Spring MVC 使用介绍(十三)数据验证 (一)基本介绍
一、消息处理功能
Spring提供MessageSource接口用于提供消息处理功能:
public interface MessageSource { String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, String defaultMessage, Locale locale); String getMessage(String code, Object[] args, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException; String getMessage(MessageSourceResolvable resolvable, Locale locale) throws NoSuchMessageException; }
Spring提供了两个默认实现:
StaticMessageSource // 测试用 ResourceBundleMessageSource // 用于生产环境
ApplicationContext接口扩展了MessageSource接口,当ApplicationContext被加载时,它会自动在context中查找已定义为MessageSource类型的bean。此bean的名称须为messageSource。如果找到,那么所有对上述方法的调用将被委托给该bean。否则ApplicationContext会在其父类中查找是否含有同名的bean。如果有,就把它作为MessageSource。如果它最终没有找到任何的消息源,一个空的StaticMessageSource将会被实例化,使它能够接受上述方法的调用。
示例如下:
属性文件
# exception.properties
message.arg=the {0} {1} is requred.
# format.properties
message=这是一条测试消息
# format_en_GB.properties
message=this is a test
spring 配置(spring-validation.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basenames"> <list> <value>classpath:format</value> <value>classpath:exception</value> </list> </property> <property name="fileEncodings"> <props> <prop key="classpath:format">utf-8</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans>
测试
public class MessageTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MessageSource ms = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-validation.xml"); String msg1 = ms.getMessage("message", null, "yeah", null); String msg2 = ms.getMessage("message.arg", new Object[] { "aa", "bb" }, "yeah", null); // 参数定制 String msg3 = ms.getMessage("message", null, "yeah", Locale.UK); // 支持国际化 System.out.println(msg1); System.out.println(msg2); System.out.println(msg3); } }
运行结果
这是一条测试消息 the aa bb is requred. this is a test
补充:spring提供了MessageSourceAware接口,用于在bean创建时自动注入MessageSource。
二、数据验证
JSR-303 (Bean Validation 1.0)定义了基于注解JavaBean数据验证规范,注解如下:
@Null 被注释的元素必须为null @NotNull 被注释的元素必须不为null @AssertTrue 被注释的元素必须为true @AssertFalse 被注释的元素必须为false @Min(value) 被注释的元素必须为一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定值 @Max(value) 被注释的元素必须为一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定值 @DecimalMin(value) 被注释的元素必须为一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定值 @DecimalMax(value) 被注释的元素必须为一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定值 @Size(max, min) 被注释的元素必须在指定范围内 @Digits(integer, fraction) 被注释的元素必须为一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 @Past 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 @Future 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 @Pattern(value) 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 @Valid 被注释的元素必须为对象,表示递归验证对象属性
hibernate validator 在JSR303的基础上对校验注解进行了扩展,扩展注解如下:
@Emai 被注释的元素必须是电子邮件格式 @Length 被注释的字符串大小必须在指定范围内 @NotEmpty 被注释的字符串必须非空 @Range 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内
所有被支持的注解列表参见:hibernate-validator -> /org/hibernate/validator/ValidationMessages.properties
spring在hibernate validator基础上对JavaBean的数据校验方式进行了封装,配置与使用方式如下:
1、添加依赖
<dependency> <groupId>javax.validation</groupId> <artifactId>validation-api</artifactId> <version>2.0.1.Final</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> <version>6.0.16.Final</version> </dependency>
2、添加配置
<!-- validator bean --> <bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean"> <property name="providerClass" value="org.hibernate.validator.HibernateValidator"/> <property name="validationMessageSource" ref="messageSource"/> </bean> <!-- 注册(注册方式与Converter相同,参见Spring MVC 使用介绍(八)—— 类型转换) --> <mvc:annotation-driven validator="validator" />
注:messageSource的配置与上例相同
# format.properties
msg.age=性别须大于{value}岁
3、使用
Java Bean
public class Person { @NotNull private String name; @Min(value = 12, message = "{msg.age2}") private int age; ... }
controller
@ControllerAdvice public class MyControllerAdvice { @ResponseBody @ExceptionHandler public Map<String, String> errorhandler(Exception ex) { BindException e = (BindException) ex; Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("error", e.getBindingResult().getFieldError().getDefaultMessage()); return map; } }
@RestController public class ValidController { @RequestMapping("/test1") public Person test1(@Valid Person person) { return person; } }
4、测试
访问:http://localhost:8080/shiro-test/test1?name=12&age=6,输出
{"error":"性别须大于12岁"}
访问:http://localhost:8080/shiro-test/test1?age=20,输出
{"error":"must not be null"}
三、错误消息
数据验证错误消息的指定有多种方式:
1、默认错误消息
默认的错误消息文件是/org/hibernate/validator/ValidationMessages.properties,如下图所示:
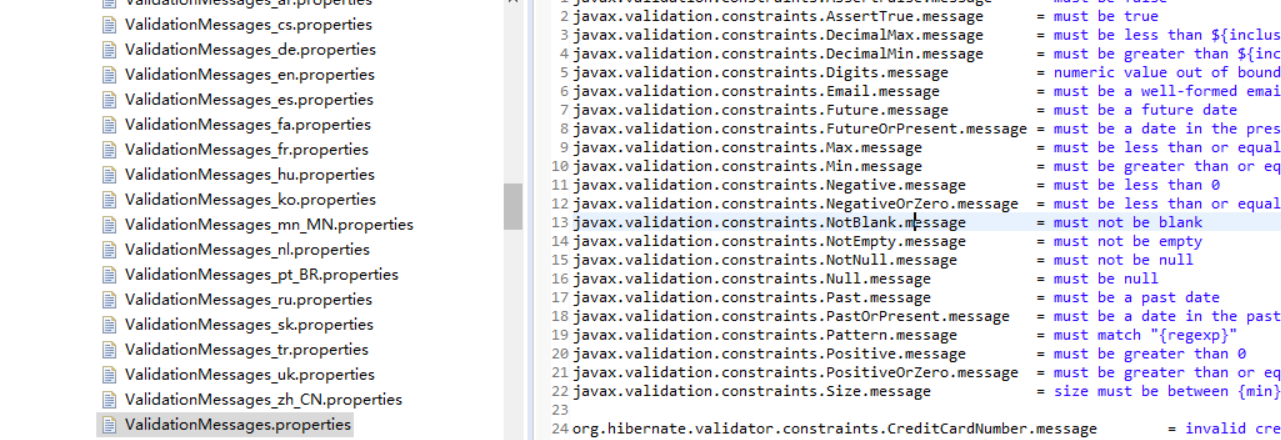
消息键默认为:验证约束注解的全限定类名.message
当不指定验证注解的message属性时,则使用默认消息
2、覆盖默认错误消息
方法很简单:在MessageSource的属性文件中依据默认消息键重新定义键值:
# format.properties javax.validation.constraints.NotNull.message = 不能为空
3、自定义错误消息
在属性文件中定义错误消息,使用注解的message属性引用:
# format.properties
msg.notnull=不能为空
public class Person { @NotNull(message = "{msg.notnull}") private String name; ... }
3.1 消息占位符
可在错误消息中使用占位符获取约束值,规则为:{验证注解属性名},如@Length有min和max属性,可在消息文件中使用{min}和{max}获取;@Max有value属性,可使用{value}获取
msg.age=性别须大于{value}岁
3.2 EL表达式
可在错误消息中使用EL表达式,规则为:${表达式},如可使用${validatedValue}获取验证值,使用${min > 1 ? '大于1' : '小于等于1'}添加逻辑判断:
javax.validation.constraints.Size.message = [${validatedValue}]须大于等于{min}字符
javax.validation.constraints.Min.message = 数量${min > 1 ? '大于1' : '小于等于1'}
在EL表达式中,可使用java.util.Formatter类型的formatter变量进行格式化:
${formatter.format("%04d", min)}
参考:
spring中ResourceBundleMessageSource的配置使用方法
SpringMVC数据验证——第七章 注解式控制器的数据验证、类型转换及格式化——跟着开涛学SpringMVC



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号