Spring 使用介绍(十三)—— Bean的生命周期
一、概述
Spring Bean的完整生命周期从创建Spring容器开始,直到最终Spring容器销毁Bean,生命周期时序图如下:
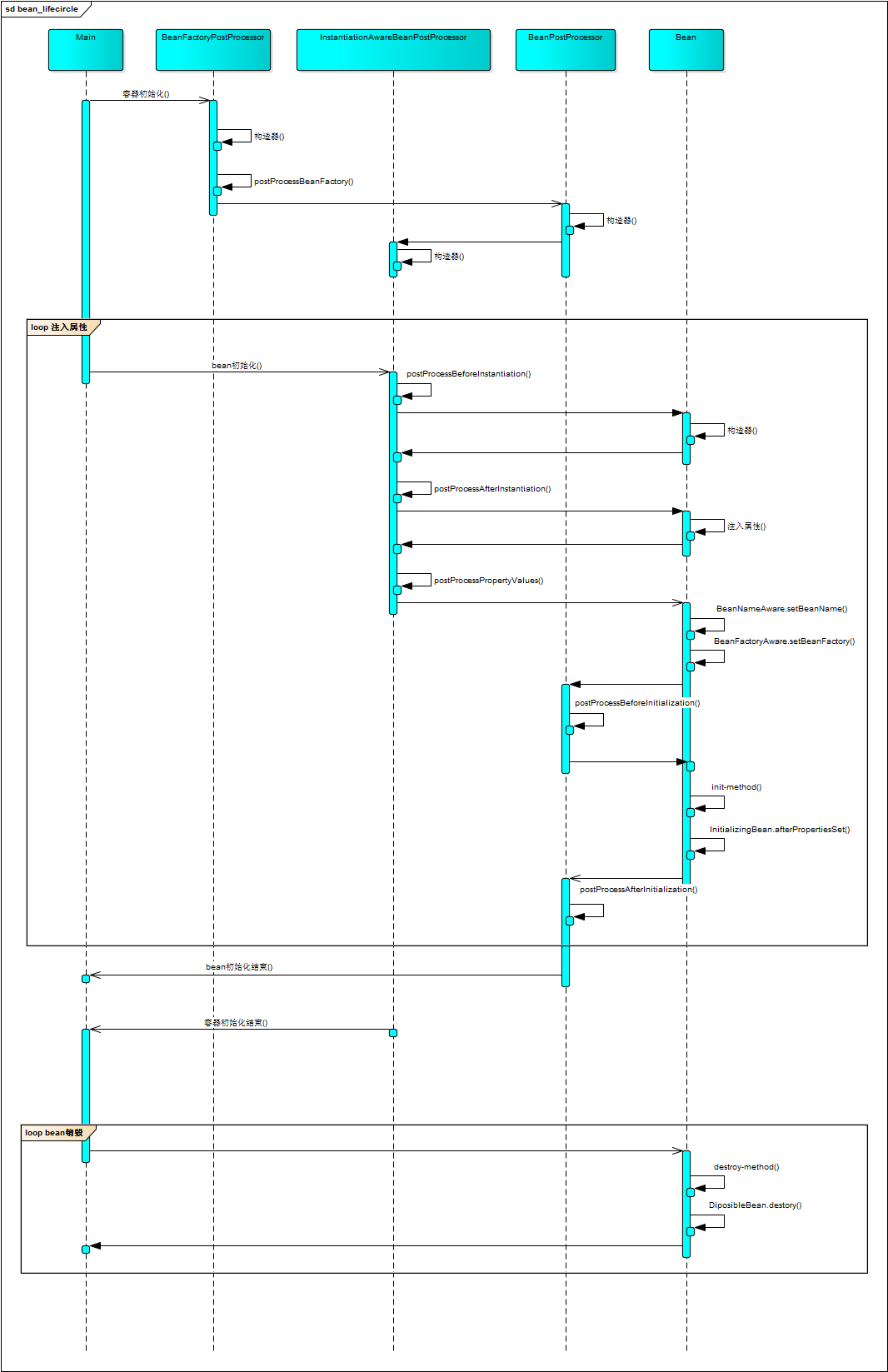
二、生命周期接口分类
Bean的生命周期经历了多个接口方法的调用,这些接口和方法可分为以下四类:
1、Bean自身方法
通过<bean>的init-method和destroy-method或注解@PostConstruct与@PreDestroy 指定的方法
2、Bean级生命周期接口
包括BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、InitializingBean、DiposableBean
// 获取bean名称 public interface BeanNameAware extends Aware { void setBeanName(String name); }
// 获取BeanFactory对象 public interface BeanFactoryAware extends Aware { void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; }
// 对象初始化,与init-method属性作用相同 public interface InitializingBean { void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception; }
// 对象销毁,与destroy-method属性作用相同 public interface DisposableBean { void destroy() throws Exception; }
3、容器级生命周期接口
包括InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 、BeanPostProcessor,注意:InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor继承自BeanPostProcessor,实际中使用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter提供空实现,从而方便使用
// 对象实例化生命周期接口 public interface InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor { Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException; boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues( PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
// 对象初始化生命周期接口 public interface BeanPostProcessor { Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException; }
4、BeanFactory后处理器接口
包括BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// 工厂后处理接口,用于修改bean配置(BeanDefinition) public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor { void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException; }
三、生命周期示例演示
Bean

@Component public class Person implements BeanFactoryAware, BeanNameAware, InitializingBean, DisposableBean { private String name; @Value("shanghai") private String address; @Value("123") private int phone; private BeanFactory beanFactory; private String beanName; public Person() { System.out.println("【构造器】调用Person的构造器实例化"); } public String getName() { return name; } @Autowired public void setName(@Value("matt") String name) { System.out.println("【注入属性】注入属性name"); this.name = name; } public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { System.out.println("【注入属性】注入属性address"); this.address = address; } public int getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(int phone) { System.out.println("【注入属性】注入属性phone"); this.phone = phone; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person [address=" + address + ", name=" + name + ", phone=" + phone + "]"; } // 这是BeanFactoryAware接口方法 @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory arg0) throws BeansException { System.out .println("【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory()"); this.beanFactory = arg0; } // 这是BeanNameAware接口方法 @Override public void setBeanName(String arg0) { System.out.println("【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName()"); this.beanName = arg0; } // 这是InitializingBean接口方法 @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { System.out .println("【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet()"); } // 这是DiposibleBean接口方法 @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { System.out.println("【DiposibleBean接口】调用DiposibleBean.destory()"); } // 通过<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法 @PostConstruct public void myInit() { System.out.println("【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法"); } // 通过<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法 @PreDestroy public void myDestory() { System.out.println("【destroy-method】调用<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法"); } }
BeanFactoryPostProcessor

@Component public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor { public MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor() { super(); System.out.println("这是BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类构造器!!"); } @Override public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory arg0) throws BeansException { System.out .println("BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用postProcessBeanFactory方法"); BeanDefinition bd = arg0.getBeanDefinition("person"); bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("phone", "110"); } }
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor

@Component public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter { public MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor() { super(); System.out.println("这是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter实现类构造器!!"); } // 接口方法、实例化Bean之前调用 @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法"); return null; } // 接口方法、实例化Bean之后调用 @Override public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessAfterInstantiation方法"); return true; } // 接口方法、设置某个属性时调用 @Override public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { System.out.println("InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessPropertyValues方法"); return pvs; } }
BeanPostProcessor

@Component public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { public MyBeanPostProcessor() { super(); System.out.println("这是BeanPostProcessor实现类构造器!!"); } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException { System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessAfterInitialization对属性进行更改!"); return arg0; } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException { System.out.println("BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessBeforeInitialization对属性进行更改!"); return arg0; } }
配置
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.matt.lifecircle"/>
测试

public class BeanLifeTest { @Test public void test() { System.out.println("现在开始初始化容器"); ApplicationContext factory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context-lifecircle.xml"); System.out.println("容器初始化成功"); //得到Preson,并使用 Person person = factory.getBean("person",Person.class); System.out.println(person); System.out.println("现在开始关闭容器!"); ((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)factory).registerShutdownHook(); } }
运行结果
现在开始初始化容器 这是BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类构造器!! BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用postProcessBeanFactory方法 这是BeanPostProcessor实现类构造器!! 这是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter实现类构造器!! InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessBeforeInstantiation方法 【构造器】调用Person的构造器实例化 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessAfterInstantiation方法 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessPropertyValues方法 【注入属性】注入属性name 【注入属性】注入属性phone 【BeanNameAware接口】调用BeanNameAware.setBeanName() 【BeanFactoryAware接口】调用BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory() BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessBeforeInitialization对属性进行更改! 【init-method】调用<bean>的init-method属性指定的初始化方法 【InitializingBean接口】调用InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet() BeanPostProcessor接口方法postProcessAfterInitialization对属性进行更改! InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor调用postProcessAfterInitialization方法 容器初始化成功 Person [address=shanghai, name=matt, phone=110] 现在开始关闭容器! 【destroy-method】调用<bean>的destroy-method属性指定的初始化方法 【DiposibleBean接口】调用DiposibleBean.destory()
四、一个应用示例
后台服务以方法调用的形式向外提供服务,在服务启动时须注册向外暴露的方法,该注册功能可利用bean的生命周期的BeanPostProcessor接口,在bean加载完毕后自动注册,代码如下:
业务类注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Component public @interface ExpoService { String value() default ""; }
业务接口与实现
public interface UserService { void doSomething(); }
@ExpoService public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { // @Async @Override public void doSomething() { System.out.println("doSomething invoked!"); } }
请求管理类
@Component public class RequestManager { private Map<String, MethodAndInstance> methodMap = new HashMap<String, MethodAndInstance>(); public void addExpoMethod(Method rawMethod, Object rawInstance, Method proxyMethod, Object proxyInstance) { methodMap.put(rawMethod.getName(), new MethodAndInstance(rawMethod, rawInstance, proxyMethod, proxyInstance)); System.out.println(String.format("****** 添加expo对外暴露方法: %s", rawMethod.getName())); } public static class MethodAndInstance { private Method rawMethod; private Object rawInstance; private Method proxyMethod; private Object proxyInstance; public MethodAndInstance(Method rawMethod, Object rawInstance, Method proxyMethod, Object proxyInstance) { this.rawMethod = rawMethod; this.rawInstance = rawInstance; this.proxyMethod = proxyMethod; this.proxyInstance = proxyInstance; } public Object getRawInstance() { return rawInstance; } public Object getProxyInstance() { return proxyInstance; } public Method getRawMethod() { return rawMethod; } public Method getProxyMethod() { return proxyMethod; } } }
使用BeanPostProcessor,注册接口
@Component public class ExpoBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { private Map<String, Object> beanMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); @Autowired private RequestManager requestManager; @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Class<?> cls = bean.getClass(); if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(ExpoService.class)) { beanMap.put(beanName, bean); System.out.println(String.format("======> 业务类原始bean: %s", bean.getClass().getName())); } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object proxyBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { try { if (beanMap.containsKey(beanName)) { System.out.println(String.format("======> 业务类代理bean: %s", proxyBean.getClass().getName())); Object rawBean = beanMap.remove(beanName); for (Class<?> cls : rawBean.getClass().getInterfaces()) { for (Method rowMethod : cls.getDeclaredMethods()) { Method proxyMethod = proxyBean.getClass().getMethod(rowMethod.getName(), rowMethod.getParameterTypes()); this.requestManager.addExpoMethod(rowMethod, rawBean, proxyMethod, proxyBean); } } } } catch (Exception e) { } return proxyBean; } }
配置
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.matt.lifecircle"/> <task:annotation-driven executor="myExecutor1"/> <task:executor id="myExecutor1" pool-size="10" />
测试
@Test public void testMethodRegistry() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-context-lifecircle.xml"); UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class); userService.doSomething(); }
运行结果
======> 业务类原始bean: cn.matt.lifecircle.UserServiceImpl
======> 业务类代理bean: cn.matt.lifecircle.UserServiceImpl
****** 添加expo对外暴露方法: doSomething
doSomething invoked!
当业务方法添加@Async时,运行结果:
======> 业务类原始bean: cn.matt.lifecircle.UserServiceImpl
======> 业务类代理bean: com.sun.proxy.$Proxy9
****** 添加expo对外暴露方法: doSomething
doSomething invoked!
补充:不存在需要aop功能时,spring bean为原始类;当存在需要aop功能时,spring bean为代理类
上述实例存在一个bug:当业务类存在循环引用时,spring会将引用链中的某个类提前构造,此时,ExpoBeanPostProcessor在该类的postProcessAfterInitialization方法中获取的是原始类,而非代理类,由于方法在原始类上调用,导致所有基于aop的功能(如事务,多数据源切换等)失效
解决方法:通过对spring初始化bean的源码的分析可知(参考Spring 依赖注入时,什么时候会创建代理类),利用SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的getEarlyBeanReference方法获取到代理类,该方法在BeanPostProcessor接口相关方法之前调用
具体修改如下:

@Component public class ExpoBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter { private Map<String, Object> beanMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); /** * @Fields proxyBeanMap : 记录bean循环引用时的代理bean */ private Map<String, Object> proxyBeanMap = new HashMap<String, Object>(); @Autowired private RequestManager requestManager; @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Class<?> cls = bean.getClass(); if (cls.isAnnotationPresent(ExpoService.class)) { beanMap.put(beanName, bean); System.out.println(String.format("======> 业务类原始bean: %s", bean.getClass().getName())); } return bean; } @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object proxyBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object originalProxyBean = proxyBean; try { if (beanMap.containsKey(beanName)) { // bean循环引用时, postProcessAfterInitialization获取不到代理类,须特殊处理 if (proxyBeanMap.containsKey(beanName)) { proxyBean = proxyBeanMap.get(beanName); } System.out.println(String.format("======> 业务类代理bean: %s", proxyBean.getClass().getName())); Object rawBean = beanMap.remove(beanName); for (Class<?> cls : rawBean.getClass().getInterfaces()) { for (Method rowMethod : cls.getDeclaredMethods()) { Method proxyMethod = proxyBean.getClass().getMethod(rowMethod.getName(), rowMethod.getParameterTypes()); this.requestManager.addExpoMethod(rowMethod, rawBean, proxyMethod, proxyBean); } } } } catch (Exception e) { } return originalProxyBean; } @Override public Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (!proxyBeanMap.containsKey(beanName)) { proxyBeanMap.put(beanName, bean); } return bean; } }
参考:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号