Floyd(弗洛伊德)算法(C语言)
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35644234/article/details/60875818
Floyd算法的介绍
算法的特点
弗洛伊德算法是解决任意两点间的最短路径的一种算法,可以正确处理有向图或有向图或负权(但不可存在负权回路)的最短路径问题,同时也被用于计算有向图的传递闭包。
算法的思路
通过Floyd计算图G=(V,E)中各个顶点的最短路径时,需要引入两个矩阵,矩阵S中的元素a[i][j]表示顶点i(第i个顶点)到顶点j(第j个顶点)的距离。矩阵P中的元素b[i][j],表示顶点i到顶点j经过了b[i][j]记录的值所表示的顶点。
假设图G中顶点个数为N,则需要对矩阵D和矩阵P进行N次更新。初始时,矩阵D中顶点a[i][j]的距离为顶点i到顶点j的权值;如果i和j不相邻,则a[i][j]=∞,矩阵P的值为顶点b[i][j]的j的值。 接下来开始,对矩阵D进行N次更新。第1次更新时,如果”a[i][j]的距离” > “a[i][0]+a[0][j]”(a[i][0]+a[0][j]表示”i与j之间经过第1个顶点的距离”),则更新a[i][j]为”a[i][0]+a[0][j]”,更新b[i][j]=b[i][0]。 同理,第k次更新时,如果”a[i][j]的距离” > “a[i][k-1]+a[k-1][j]”,则更新a[i][j]为”a[i][k-1]+a[k-1][j]”,b[i][j]=b[i][k-1]。更新N次之后,操作完成!
补充:以下面图为例子,b[i][j]中存储的是Vi~Vj之间的中介点,b[i][j]初始值为j,比如V0~V3最短路径是V0-->V2-->V1-->v3,在计算最短路径时转换为V0-->V2的距离加上V2-->V3的最短距离,接下来类似于递归,V2-->V3的最短路径就是以V1为中介点,V2-->V1的距离加上V1-->V3的距离。因此,b[0][3]=2
实例说明
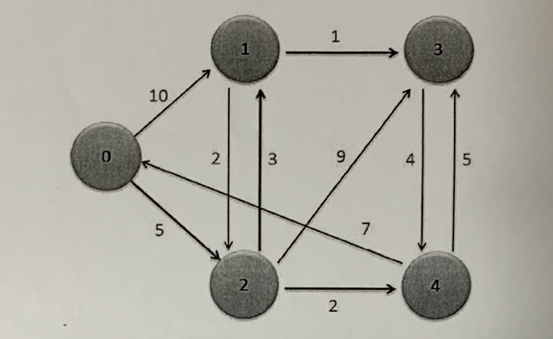
将整体分为两个步骤
1.计算metrixD矩阵(两顶点之间的最短距离)和P矩阵(两顶点的中介点)
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void Create_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P ,int VerNum, int EdgNum) { int x, y, Weight, edg_count = 0; int i, j, k; for (i = 0; i < VerNum; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < VerNum; ++j) { metrixD[i][j] = INT_MAX; P[i][j] = j; } } while (edg_count < EdgNum) { scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &Weight); metrixD[x - 1][y - 1] = Weight; edg_count++; } } //Floyd algorithm void Floyd(int **metirxD, int **P, int VerNum) { int n, x, y, temp = 0; //The triple loop looks for shortest paths and weights for (n = 0; n < VerNum; ++n) { for (x = 0; x < VerNum; ++x) { for (y = 0; y < VerNum; ++y) { //The distance between two vertices is compared to the distance through a vertex temp = (metirxD[x][n] == INT_MAX || metirxD[n][y] == INT_MAX) ? INT_MAX : (metirxD[x][n] + metirxD[n][y]); if (temp < metirxD[x][y]) { //Update matrix information metirxD[x][y] = temp; P[x][y] = n; } } } } } void Show_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P, int VerNum) { int x, y; printf("metrixD:\n"); for (x = 0; x < VerNum; ++x) { for (y = 0; y < VerNum; ++y) { if (metrixD[x][y] == INT_MAX) { printf("∞ "); } else { printf("%d ", metrixD[x][y]); } } printf("\n"); } printf("P:\n"); for (x = 0; x < VerNum; ++x) { for (y = 0; y < VerNum; ++y) { printf("%d ", P[x][y]); } printf("\n"); } } int main(void) { int VerNum, EdgNum, i; int** metrixD, ** P; printf("Enter the number of vertices and edges:"); scanf("%d%d", &VerNum, &EdgNum); metrixD = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); P = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); for (i = 0; i < VerNum; ++i) { metrixD[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); P[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); } printf("Input vertices and weights:"); Create_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum, EdgNum); Floyd(metrixD, P, VerNum); Show_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum); for (i = 0; i < VerNum; ++i) { free(metrixD[i]); free(P[i]); } free(metrixD); free(P); return 0; }
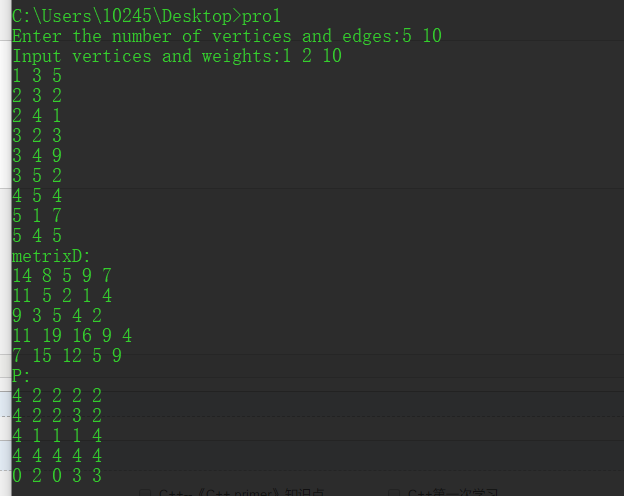
2.输出顶点之间的最短距离与路径
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define VEXNUM 5 //Adjacency matrix: shows the distance between vertices int metirxD[VEXNUM][VEXNUM] = { INT_MAX,10, 5, INT_MAX,INT_MAX, INT_MAX,INT_MAX,2, 1, INT_MAX, INT_MAX,3, INT_MAX,9, 2, INT_MAX,INT_MAX,INT_MAX,INT_MAX,4, 7, INT_MAX,INT_MAX,5, INT_MAX }; //Path: passing vertex between two vertices int P[VEXNUM][VEXNUM] = { 0,1,2,3,4, 0,1,2,3,4, 0,1,2,3,4, 0,1,2,3,4, 0,1,2,3,4 }; //Floyd algorithm void Floyd() { int n, x, y, temp = 0; //The triple loop looks for shortest paths and weights for (n = 0; n < VEXNUM; ++n) { for (x = 0; x < VEXNUM; ++x) { for (y = 0; y < VEXNUM; ++y) { //The distance between two vertices is compared to the distance through a vertex temp = (metirxD[x][n] == INT_MAX || metirxD[n][y] == INT_MAX) ? INT_MAX : (metirxD[x][n] + metirxD[n][y]); if (temp < metirxD[x][y]) { //Update matrix information metirxD[x][y] = temp; P[x][y] = n; } } } } } void Show_Path() { int x, y, temp = 0; //Output the shortest path between two vertices for (x = 0; x < VEXNUM - 1; ++x) { for (y = x + 1; y < VEXNUM; ++y) { printf("V%d-->V%d weight:%d path:V%d", x, y, metirxD[x][y], x); temp = P[x][y]; while (temp != y) { printf("-->V%d", temp); temp = P[temp][y]; } printf("-->V%d", y); printf("\n"); } } } int main(void) { Floyd(); Show_Path(); return 0; }

完整代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> void Create_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P ,int VerNum, int EdgNum) { int x, y, Weight, edg_count = 0; int i, j, k; for (i = 0; i < VerNum; ++i) { for (j = 0; j < VerNum; ++j) { metrixD[i][j] = INT_MAX; P[i][j] = j; } } while (edg_count < EdgNum) { scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &Weight); metrixD[x - 1][y - 1] = Weight; edg_count++; } } //Floyd algorithm void Floyd(int **metirxD, int **P, int VerNum) { int n, x, y, temp = 0; //The triple loop looks for shortest paths and weights for (n = 0; n < VerNum; ++n) { for (x = 0; x < VerNum; ++x) { for (y = 0; y < VerNum; ++y) { //The distance between two vertices is compared to the distance through a vertex temp = (metirxD[x][n] == INT_MAX || metirxD[n][y] == INT_MAX) ? INT_MAX : (metirxD[x][n] + metirxD[n][y]); if (temp < metirxD[x][y]) { //Update matrix information metirxD[x][y] = temp; P[x][y] = n; } } } } } void Show_metrixD_P(int** metrixD, int **P, int VerNum) { int x, y; printf("metrixD:\n"); for (x = 0; x < VerNum; ++x) { for (y = 0; y < VerNum; ++y) { if (metrixD[x][y] == INT_MAX) { printf("∞ "); } else { printf("%d ", metrixD[x][y]); } } printf("\n"); } printf("P:\n"); for (x = 0; x < VerNum; ++x) { for (y = 0; y < VerNum; ++y) { printf("%d ", P[x][y]); } printf("\n"); } } void Show_Path(int **metirxD, int **P, int VerNum) { int x, y, temp = 0; //Output the shortest path between two vertices for (x = 0; x < VerNum - 1; ++x) { for (y = x + 1; y < VerNum; ++y) { printf("V%d-->V%d weight:%d path:V%d", x, y, metirxD[x][y], x); temp = P[x][y]; while (temp != y) { printf("-->V%d", temp); temp = P[temp][y]; } printf("-->V%d", y); printf("\n"); } } } int main(void) { int VerNum, EdgNum, i; int** metrixD, ** P; printf("Enter the number of vertices and edges:"); scanf("%d%d", &VerNum, &EdgNum); metrixD = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); P = (int**)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); for (i = 0; i < VerNum; ++i) { metrixD[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); P[i] = (int*)malloc(VerNum * sizeof(int)); } printf("Input vertices and weights:"); Create_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum, EdgNum); Floyd(metrixD, P, VerNum); Show_metrixD_P(metrixD, P, VerNum); Show_Path(metrixD, P, VerNum); for (i = 0; i < VerNum; ++i) { free(metrixD[i]); free(P[i]); } free(metrixD); free(P); return 0; }



