.join(threads) return None if __name__ == "__main__": tf.compat.v1.disable_eager_execution() cifar = Cifar() #image_value, label_value=cifar.read_binary() #cifar.write_to_tfrecords(image_value, label_value) cifar.read_tfrecords()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号