如图,在平面直角坐标系\(xOy\)中,已知椭圆\(C_1:\dfrac{x^2}{4}+y^2=1\),椭圆\(C_2:\dfrac{x^2}{a^2}+\dfrac{y^2}{b^2}=1\) \((a>b>0)\).\(C_2\)与\(C_1\)的长轴之比为\(\sqrt2: 1\),离心率相同.
\((1)\) 求椭圆\(C_2\)的标准方程;
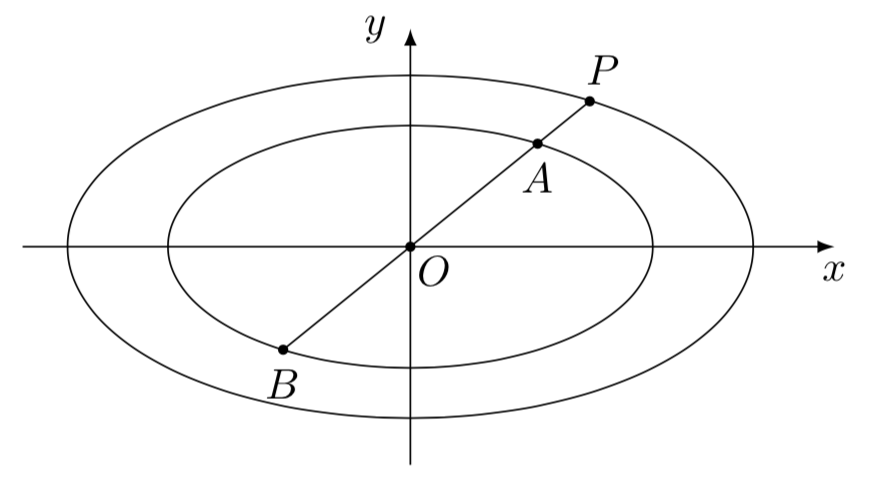
\((2)\) 设点\(P\)为椭圆\(C_2\)上任意一点.射线\(PO\)与椭圆\(C_1\)依次交于点\(A,B\),求证:\(\dfrac{|PA|}{|PB|}\)为定值;
\((3)\) 过\(C_2\)上任意一点\(P\)作两条斜率分别为\(k_1,k_2\)的直线\(l_1,l_2\),且直线\(l_1,l_2\)与椭圆\(C_1\)均有且只有一个公共点,求证:\(k_1\cdot k_2\)为定值.
解析
\((1)\)由题\(a=2\sqrt{2}\),\(b=\sqrt2\),因此所求椭圆方程为\(C_2:\dfrac{x^2}{8}+\dfrac{y^2}{2}=1\).
\((2)\) 由于$$\dfrac{|PA|}{|PB|}=\dfrac{|OP|-|OA|}{|OP|+|OA|}.$$因此仅需证明\(\dfrac{|OP|}{|OA|}\)为定值,若设\(P\left(2\sqrt{2}\cos\theta,\sqrt{2}\sin\theta\right)\),则\(A\left(2\cos\theta,\sin\theta\right)\),显然恒有\(\dfrac{|OP|}{|OA|}=\sqrt{2}.\)证毕.\
\((3)\) 设\(P(2\sqrt2\cos\theta,\sqrt{2}\sin\theta)\),直线\(l_1,l_2\)的斜率统一记为\(k\),
则直线\(l_{1,2}\)可表示为$$
kx-y+\sqrt{2}\sin\theta-2\sqrt{2}k\cos\theta=0.$$
由于\(l_{1,2}\)与椭圆\(C_1\)相切,由等效判别式可得关于\(k\)的一元二次方程$$
k^2\cdot 4+(-1)^2\cdot 1-\left(\sqrt{2}\sin\theta-2\sqrt{2}k\cos\theta\right)^2=0.$$即$$
(4-8\cos^2\theta)\cdot k^2+8\sin\theta\cos\theta\cdot k+1-2\sin2\theta=0.$$这个方程的两个解即$k_1,k_2$,从而由韦达定理可得$$k_1k_2=\dfrac{1-2\sin2\theta}{4-8\cos^2\theta}=-\dfrac{1}{4}.$$
证毕.



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号