A. Strictly Increasing?
模拟
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i) using namespace std; int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); rep(i, n) cin >> a[i]; rep(i, n-1) { if (a[i] >= a[i+1]) { puts("No"); return 0; } } puts("Yes"); return 0; }
B. Make Target
模拟
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i) using namespace std; int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector<string> s(n, string(n, '.')); rep(l, n) { int r = n-1-l; if (l > r) continue; char c = '#'; if (l%2) c = '.'; for (int i = l; i <= r; ++i) { for (int j = l; j <= r; ++j) { s[i][j] = c; } } } rep(i, n) cout << s[i] << '\n'; return 0; }
C. Shortest Duplicate Subarray
遍历同一个数的相邻两个位置差+1求最小值
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i) using namespace std; int main() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n); rep(i, n) cin >> a[i]; vector<int> cnt(1000005); int mult = 0; const int INF = 1001001001; int ans = INF; int r = 0; rep(l, n) { while (r < n and mult == 0) { cnt[a[r]]++; if (cnt[a[r]] == 2) mult++; r++; } if (mult == 0) break; ans = min(ans, r-l); if (cnt[a[l]] == 2) mult--; cnt[a[l]]--; } if (ans == INF) ans = -1; cout << ans << '\n'; return 0; }
D. Pigeon Swap
考虑将巢里的鸽子看成一个整体,也就是将巢里的鸽子视为放入一个袋子 里,然后维护以下三种映射:
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i) using namespace std; int main() { int n, q; cin >> n >> q; vector<int> p2b(n); vector<int> b2h(n); vector<int> h2b(n); rep(i, n) p2b[i] = i; rep(i, n) b2h[i] = i; rep(i, n) h2b[i] = i; rep(qi, q) { int type; cin >> type; if (type == 1) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; --a; --b; p2b[a] = h2b[b]; } else if (type == 2) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; --a; --b; swap(h2b[a], h2b[b]); b2h[h2b[a]] = a; b2h[h2b[b]] = b; } else { int a; cin >> a; --a; int ans = b2h[p2b[a]]; cout << ans+1 << '\n'; } } return 0; }
E. Flip Edge
扩展Dijkstra
第二维用来维护是否翻转
那么只需要开2倍点即可
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i) using namespace std; using ll = long long; using P = pair<ll, int>; int main() { int n, m, x; cin >> n >> m >> x; n *= 2; vector<vector<int>> to(n); rep(i, m) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; --a; --b; to[a*2].push_back(b*2); to[b*2+1].push_back(a*2+1); } const ll INF = 1e18; priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P>> q; vector<ll> dist(n, INF); auto push = [&](int v, ll d) { if (dist[v] <= d) return; dist[v] = d; q.emplace(d, v); }; push(0, 0); while (q.size()) { auto [d, v] = q.top(); q.pop(); if (dist[v] != d) continue; for (int u : to[v]) push(u, d+1); push(v^1, d+x); } ll ans = min(dist[n-1], dist[n-2]); cout << ans << '\n'; return 0; }
F. Smooth Occlusion
注意到 满足单调性( 可行, 一定也可行)
费用为 ,可以看出 越大,费用越小
我们可以二分出满足条件的最大的H
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i) using namespace std; using ll = long long; int main() { int n, x; cin >> n >> x; vector<int> u(n), d(n); rep(i, n) cin >> u[i] >> d[i]; auto judge = [&](ll h) { ll l = 0, r = h; rep(i, n) { ll nl = h-d[i], nr = u[i]; nl = max(nl, 0ll); nr = min(nr, h); nl = max(nl, l-x); nr = min(nr, r+x); l = nl; r = nr; if (l > r) return false; } return true; }; ll ac = 0, wa = 3e9; while (ac+1 < wa) { ll wj = (ac+wa)/2; if (judge(wj)) ac = wj; else wa = wj; } ll ans = 0; rep(i, n) ans += u[i]+d[i]; ans -= ac*n; cout << ans << '\n'; return 0; }
G. Minimum Steiner Tree 2
steiner树dp+flyod最短路
考虑 和 这两点间的最短路
记 dp[v][S] 表示在 的最短路及其路径上挂着的支路中选择若干个点使得 , , 连通的最小费用
时间复杂度为
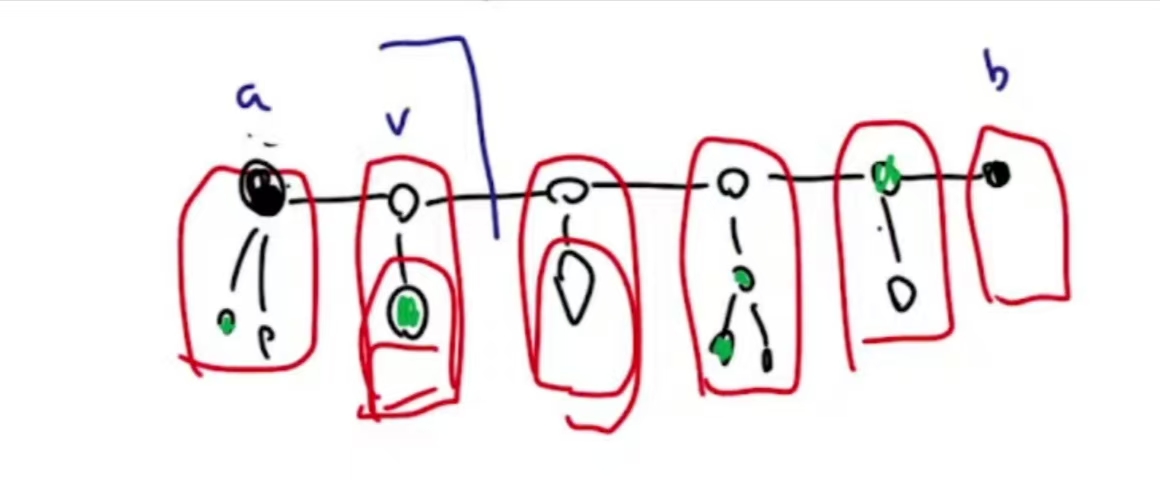
代码实现
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define rep(i, n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i) using namespace std; using ll = long long; inline void chmin(ll& x, ll y) { if (x > y) x = y; } int main() { cin.tie(nullptr) -> sync_with_stdio(false); int n, k; cin >> n >> k; int k2 = 1<<k; vector c(n, vector<ll>(n)); rep(i, n)rep(j, n) cin >> c[i][j]; rep(k, n)rep(i, n)rep(j, n) chmin(c[i][j], c[i][k]+c[k][j]); const ll INF = 1e18; vector dp1(n, vector<ll>(k2, INF)); // dp1[v][S]: 以 v 为根且包含点集 S 的最小费用 vector dp(n, vector(n, vector<ll>(k2, INF))); rep(i, n) dp1[i][0] = 0; rep(i, k) dp1[i][1<<i] = 0; rep(s, k2) { for (int t = s; t; t = (t-1)&s) { rep(i, n) chmin(dp1[i][s], dp1[i][t]+dp1[i][s^t]); } rep(i, n)rep(j, n) chmin(dp1[i][s], dp1[j][s]+c[j][i]); } rep(sv, n) { auto& ndp = dp[sv]; ndp[sv][0] = 0; rep(s, k2) { for (int t = s; t; t = (t-1)&s) { rep(i, n) chmin(ndp[i][s], dp1[i][t]+ndp[i][s^t]); } rep(i, n)rep(j, n) chmin(ndp[i][s], ndp[j][s]+c[j][i]); } } int q; cin >> q; rep(qi, q) { int a, b; cin >> a >> b; --a; --b; ll ans = dp[a][b][k2-1]; cout << ans << '\n'; } return 0; }




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 按钮权限的设计及实现