numpy-----01
1 import numpy as np 2 3 def npSum(): 4 a=np.array([0,1,2,3,4]) 5 b=np.array([9,8,7,6,5]) 6 c=a**2+b**3 7 return c 8 9 print(npSum())
NumPy是一个开源的Python科学计算基础库,包含:
• 一个强大的N维数组对象 ndarray
• 广播功能函数
• 整合C/C++/Fortran代码的工具
• 线性代数、傅里叶变换、随机数生成等功能
NumPy是SciPy、Pandas等数据处理或科学计算库的基础
ndarray实例
轴(axis):保存的数据的维度
秩(rank):轴的数量
| 属性 | 说明 |
| .ndim | 秩,轴的数量或者维度的数量 |
| .shape | ndarray对象的尺度,对于矩阵,n行m列 |
| .size | ndarray对象的元素的个数。相当于.shape中的n*m |
| .dtype | ndarray对象的元素类型 |
| .itemsize | ndarray对象中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位 |
1 Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.17134.407] 2 (c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。 3 4 D:\python入门>python 5 Python 3.7.0 (default, Jun 28 2018, 08:04:48) [MSC v.1912 64 bit (AMD64)] :: Anaconda, Inc. on win32 6 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. 7 >>> import numpy as np 8 >>> x=np.array([[0,1,2,3,4],[9,8,7,6]]) 9 >>> x.shape 10 (2,) 11 >>> x.dtype 12 dtype('O') 13 >>> x.itemsize 14 8 15 >>> x 16 array([list([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]), list([9, 8, 7, 6])], dtype=object) 17 >>> x.size 18 2 19 >>> x=np.array([[0,1,2,3,4],[9,8,7,6,5]]) 20 >>> x.shape 21 (2, 5) 22 >>> x.dtype 23 dtype('int32') 24 >>> x.itemsize 25 4 26 >>> x.size 27 10 28 >>>
ndarrary的创建
从Python中的列表、元组等类型创建ndarray数组
从Python中的列表、元组等类型创建ndarray数组x= np.array(list/tuple) x= np.array(list/tuple, dtype=np.float32)
当np.array()不指定dtype时,NumPy将根据数据情况关联一个dtype类型
• 使用NumPy中函数创建ndarray数组,如:arange, ones, zeros等

• 从字节流(raw bytes)中创建ndarray数组
• 从文件中读取特定格式,创建ndarray数组
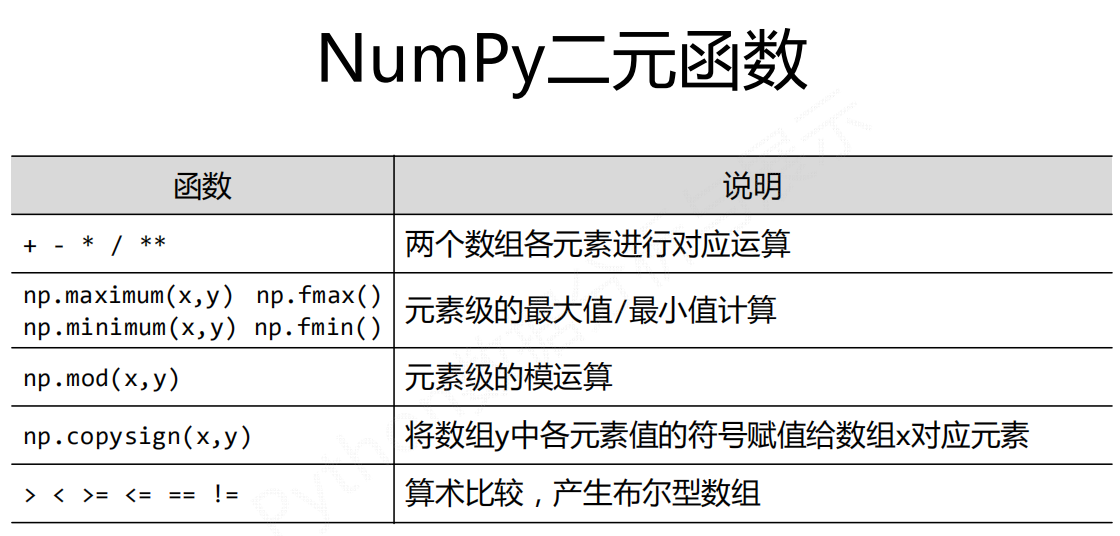
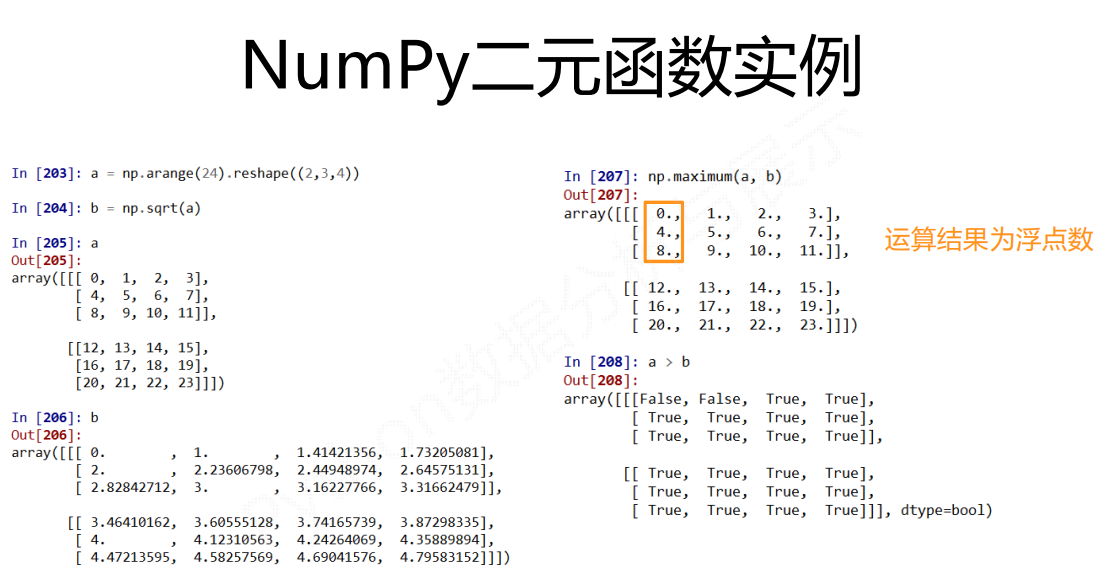
运算
a
Out[35]:
array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11]],
[[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23]]])
a.mean()#求数组的平均数
Out[36]: 11.5
a=a/a.mean()
a
Out[38]:
array([[[0. , 0.08695652, 0.17391304, 0.26086957],
[0.34782609, 0.43478261, 0.52173913, 0.60869565],
[0.69565217, 0.7826087 , 0.86956522, 0.95652174]],
[[1.04347826, 1.13043478, 1.2173913 , 1.30434783],
[1.39130435, 1.47826087, 1.56521739, 1.65217391],
[1.73913043, 1.82608696, 1.91304348, 2. ]]])
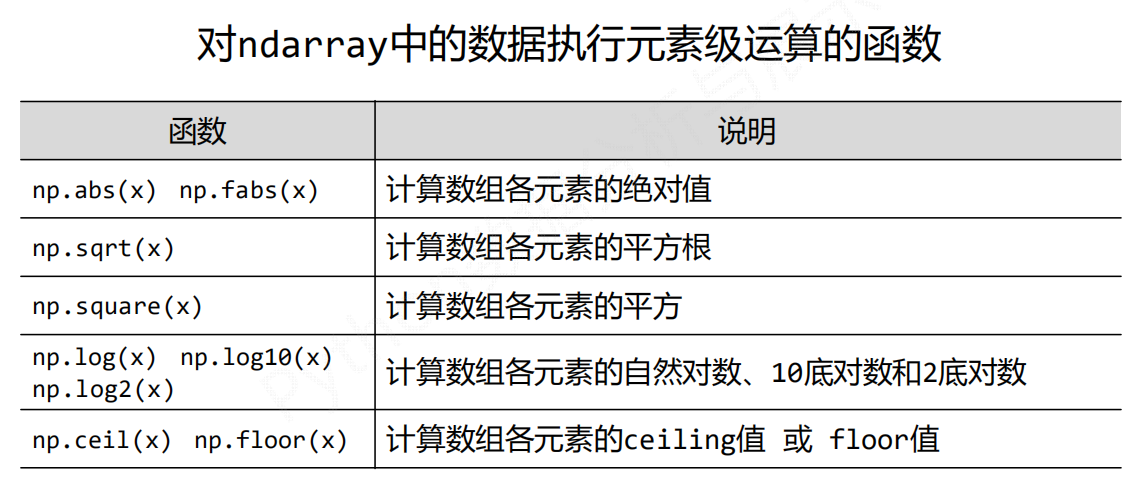
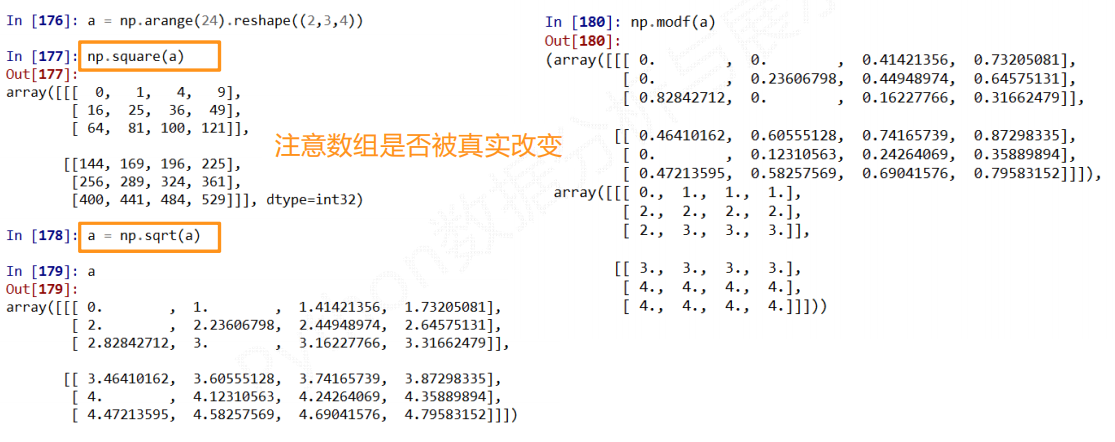
np.ceil(x) 不超过这个元素的整数值
np.floor(x) 小于这个元素的最大整数值

numpy读取保存文件
np.savetxt(frame, array, fmt='%.18e', delimiter=None)
• frame : 文件、字符串或产生器,可以是.gz或.bz2的压缩文件
• array : 存入文件的数组
• fmt : 写入文件的格式,例如:%d %.2f %.18e
• delimiter : 分割字符串,默认是任何空格
Python 3.6.6 (v3.6.6:4cf1f54eb7, Jun 27 2018, 03:37:03) [MSC v.1900 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32
Type "copyright", "credits" or "license()" for more information.
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a=np.arange(100).reshape(5,20)
>>> a
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15,
16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35,
36, 37, 38, 39],
[40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55,
56, 57, 58, 59],
[60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 75,
76, 77, 78, 79],
[80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 88, 89, 90, 91, 92, 93, 94, 95,
96, 97, 98, 99]])
>>> np.savetxt('a.csv',a,fmt='%d',delimiter=',')
>>>
np.loadtxt(frame, dtype=np.float, delimiter=None, unpack=False)
• frame : 文件、字符串或产生器,可以是.gz或.bz2的压缩文件
• dtype : 数据类型,可选
• delimiter : 分割字符串,默认是任何空格
• unpack : 如果True,读入属性将分别写入不同变量
CSV只能有效存储一维和二维数组
np.savetxt() np.loadtxt()只能有效存取一维和二维数组
a.tofile(frame, sep='', format='%s')
• frame : 文件、字符串
• sep : 数据分割字符串,如果是空串,写入文件为二进制
• format : 写入数据的格式
np.fromfile(frame, dtype=float, count=‐1, sep='')
• frame : 文件、字符串
• dtype : 读取的数据类型
• count : 读入元素个数,‐1表示读入整个文件
• sep : 数据分割字符串,如果是空串,写入文件为二进制
该方法需要读取时知道存入文件时数组的维度和元素类型 a.tofile() 和np.fromfile()需要配合使用可以通过元数据文件来存储额外信
np.save(fname, array) 或 np.savez(fname, array)
• fname : 文件名,以.npy为扩展名,压缩扩展名为.npz
• array : 数组变量
np.load(fname)
• fname : 文件名,以.npy为扩展名,压缩扩展名为.npz
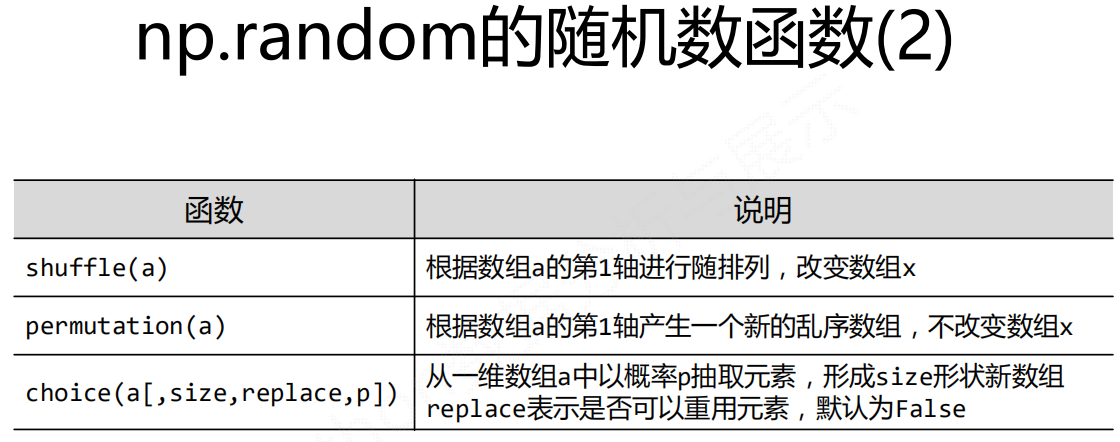
NumPy的random子库
np.random.*
np.random.rand()
np.random.randn()
np.random.randint()

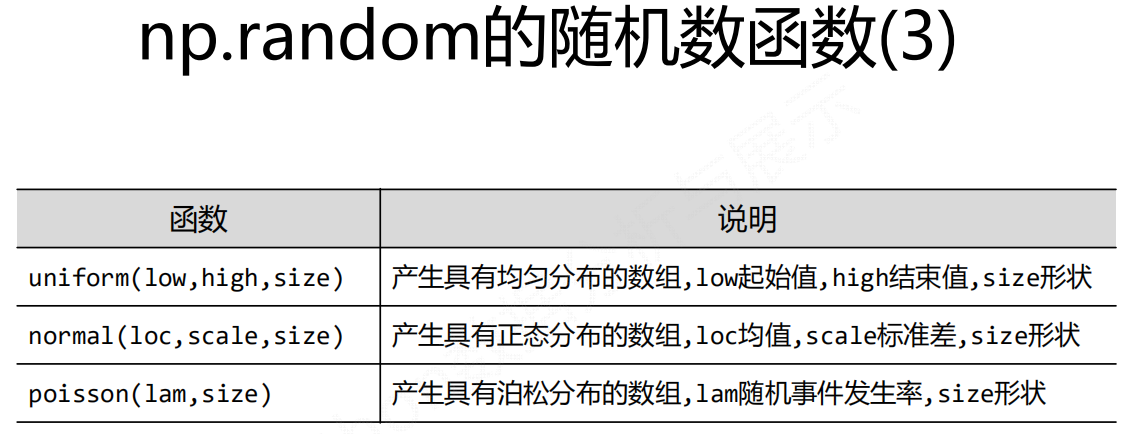
NumPy直接提供的统计类函数
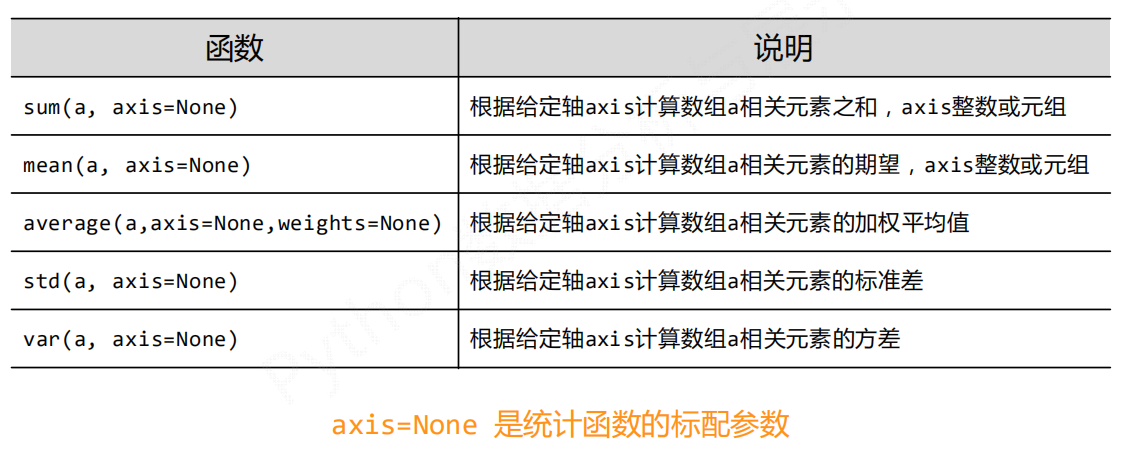
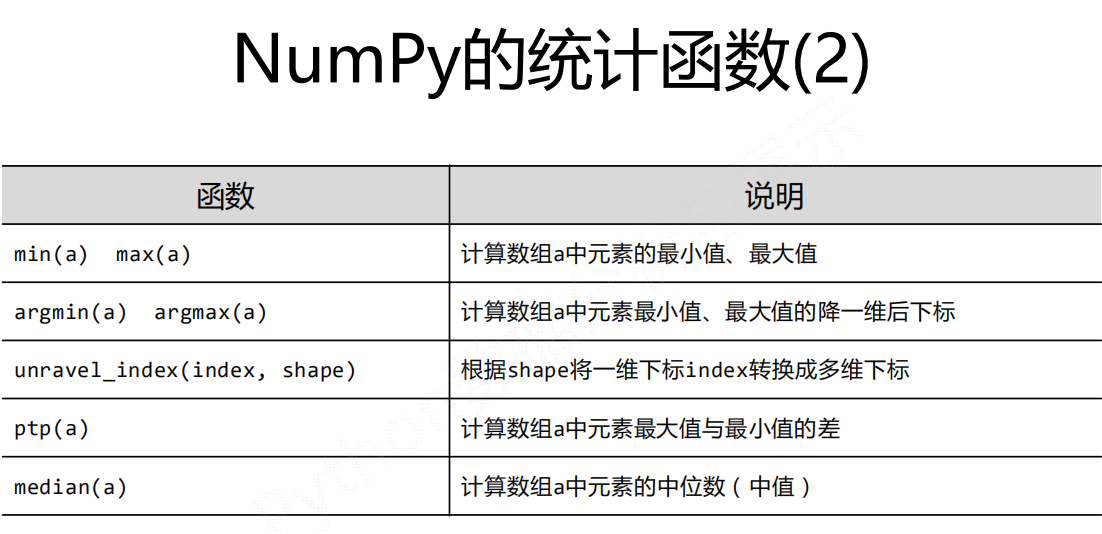
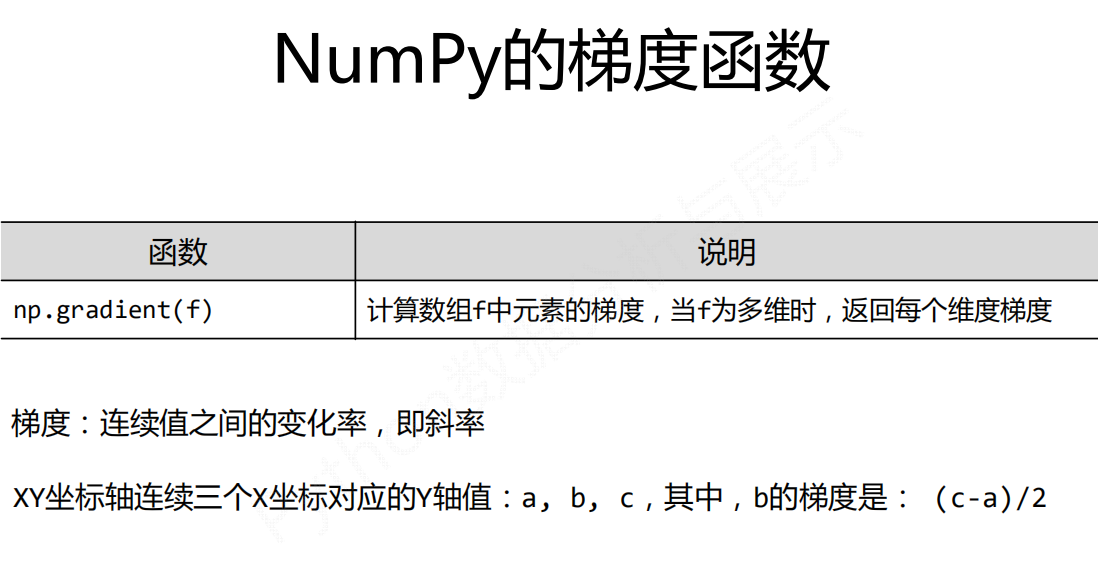
np.*
np.std() np.var() np.average()

>>> a=np.arange(10) >>> a array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]) >>> a.dtype dtype('int32') >>> b=np.ones(2,3) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> File "D:\Users\admin\Anaconda3\lib\site-packages\numpy\core\numeric.py", line 203, in ones a = empty(shape, dtype, order) TypeError: data type not understood >>> b=np.ones((2,3)) >>> b array([[1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1.]]) >>> b.dtype dtype('float64') >>> c=np.zeros((2,3)) >>> c array([[0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0.]]) >>> c.dtype dtype('float64') >>> d=full((2,4,9)) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> NameError: name 'full' is not defined >>> d=full((2,4),9) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> NameError: name 'full' is not defined >>> np.eye(5) array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 1., 0., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 1., 0., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 1., 0.], [0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]]) >>> d=full(2,4) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> NameError: name 'full' is not defined >>> d=np.full((2,4),9) >>> d array([[9, 9, 9, 9], [9, 9, 9, 9]]) >>> d.dtype dtype('int32') >>> np.linspace(4,9,2) array([4., 9.]) >>> np.linspace(4,9,5) array([4. , 5.25, 6.5 , 7.75, 9. ]) >>> np.linspace(4,9,4) array([4. , 5.66666667, 7.33333333, 9. ]) >>> np.linspace(4,9,6) array([4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.]) >>> np.linspace(4,9,6) array([4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.]) >>> np.linspace(5,9,5) array([5., 6., 7., 8., 9.]) >>> np.linspace(5,9,3) array([5., 7., 9.]) >>> np.linspace(5,9,3,endpoint=False) array([5. , 6.33333333, 7.66666667]) >>> np.linspace(5,9,4,endpoint=False) array([5., 6., 7., 8.]) >>> a=np.linspace(1,7,5) >>> a array([1. , 2.5, 4. , 5.5, 7. ]) >>> b=np.linspace(8,10,4) >>> b array([ 8. , 8.66666667, 9.33333333, 10. ]) >>> c=np.concatenate >>> c <built-in function concatenate> >>> c=np.concatenate(a,b) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> TypeError: only integer scalar arrays can be converted to a scalar index >>> c=np.concatenate((a,b)) >>> c array([ 1. , 2.5 , 4. , 5.5 , 7. , 8. , 8.66666667, 9.33333333, 10. ]) >>>

Jupyter QtConsole 4.4.1 Python 3.7.0 (default, Jun 28 2018, 08:04:48) [MSC v.1912 64 bit (AMD64)] Type 'copyright', 'credits' or 'license' for more information IPython 6.5.0 -- An enhanced Interactive Python. Type '?' for help. import numpy as np a=np.ones((2,3,4),dtype=np.int32) a Out[3]: array([[[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]], [[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]]]) a.reshape((3,8)) Out[4]: array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]) a Out[5]: array([[[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]], [[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]]]) a.resize((3,8)) a Out[7]: array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]) a.flatten() Out[8]: array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]) a Out[9]: array([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]]) b --------------------------------------------------------------------------- NameError Traceback (most recent call last) <ipython-input-10-89e6c98d9288> in <module>() ----> 1 b NameError: name 'b' is not defined b=a.flatten() b Out[12]: array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1])

a=np.ones((2,3,4),dtype=np.int) a Out[14]: array([[[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]], [[1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1, 1]]]) b=a.astype(np.float) b Out[16]: array([[[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]], [[1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.], [1., 1., 1., 1.]]]) a=np.full((2,3,4),25,dtype=np.int32) a Out[18]: array([[[25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25]], [[25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25]]]) a.tolist() Out[19]: [[[25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25]], [[25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25], [25, 25, 25, 25]]]

print("数组的索引和切片") 数组的索引和切片 a=np.array([9,8,7,6,5]) a exit exit() kadfsdafasf ) File "<ipython-input-21-a09c2020f0e1>", line 6 ) ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax a=np.array([9,8,7,6,5]) a Out[23]: array([9, 8, 7, 6, 5]) a[2] Out[24]: 7 a[0] Out[25]: 9 a[1:4:2] Out[26]: array([8, 6])

print("数组的索引和切片") 数组的索引和切片 a=np.array([9,8,7,6,5]) a exit exit() kadfsdafasf ) File "<ipython-input-21-a09c2020f0e1>", line 6 ) ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax a=np.array([9,8,7,6,5]) a Out[23]: array([9, 8, 7, 6, 5]) a[2] Out[24]: 7 a[0] Out[25]: 9 a[1:4:2] Out[26]: array([8, 6]) a=np.arange(24).reshape((2,3,4)) a Out[28]: array([[[ 0, 1, 2, 3], [ 4, 5, 6, 7], [ 8, 9, 10, 11]], [[12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19], [20, 21, 22, 23]]]) a[1,2,3] Out[29]: 23 a[1,0,0] Out[30]: 12 a[0,1,2] Out[31]: 6 a[-1,-2,-3] Out[32]: 17 a[:,1,-3] Out[33]: array([ 5, 17]) a[:,:,::2] Out[34]: array([[[ 0, 2], [ 4, 6], [ 8, 10]], [[12, 14], [16, 18], [20, 22]]])




