设计模式:迭代器模式(Iterator Pattern)
作者:TerryLee 创建于:2006-09-16 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/Terrylee/archive/2006/09/16/Iterator_Pattern.html 收录于:2013-02-28
结构图
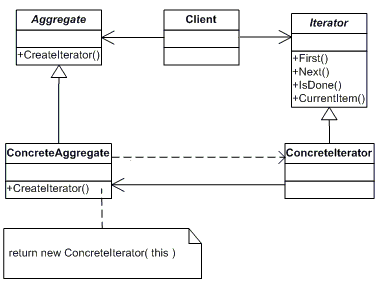
意图
提供一种方法顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素, 而又不需暴露该对象的内部表示。
适用性
- 访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示。
- 支持对聚合对象的多种遍历。
- 为遍历不同的聚合结构提供一个统一的接口(即, 支持多态迭代)。
实现代码
在面向对象的软件设计中,我们经常会遇到一类集合对象,这类集合对象的内部结构可能有着各种各样的实现,但是归结起来,无非有两点是需要我们去关心的:一是集合内部的数据存储结构,二是遍历集合内部的数据。面向对象设计原则中有一条是类的单一职责原则,所以我们要尽可能的去分解这些职责,用不同的类去承担不同的职责。Iterator模式就是分离了集合对象的遍历行为,抽象出一个迭代器类来负责,这样既可以做到不暴露集合的内部结构,又可让外部代码透明的访问集合内部的数据。下面看一个简单的示意性例子,类结构图如下
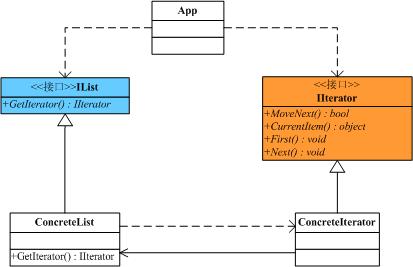
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 class Program 3 { 4 static void Main(string[] args) 5 { 6 IIterator iterator; 7 IList list = new ConcreteList(); 8 iterator = list.GetIterator(); 9 while (iterator.MoveNext()) 10 { 11 int i = (int)iterator.CurrentItem(); 12 Console.WriteLine(i.ToString()); 13 iterator.Next(); 14 } 15 Console.Read(); 16 } 17 } 18 public interface IList 19 { 20 IIterator GetIterator(); 21 } 22 public interface IIterator 23 { 24 bool MoveNext(); 25 Object CurrentItem(); 26 void First(); 27 void Next(); 28 } 29 public class ConcreteList : IList 30 { 31 int[] list; 32 public ConcreteList() 33 { 34 list = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; 35 } 36 public IIterator GetIterator() 37 { 38 return new ConcreteIterator(this); 39 } 40 public int Length 41 { 42 get { return list.Length; } 43 } 44 public int GetElement(int index) 45 { 46 return list[index]; 47 } 48 } 49 public class ConcreteIterator : IIterator 50 { 51 private ConcreteList list; 52 private int index; 53 public ConcreteIterator(ConcreteList list) 54 { 55 this.list = list; 56 index = 0; 57 } 58 public bool MoveNext() 59 { 60 if (index < list.Length) 61 return true; 62 else 63 return false; 64 } 65 public Object CurrentItem() 66 { 67 return list.GetElement(index); 68 } 69 public void First() 70 { 71 index = 0; 72 } 73 public void Next() 74 { 75 if (index < list.Length) 76 { 77 index++; 78 } 79 } 80 }
.NET中的Iterator模式
在.NET下实现Iterator模式,对于聚集接口和迭代器接口已经存在了,其中IEnumerator扮演的就是迭代器的角色NET中的Iterator模式
 View Code
View Code
1 using System; 2 class Client 3 { 4 static void Main(string[] args) 5 { 6 Persons arrPersons = new Persons("Michel", "Christine", "Mathieu", "Julien"); 7 foreach (string s in arrPersons) 8 { 9 Console.WriteLine(s); 10 } 11 Console.ReadLine(); 12 } 13 } 14 public interface IEumerator 15 { 16 object Current 17 { 18 get; 19 } 20 bool MoveNext(); 21 void Reset(); 22 } 23 public interface IEnumerable 24 { 25 IEumerator GetEnumerator(); 26 } 27 public class Persons : IEnumerable 28 { 29 public string[] m_Names; 30 public Persons(params string[] Names) 31 { 32 m_Names = new string[Names.Length]; 33 Names.CopyTo(m_Names,0); 34 } 35 36 public IEumerator GetEnumerator() 37 { 38 return new PersonsEnumerator(this); 39 } 40 } 41 42 public class PersonsEnumerator : IEumerator 43 { 44 private int index = -1; 45 private Persons P; 46 public PersonsEnumerator(Persons P) 47 { 48 this.P = P; 49 } 50 public bool MoveNext() 51 { 52 index++; 53 return index < P.m_Names.Length; 54 } 55 public void Reset() 56 { 57 index = -1; 58 } 59 public object Current 60 { 61 get 62 { 63 return P.m_Names[index]; 64 } 65 } 66 }
效果及实现要点
1.迭代抽象:访问一个聚合对象的内容而无需暴露它的内部表示。
2.迭代多态:为遍历不同的集合结构提供一个统一的接口,从而支持同样的算法在不同的集合结构上进行操作。
3.迭代器的健壮性考虑:遍历的同时更改迭代器所在的集合结构,会导致问题。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号