day1 java基础回顾-IO流
IO流的分类
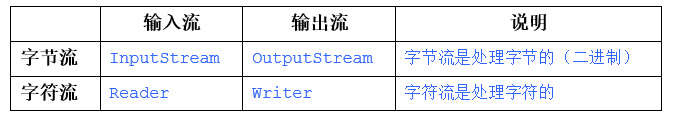
注:这几个类都是抽象类。
IO解决问题: 解决设备与设备之间 的数据传输问题。 比如: 硬盘--->内存 内存----->硬盘
字节流:
输入字节流:
---------| InputStream 所有输入字节流的基类。 抽象类。
------------| FileInputStream 读取文件的输入字节流。
------------| BufferedInputStream 缓冲输入字节流。 该类内部其实就是维护了一个8kb字节数组而已。 该类出现的目的是为了提高读取文件数据的效率。
输出字节流:
---------| OutputStream 所有输出字节流的基类。 抽象类。
------------| FileOutputStream 向文件输出数据 的输出字节流。
------------| BufferedOutputStream 缓冲输出字节流。 该类出现的目的是为了提高向文件写数据的效率。 该类内部其实也是维护了一个8kb的字节数组而已。
什么情况使用字节流: 读取到数据不需要经过编码或者解码的情况情况下这时候使用字节流。比如:图片数据
字符流 = 字节流 + 编码(解码)
字符流:
输入字符流
--------| Reader 所有输入字符流的基类。 抽象类。
-----------| FileReader 读取文件字符的输入字符流。
-----------| BufferedReader 缓冲输入字符流。 该类出现的目的是为了提高读取文件字符的效率并且拓展了功能(readLine()),它内部 其实就是维护了一个8192个长度的字符数组。
输出字符流
-------| Writer 所有输出字符流的基类。 抽象类。
------------| FileWriter 向文件输出字符数据的输出字符流。
---------------| BufferedWriter 缓冲输出字符流。该类出现的目的是为了提高写文件字符的效率并且拓展了功能(newLine())。
什么情况下使用字符流:如果读写的都是字符数据,这时候我们就使用字符流。
转换流:
输入字节流的转换流 输入字节流---------输入字符流
InputSrteamReader
输出字节流的转换流
OutputStreamWriter
转换流的作用:
1. 可以把对应的字节流转换成字符流使用。
2. 可以指定码表进行读写文件的数据。
FileReader, FileWriter这两个类默认是使用的是gbk编码 表。不能由你来指定码表读写文件数据。
读文件的代码
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 String path = "c:/a.txt"; 3 FileInputStream in = null; 4 try { 5 // 打开流 6 in = new FileInputStream(path); 7 // 使用流读文件内容 8 int b = in.read(); 9 while (b != -1) { 10 System.out.print((char) b); 11 b = in.read(); 12 } 13 } catch (Exception e) { 14 throw new RuntimeException(e); 15 } finally { 16 // 释放资源 17 if (in != null) { 18 try { 19 in.close(); 20 } catch (IOException e) { 21 throw new RuntimeException(e); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 }
拷贝文件的代码
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 String srcPath = "c:/a.txt"; 3 String destPath = "c:/b.txt"; 4 5 // 一定要使用字节流 6 InputStream in = null; 7 OutputStream out = null; 8 try { 9 // 打开流 10 in = new FileInputStream(srcPath); 11 out = new FileOutputStream(destPath); 12 // 使用流 13 byte[] buf = new byte[1024 * 8]; 14 for (int len = -1; (len = in.read(buf)) != -1;) { 15 out.write(buf, 0, len); 16 } 17 } catch (Exception e) { 18 e.printStackTrace(); 19 } finally { 20 // 释放资源 21 try { 22 if (in != null) { 23 in.close(); 24 } 25 } catch (IOException e) { 26 throw new RuntimeException(e); 27 } finally { 28 if (out != null) { 29 try { 30 out.close(); 31 } catch (IOException e) { 32 throw new RuntimeException(e); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 }
例子
1 2 public static void readFile() throws IOException{ 3 //建立文件与程序的输入数据通道 4 FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("F:\\a.txt"); 5 //创建输入字节流的转换流并且指定码表进行读取 6 InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream,"utf-8"); 7 int content = 0; 8 while((content = inputStreamReader.read())!=-1){ 9 System.out.println((char)content); 10 } 11 //关闭资源 12 inputStreamReader.close(); 13 14 15 //指定使用utf-8码表把数据写出到文件上。 16 public static void writeFile() throws IOException{ 17 //建立了文件与程序的数据 通道 18 FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("F:\\a.txt"); 19 //创建一个输出字节流的转换流并且指定码表进行写数据 20 OutputStreamWriter outputStreamWriter = new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream,"utf-8"); 21 outputStreamWriter.write("大家好"); //中文在utf-8码表中占三个字节。 22 23 //关闭资源 24 outputStreamWriter.close(); 25 }
posted on 2016-10-09 19:29 Michael2397 阅读(223) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报

